![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
230 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
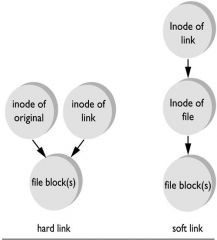
difference between soft and hard links
|
|
|
|
command: &
|
Run the specified program in the background.
|
|
|
command: ^z
|
Suspend the current foreground process.
|
|
|
command: bg
|
put specified process in the background
|
|
|
command: fg
|
put specified process in the foreground
|
|
|
fuser
|
Display the PID of any process using a specified file.
|
|
|
command: fuser
|
identify processes using files or sockets
|
|
|
command: jobs
|
show list of background processes
|
|
|
kill
|
Stop the execution of a process
|
|
|
killall
|
kill all processes executing a specified command.
|
|
|
nice
|
Change the priority of a process.
|
|
|
command: nohup
|
no hangup -- Run a command immune to hangups.
|
|
|
command: pidof
|
locate and print the process id of the specified program.
|
|
|
command: ps
|
get process status information.
|
|
|
command: pstree
|
display the family tree of running processes.
|
|
|
command: renice
|
Change the id of a running process.
|
|
|
command: top
|
Display Linux tasks .... and their resource use.
|
|
|
signal for: hang up
|
(1) SIGHUP
|
|
|
signal for: Interrupt from keyboard
|
(2) SIGINT (default action:terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: Quit from keyboard
|
(3) SIGQUIT (default action is: terminate and do CORE dump)
|
|
|
signal for: Illegal Instruction
|
(4) SIGILL (default action is: terminate and do CORE dump)
|
|
|
signal for: Abort signal from abort(3)
|
(6) SIGABRT (default action is: terminate and do CORE dump)
|
|
|
signal for: Floating point exception
|
(8) SIGFPE (default action is: terminate and do CORE dump)
|
|
|
signal for: Kill signal
|
(9) SIGKILL (default action: term)
NOTE: SIGKILL cannot be caught, blocked, or trapped |
|
|
signal for: Invalid memory reference
|
(11) SIGSEGV (default action is: terminate and do CORE dump)
|
|
|
signal for: Broken pipe: write to pipe with no readers
|
(13) SIGPIPE (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: Timer signal from alarm(2)
|
(14) SIGALRM (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: Termination signal
|
(15) SIGTERM (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: User-defined signal 1
|
(30,10,16) SIGUSR1 (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: User-defined signal 2
|
SIGUSR2 31,12,17 (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: Child stopped or terminated
|
(20,17,18) SIGCHLD (default action is IGNore)
|
|
|
signal for: Continue if stopped
|
(19,18,25) SIGCONT (default action is: CONTinue process if stopped)
|
|
|
signal for: Stop process
|
(17,19,23) SIGSTOP default action:stop)
NOTE: SIGKILL cannot be caught, blocked, or trapped |
|
|
signal for: Stop typed at tty
|
(18,20,24) SIGTSTP (default action is: stop)
|
|
|
signal for: tty input for background process
|
(21,21,26) SIGTTIN (default action is: stop)
|
|
|
signal for: tty output for background process
|
(22,22,27) SIGTTOU (default action is: stop)
|
|
|
signal for: Pollable event (Sys V).
|
SIGPOLL (default action: Terminate)
Synonym of SIGIO |
|
|
signal for: Profiling timer expired
|
(27,27,29) SIGPROF (default action is: Terminate)
|
|
|
signal for: Bad argument to routine (SVr4)
|
(12,-,12) SIGSYS (default action is: Terminate and dump CORE)
|
|
|
signal for: Trace/breakpoint trap
|
(5) SIGTRAP (default action is: Core)
|
|
|
Signal for: Urgent condition on socket (4.2BSD)
|
(16,23,21) SIGURG (default action: Ignore)
|
|
|
TRAP syntax?
|
trap [COMMANDS] [SIGNALS]
example: trap "echo VARIABLE used" DEBUG |
|
|
redirection: script
|
Save the activity on your screen to a file.
|
|
|
redirection: tee
|
...copy to stdin to file and screen
|
|
|
redirection: xargs
|
Read multiple arguments from standard input and use them as arguments to some specified command.
|
|
|
redirection: 2>
|
redirect standard-error as specified
|
|
|
command:
make prompt show current working directory (pwd) |
export PS1='$PWD> '
NOTE: to make it permanent, add to ~/.bashrc |
|
|
command (users): change information displayed by finger
|
chfn
|
|
|
command (users): change user information in bulk
|
chpasswd
|
|
|
command (users): display information about a user
|
finger
|
|
|
command (users): modify information in the system group files
|
groupmod
|
|
|
commands (user): check system group files for validity
|
grpck
|
|
|
commands (user): display group information for a user
|
groups
|
|
|
commands (user): display information about a user
|
id
|
|
|
commands (user): change user password
|
passwd
|
|
|
commands (user): check system password for validity
|
pwck
|
|
|
commands (user): change to a new user id.
|
su
|
|
|
commands (user): add a new user
|
useradd
|
|
|
commands (user): delete a user
|
userdel
|
|
|
commands (user): modify user information
|
usermod
|
|
|
commands (user): display a list of current users
|
users OR who
|
|
|
commands (user): Secure group information
|
/etc/gshadow
|
|
|
commands: check paths for portability and validity?
|
pathchk
|
|
|
commands: Follow a path to the end, if it has one?
|
namei
|
|
|
commands: take a full path...and display all but the last element
|
dirname
|
|
|
commands: take a full path...and display only the last element
|
basename
|
|
|
commands: Display your current environment variables and their values with the command.
|
env
|
|
|
files: executed when starting a bash subshell
|
~/.bashrc
|
|
|
files: executed at login time
|
~/.bash_profile
|
|
|
files: system-wide profile
|
/etc/profile
|
|
|
files: Synonym for bash_profile
|
~/.bash_login
|
|
|
files: executed when a bash shell exits.
|
~/.bash_logout
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: don't read the "~/.bashrc" initialization file in an interactive shell.
|
-norc
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: Execute commands from the specified file rather than ~/.bashrc in an interactive shell.
|
-rcfile FILENAME
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: Don't load the system-wide startup file /etc/profile OR any of the personal initialization files (~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, ~/.profile).
|
-noprofile
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: display version information
|
-version
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: Make this shell act as if it were directly invoked from login.
|
-login
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: do not perform curly brace expansion.
|
-nobraceexpansion
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: do not use the GNU Readline library to read interactive command lines.
|
-nolineediting
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: force bash to conform to the Posiz 1003.2 standard
|
-posix
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: read and execute commands from STRING after processing the options and then exit.
|
-c STRING
|
|
|
INVOKING BASH: force the shell to run interactively.
|
-i
|
|
|
STEPS: Interactive bash...at login
|
1. If /etc/profile exists, then source it.
2. If ~/.bash_profile exists, then source it, else if ~/.bash_login exists then source it, else if ~/.profile exists then source it. |
|
|
STEPS: Interactive bash...at logout
|
If ~/.bash_logout exists,
source it. |
|
|
STEPS: NON-login Interactive bash at Startup Time.
|
If ~/.bashrc exists,
then source it. |
|
|
STEPS: NON-interactive Shells at Startup Time.
|
If the environment variable ENV is non-null......expand the variable and source the file named by the value.
If bash is not started in Posix mode.....it looks for BASH_ENV before ENV. So, typically, your ~/.bash_profile contains the following line: if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then source ~/.bashrc; fi |
|
|
alias syntax
|
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ]
note: -p option prints the list of aliases (same as alias with no argument) |
|
|
command: remove an alias
|
unalias
note: -a would remove all aliases |
|
|
history shortcut: move up
|
arrow up
or <Ctrl>-P |
|
|
history shortcut: move down
|
arrow down
or <CTRL>-n |
|
|
history shortcut: move to the first line in history.
|
<Meta>-<
|
|
|
history shortcut: move to the end of input history.
|
<Meta>->
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: search backward starting at the current line and moving "up" through the history as necessary.
|
<Ctrl>-r
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: search forward starting at the current line and moving "down" through the history as necessary.
|
<Ctrl>-s
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: search backward starting at the current line and moving "up" through the history as necessary....using a non-incremental search for a string supplied by the user.
|
<Meta>-p
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: search forward starting at th ecurrent line and moving "down" through history as necessary .... using non-incremental search for a string supplied by the user.
|
<Meta-n
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: yank nth argument of previous command.
|
<Meta>-Ctrl>-y
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: Insert last argument to the previous command.
|
<Meta>-. , M-_
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: start a history substitution, except when followed by a space, tab, the end of the line, = or (
|
! (bang)
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: refer to the previous command. This the synonym for !-1
|
!! (bang bang)
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: refer to command line N.
|
!n (bang number)
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: refer to the command N lines back
|
!-n
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: refer to the most recent command starting with STRING
|
!string
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: refer to the most recent command containing STRING
|
!?string[`?]
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT: the entire command line typed so far.
|
!# (bang sharp)
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT:
quick substitution. Repeat the last command, replacing STRING1 with STRING2. Equivalent to "!!:s/string1/string2". |
^string1^string2^
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT:
write out the current history to the history file. |
history -w
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT:
read the current history file and make its contents the history list. |
history -r
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT:
append the new history lines. |
history -a
|
|
|
HISTORY SHORTCUT:
read the history lines not already read from the history file into the current list. |
history -n
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
attempt to do completion on the text before the cursor. |
<Tab>
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
list the possible completions of the text before the cursor. |
<Meta>-?
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
read in the contents of your init file and incorporate any bindings or variable assignments found there. |
<ctrl>-x, <ctrl>-r
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
abort the current editing command and ring the terminal's bell (subject to the setting of "bell-style" |
<ctrl>-g
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
make the next character that you type metafied. |
<Esc>
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
incremental undo, separately remembered for each line. |
<Ctrl>-_, <Ctrl>-x, <Ctrl>-u
|
|
|
COMMAND COMPLETION:
Undo all changes made to this line. |
<Meta>-r
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move back one character |
<ctrl>-b
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move forward one character |
<ctrl>-f
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
delete the character to the left of the cursor |
<del> , <backspace>
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
delete the character underneath the cursor |
<Ctrl>-d
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
undo the last thing that you did. |
<Ctrl>-u
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move to the start of the line |
<Ctrl>-a
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move to the end of the line. |
<Ctrl>-e
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move forward a word.<Anchor2> |
<Meta>-f
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
move backward a word. |
<Meta>-b
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
clear the screen, reprinting the current line at the top. |
<Ctrl>-I
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Kill the text from the current cursor position to the end of the line. |
<ctrl>-k
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Kill from the cursor to the end of the current word, or, if between words, to the end of the next word. |
<Meta>-d
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Kill from the cursor the start of the previous word, or, if between words, to the start of the previous word |
<Meta>-DEL
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
kill from the cursor to the previous whitespace. This is different from M-DEL because the word boundaries differ. |
<Ctrl>-w
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Yank the most recently killed taext back into the buffer at the cursor |
<Ctrl>-y
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Rotate the kill-ring, and yank the new top. You can do this only if the prior command is yank or yank-pop. |
<Meta>-y
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Delete the character under the cursor. |
<Ctrl>-d
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Add the next character that you type to the line vertabim. |
<Ctrl>-q, C-w
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Insert a tab character. |
<Meta>-<Tab>
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Drag the chaaracter before the cursor forward over the character at the cursor....moving the cursor forward as well. |
<Ctrl>-t
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Drag the word behind the cursor, past the word in front of the cursor....moving the cursor over that word as well. |
<Meta>-t
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Uppercase the current (or following) word. |
<Meta>-u
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Lowercase the current (or following) word. |
<Meta>-I
|
|
|
Command Line Editing:
Capitalize the current (or following) word. |
<Meta>-c
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The time, in HH:MM:SS format |
\t
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The time in 12-hour HH:MM:SS format. |
\T
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The time in 12-hour am/pm format. |
\@
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The date, in "Weekday Month Date" format (e.g., "Tue May 26"). |
\d
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
ASCII escape character. |
\e
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
newline |
\n
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The name of the shell. |
\s
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The current working directory. |
\w
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The basename of $PWD. |
\W
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
Your username. |
\u
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
hostname |
\h
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The command number of this command. |
\#
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The history number of this command. |
\!
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
The character corresponding to the octal number nnn. |
\nnn
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
If the effective uid is 0, #; otherwise, $. |
\$
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
A backslash. |
\\
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
Begin a sequence of nonprinting characters. |
\[
|
|
|
SHELL PROMPT (special characters):
End a sequence of nonprinting characters. |
\]
|
|
|
SHELL ARITHMETIC:
two formats for math expansion |
$[ expression ]
or $(( expression )) |
|
|
SHELL ARITHMETIC:
builtin for performing math on variables |
let
|
|
|
SYNTAX:
"for" loop statement (simple) |
for name in word1 word2 ... wordN
do list done OR: for name in wordlist; do list; done |
|
|
SYNTAX:
"until" loop statement (simple) |
until [ condition ]
do list done OR: until cmd; do list; done |
|
|
SYNTAX:
"while" loop statement (simple) |
while [ condition ]
do list done OR: while test-cmd; do list; done |
|
|
SYNTAX:
"case" flow control statement (simple) |
case word in
pattern1) list1 ;; pattern2) list2 ;; pattern3) list2 ;; patternN) list-N ;; esac |
|
|
SYNTAX:
"if then else" flow control statement |
if [ condition ]
then perform-list-2 elif [ condition ] then perform-list-4 else perform-list-5 fi |
|
|
Login Banner location?
|
/etc/issue
|
|
|
Message of the day (at login)?
|
/etc/motd
|
|
|
If this file exists, ONLY root may login.
|
/etc/nologin
|
|
|
If this file exists, login is quiet.
|
.hushlogin
|
|
|
database of users currently logged in?
|
/var/run/utmp
|
|
|
Store login and logout history?
|
/var/log/wtmp
|
|
|
File that defines which ttys that root may log in from.
|
/etc/securetty
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...that will set terminal config values. |
setterm
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display or set tty config values |
stty
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display information about filesystems |
df
|
|
|
KERNEL:
...program to add and remove modules from the linux kernel |
modprobe
|
|
|
KERNEL:
...a module to create a module dependency list. |
depmod (creates modules.dep)
|
|
|
KERNEL:
...simple tool for installing modules |
insmod (modprobe is "cleverer")
|
|
|
KERNEL:
...show the status of modules in the Linux kernel |
lsmod
(formats contents of /proc/modules) |
|
|
KERNEL:
...remove modules from kernel |
rmmod
OR modprobe -r |
|
|
COMMAND:
...concatenate and print files in reverse |
tac (remember cat backwards)
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...reverse lines |
rev (think forward = drawrof)
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...compare two sorted files line by line |
comm
(this outputs common lines) |
|
|
COMMAND:
..compare two files, usually binary files |
cmp
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...find the difference between two files |
diff
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...find the difference between three files |
diff3
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...merge differences between two files (interactively) |
sdiff
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...columnate input |
column
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...remove columns from a file |
colrm
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...split a file into sections determined by context lines |
csplit
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...remove sections from each line of files |
cut
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...convert tabs to spaces |
expand
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...Reformat each paragraph (width) in the FILE(s), writing to standard output. |
fmt
|
|
|
COMMAND:
... wrap each input line to fit in specified width |
fold
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...merge lines of files. Write lines consisting of the sequentially corresponding lines from each FILE, separated by TABs, to standard output. |
paste
|
|
|
COMMAND:
... split a file into pieces |
split
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...Translate, squeeze, and/or delete characters from standard input, writing to standard output. |
tr
|
|
|
COMMAND:
... convert spaces to tabs |
unexpand
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...Discard all but one of successive identical lines from INPUT |
uniq
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...show current run level |
runlevel
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display bootup messages |
dmesg
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...add a job to the scheduling queue. |
at
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display the contents of the scheduling queue. |
atq
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...remove a job from the scheduling queue. |
atrm.
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...wait some number of seconds |
sleep n
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...wait some number of micro-seconds |
usleep n
|
|
|
COMMAND:
... batch executes commands when system load levels permit; in other words, when the load average drops below 0.8, or the value specified in the invocation of atrun. |
batch
|
|
|
FILE:
..defines users permitted to use 'at' |
/etc/at.allow
|
|
|
FILE:
...defines users permitted to use 'cron' |
/etc/cron.allow
|
|
|
FILE:
...defines users NOT permitted to use 'at' |
/etc/cron.deny
|
|
|
FILE:
...defines users NOT permitted to use 'cron.deny' |
/etc/cron.deny
|
|
|
FILE:
..contains system load average |
/proc/loadavg
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display amount of free and used memory in the system |
free
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...graphic representation of system load average |
tload
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...report virtual memory statistics |
vmstat
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display shared memory, semaphores, message queues. |
ipcs
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...an encryption and signing tool |
gpg (GNU Privacy Guard)
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...a signature verification tool |
gpgv
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display a calendar |
cal
|
|
|
COMMAND:
... a spell checker designed to eventually replace Ispell. It can either be used as a library or as an independent spell checker. |
aspell
|
|
|
OSI Reference Model
...layers? (just another reminder :-) |
1. Physical
2. Data Link 3. Network 4. Transport 5. Session 6. Presentation 7. Application |
|
|
TCP MODEL
..."five layer Internet Model" |
5. Application
4. Transport 3. Network 2. Data Link 1. Physical |
|
|
COMMAND:
...network status information |
netstat
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...display and manipulate routing information |
route
|
|
|
FILE:
...contains Internet services by number |
/etc/services
|
|
|
FILE:
...contains DNS server information |
/etc/resolv.conf
|
|
|
COMMANDS:
...is a program to maintain identical copies of files over multiple hosts. |
rdist
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...list open files for a user |
lsof -u username
|
|
|
COMMAND:
...list active processes for a particular program |
lsof -c sshd (example)
|

