![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the usual age at presentation for ALL? |
2-10yrs with a second peak at 40 |
|
|
what is the usual age of presentation for AML |
usually 50-60yrs |
|
|
what are some symptoms kids will show with leukaemia? |
increasing paleness (80%) pain on walking or being held (80%) miserable, irritable (80%) bruising (80%) joint pain (10%) testicular enlargement (2%) raised ICP (2%) |
|
|
what are general groups of symptoms in acute leukaemia? |
General constitutional (e.g. malaise) Symptoms of anaemia Susceptibility to infection (e.g. sore throat, mouth ulceration, chest infection) Easy bruising and bleeding (e.g. epistaxis, gingival bleeding) Bone pain (notably in children with ALL) and joint pain Symptoms due to infiltration of tissues with blast cells (e.g. gingival hypertrophy in AML) |
|
|
what do you expect on FBE in acute leukaemia? |
FBE and film: normochromic/normocytic anaemia; pancytopenia with circulatory blast cells; platelets: usually reduced |
|
|
what's the 5 year survival rate for ALL and AML? |
The mean 5-year survival rate for childhood ALL is about 75–80%, for adult ALL 30%; for AML it varies with age with poorer survival, about 20%, over 55 years of age. |
|
|
what age group does chronic myeloid leukaemia affect? |
age 40-60yrs |
|
|
what are some symptoms of CML? |
general constitutional symptoms (malaise, night sweats, fever, weight loss) symptoms of anaemia priapism gout abdo disomfort from splenomegaly |
|
|
what do you expect in FBE with CML? |
Markedly elevated white cell count (granulocytes) Marked left shift in myeloid series Presence of Philadelphia chromosome |
|
|
what age group usually gets chronic lymphocytic leukaemia? |
late middle age and elderly |
|
|
what are some symptoms of CLL? |
constitutional symptoms (fever, wt loss, malaise, night sweats) symptoms of anaemia rubbery lymphadenopathy - groin, axilla, cervical heatosplenomegaly |
|
|
what do you expect on FBE in CLL? |
mature lymphocytosis >15 mild anaemia |
|
|
what is the classic finding on histology that differentiates hodgkins from non hodgkins lymphoma? |
reed-sternberg cells |
|
|
the following are features of what? Painless (rubbery) lymphadenopathy, especially cervical nodes Constitutional symptoms (e.g. malaise, weakness, weight loss) Fever and drenching night sweats—undulant (Pel–Ebstein) fever Pruritus Alcohol-induced pain in any enlarged lymph nodes Possible enlarged spleen and liver |
hodgkins lymphoma |
|
|
how is diagnosis of hodgkins lymphoma confirmed? what are the tests to workup HL? |
histology of lymph node biopsy. FBE, CXR, CT/MRI (to stage), bone marrow biopsy, functional isotopic scanning. Staging is by using Ann Arbor nomenclature |
|
|
what are some signs and symptoms of non-hodgkins lymphoma? |
Painless lymphadenopathy—localised or widespread Constitutional symptoms possible, especially sweating Pruritus is uncommon Extra nodal sites of disease (e.g. CNS, bone, skin, GIT) Possible enlarged liver and spleen Possible nodular infiltration of skin (e.g. mycosis fungoides) |
|
|
what are the different kinds of lymphomas? |
hodgkins and non-hodgkins. non-hodgkins is further divided in to T cell or B cell. There are >40 different kinds of lymphomas so careful workup is needed to tailor treatment. there are also some lymphomas associated with infections and autoimmune disease (burkett lymphoma in endemic EBV, mucosa associate lymphoid tissue lymphoma from H pylori infection, HIV associated lymphoma, T cell lymphoma from untreated coeliac disease) |
|
|
what age group gets non-hodgkins lymphoma? |
average age at diagnosis is 65, more common in males. its rare though - 23 cases per 100,000 males and 15 cases per 100,000 females. |
|
|
what age group gets hodgkins lymphoma? |
there is a gradual rise to a peak in the 3rd decade (20's), then again a peak later in life |
|
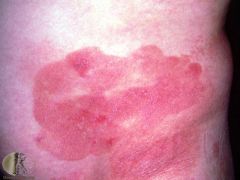
whats this |
patch stage of mycosis fungoides - difficult to distinguish from psoriasis or discoid eczema |
|
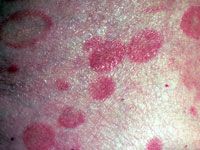
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
patch stage of mycosis fungoides |
|
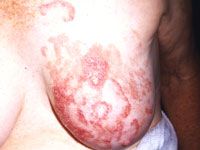
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
patch stage of mycosis fungoides |
|
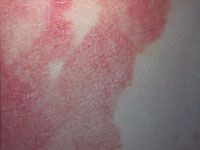
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
Poikiloderma atrophicans vasculare is an unusual variant in which the skin shows areas of thinning, pigmentary change and dilation of the capillaries |
|
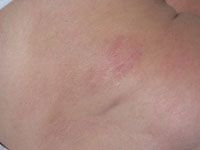
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
Poikiloderma atrophicans vasculare is an unusual variant in which the skin shows areas of thinning, pigmentary change and dilation of the capillaries |
|
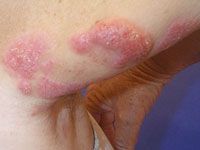
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
In plaque stage mycosis fungoides, the patches become thickened and may resemble psoriasis. They are usually itchy. |
|
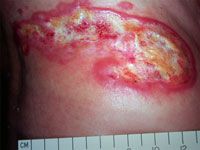
cutaenous T cell lymphoma |
tumor phase of cutaenous T cell lymphoma |

