![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Limbic System Overview
|
- expresses behavioural & emotional expression by way of the hypothalamus & the ANS
|
|
|
Major Components & Connections
|
1. Orbitofrontal cortex
2. Mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus 3. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus 4. Septal area 5. Limbic Lobe 6. Hippocampal formation 7. Amygdaloid complex 8. Hypothalamus 9. Limbic midbrain nuclei |
|
|
Orbitofrontal cortex
|
F: conscious perception of smell
- reciprocal connections with mediodorsal thalamus - interconnected through medial forebrain bundle with septal area & hypothalamic nuclei |
|
|
Mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus
|
- input from mamillary nucleus through amillothalamic tract & fornix
- projects to cingulate gyrus & a major link in Papez Circuit |
|
|
Septal Area
|
- telencephalic structure
- reciprocal connections with the hipocampal formation through fornix & with hypothalamus through medial forebrain bundle - projects through stria medullaris to the habenular nucleus |
|
|
Limbic Lobe
|
- includes suncallosal area, paraterminal gyrus, cingulate gyrus & isthmus & parahippocampal gyrus which includes the uncus
- also contains hippocampal formation & amygldala |
|
|
Hippocampal formation
|
sheet of archicortex that is jelly-rolled into parahippocamplal gyrus
- F; learing, memory & recognition of novelty INPUTS: entorhinal cortex OUTPUTS; fornix 1. denatate gyrus; recieve hippocampal input and projects to pyramidal cells of hippocampus & subiculum 2. Hippocampus; pyramidal cells that project through fornix to sepatal area & hypothalamus 3. Subiculum: input through hippocampal pyramidal cells, projects through fornix to mamillary nuclei & anterior nucleus of the thalamus |
|
|
Amygdala
|
basal gagnlion underlies parahippocamapal uncus.
- stimulaion causes fear & signs of SNS overactivity - lesions can cause placidity & hypersexual behaviour INPUT: sensory assoc. cortex, olfactory bulb & cortex, hypothalamus, sepatal area, hippocampal formation OUTPUT: stria terminalis to hypothalamus & septal area & to mediodrorsal thalamus |
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
reciprocal connections with amygdala
|
|
|
Limbic midbrain nuclei
|
VTA (DA)
Raphe nuclei (5HT) locus ceruleus (NA) |
|
|
Papez Circuit
|
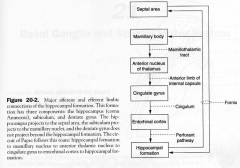
1. Hippocampal formation to
2. Mammillary nucleus 3. Anterior Thalamus 4. Cingulate Gyrus 5. Enterohinal area 6. Hippocampal formation |
|
|
Kluver-Bucy Syndrome
|
bilateral ablation of anterior temporal lobes including amydala.
- causes psychic blindness, hyperphagia, docility, hypersexuality |
|
|
Amnestic Syndrome
|
bilateral infarction of hippocampal formation
- causes anterograde amnesia, memory loss (hippocampal pathology) |
|
|
Foster Kennedy Syndrome
|
meningioma of lofactory groove, compresses both olfactory and optic nerves thus
- ipsilateral anosmia and optic atrophy & contralateral papilledema (due to INC. ICP) |
|
|
Epilepsy
|
Hippocampus most epileptogenic part of cerebrum
|
|
|
Bilateral transection of fornix
|
acute amnestic syndrome
|
|
|
Wernickes Encephalopathy
|
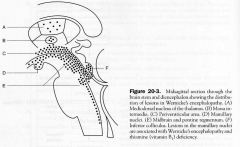
due to B1 def.
- TRIAD 1. ocular disturbances & nystagmus 2. gait ataxia 3. mental dysfunction |
|
|
Strachan's Syndrome
|
due to high dose B1
- TRIAD 1. spinal ataxia 2. optic atrophy 3. nerve deafness |
|
|
Bilateral Destruction of cingulate gyri
|
causes loss of initiative and inhibition as well as dulling of the emotions
- memory is unaffected - lesions cause placidity - Cingulectomy used to treat sever anxiety & depression |

