![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
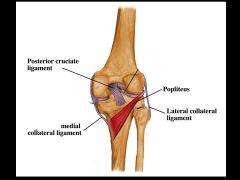
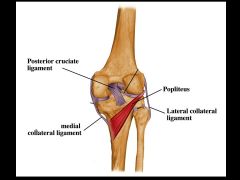
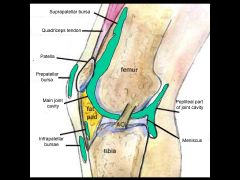
Posterior view of right knee joint. The posterior cruciate ligament is noted as well as the popliteus muscle. This muscle unlocks the knee joint (from the extended locked position). Also note that the tendon of popliteus separates the lateral collateral ligament from the lateral meniscus. Thus, the lateral meniscus is not as likely to tear as is the medial meniscus, which is attached to the medial collateral ligament.
|
|
|
A bursa is a small fluid filled sac, lined with endothelium. Note that the suprapatellar bursa extends a handbreadth above the knee and 100ml of fluid from an inflamed knee can be withdrawn above the knee joint. Several of the bursae communicate with the knee joint (e.g., suprapatellar bursa) while others (e.g., prepatellar bursa) do not.
|
|
|
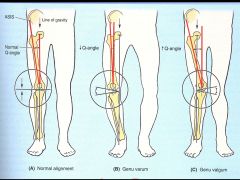
Genu Varum (bowl legs) and Genu Valgum (knock knee); latter promotes lateral dislocation of patella in women. Greater lateral pull by quads on the patella - due to wider hips.
|
|
|
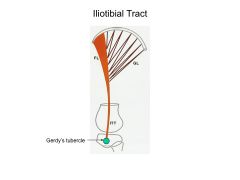
The iliotibial tract (ITT) is the thickening of the fascia lata (deep fascia) on the lateral side of the thigh. The gluteus maximus (GL) and the tensor fascia lata muscle (FL) insert into this tract. The iliotibial tract inserts into Gerdy’s tubercle - lateral tubercle of the tibia.
These 2 muscles and the ITT help to support the knee joint particularly in standing for long periods of time. Iliotibial tract (ITT) syndrome common knee pain in runners; ITT rubs over lateral femoral condyle |
|
|
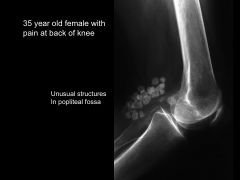
Clinical Notes for Knee
|

|
|

|
|
|
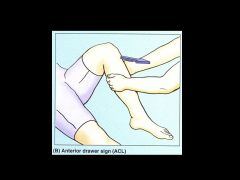
|
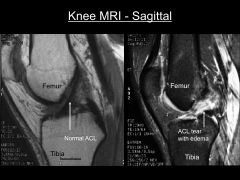
|
|

|
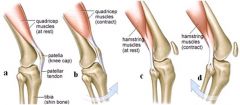
the quads can relax when the knee is extended
|
|

|
|
|

|
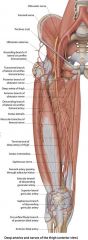
|
|
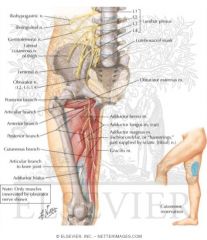
|

|
|
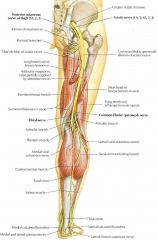
|

|
|
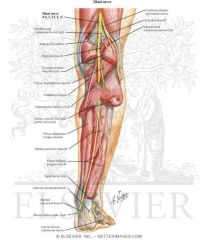
|

|
|
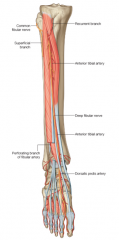
|

It gives motor supply to the extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, peroneus tertius, and extensor digitorum brevis.
It gives cutaneous supply to the region between the 1st and 2nd toes. It can be tested here. |
|
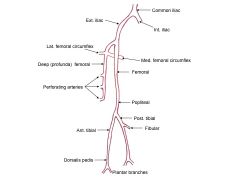
|
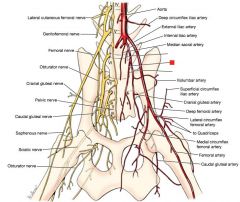
|

