![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What neurons comprise the splanchnic nerves?
|
Sympathetic (visceral motor) neurons and visceral sensory neurons
|
|
|
Preganglionic axons in the sympathetic trunk of what spinal nerves course to the major splanchnic n.?
|
T10-T13
|
|
|
What does the splanchnic nerve course through into the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity?
|
The lumbocostal arch.
|
|
|
Where does the splanchnic nerve course to?
|
The adrenal and celiacomesenteric ganglia and plexuses.
|
|
|
Where in the spinal cord do the minor splanchnic nn. come from? What do they supply?
|
They may leave the last thoracic and first lumbar sympathetic ganglia. They supply nerves to the adrenal gland, ganglion, celiacomesenteric ganglia and plexus.
|
|
|
Where do the lumbar splanchnic nn. arise from? Where do they course to?
|
They arise from the 2nd and 5th lumbar sympathetic ganglia. They course to the aorticorenal, cranial mesenteric, and caudal mesenteric ganglia and plexuses.
|
|
|
What do the sympathetic ganglia of the abdomen contain?
|
Cell bodies of sympathetic postganglionic neurons
|
|
|
Branches of what nerves make up the plexuses of the abdomen?
|
Branches of vagus and splanchnic sympathetic nerves and visceral afferents.
|
|
|
Are the celiac and cranial mesenteric ganglion sympathetic or parasympathetic?
What nerves contribute to the celiacomesenteric plexus? |
Sympathetic.
They receive contributions from the major splanchnic n., minor splanchnic n., and the first three lumbar splanchnic nn. |
|
|
Is the caudal mesenteric plexus sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Where do the nerves in the caudal mesenteric plexus come from? |
Sympathetic.
The nerves derive from the abdominal aortic plexus and from the more caudally located lumbar splanchnic nn. |
|
|
Are the hypogastric nn. pre or post-ganglionic?
|
Post-ganglionic.
|
|
|
Where does the urinary bladder get its innervation from?
|
The hypogastric nn.
|
|
|
What nerve provides sympathetic innervation to the pelvic viscera?
|
The hypogastric nn.
|
|
|
What is the adrenal plexus located between?
Where does it receive nerves from? |
It's located between the adrenal gland and the diaphragm.
It receives fibers from the major and minor splanchnic nn. and the celiac ganglion. |
|
|
What do the lumbar arteries supply blood to?
|
The lumbar region of the spinal cord, meninges, lumbar muscles and skin.
|
|
|
What does the celiac artery supply blood to?
|
The celiac artery supplies blood to the stomach and several other abdominal organs.
|
|
|
What vessel supplies blood to the small and large intestine?
|
The cranial mesenteric artery.
|
|
|
Which of these vessels are unpaired?
Lumbar Celiac Cranial mesenteric Phrenicoabdominal Renal Testicular/Ovarian Caudal mesenteric Deep circumflex iliac External iliac Internal iliac |
Celiac
Cranial mesenteric Caudal mesenteric |
|
|
What do the phrenicoabdominal arteries branch into?
What is the clinical signifigance of the phrenicoabdominal arteries? |
The caudal phrenic artery going to the diaphragm.
The cranial abdominal artery which goes to the craniodorsal abdominal wall. The phrenicoabdominal artery is the one that you need to be careful of while performing adrenal surgery. |
|
|
Where do branches off the ovarian and testicular arteries supply blood to?
|
The ovarian arteries branch to the uterus.
The testicular artery courses to the vaginal ring and then to the testis inside the spermatic cord. |
|
|
What does the caudal mesenteric artery supply blood to?
|
The distal region of the intestinal tract.
|
|
|
What do the iliac arteries supply blood to?
|
Deep circumflex supplies the caudodorsal abdominal wall.
The external supplies the pelvic limbs, the internal the pelvic cavity and pelvic limbs. |
|
|
What does the aorta continue as?
|
The median sacral artery.
|
|
|
What are the three main blood supplies to the stomach and intestine?
|
The celiac, cranial, and caudal mesenteric artery.
|
|
|
What are the three branches off of the celiac artery?
|
Hepatic a., left gastric a., and splenic a.
|
|
|
The hepatic a. has three branches, describe the tree of branches that come from the hepatic artery and what they supply blood to.
|
The hepatic artery branches into the hepatic, gastric, and gastroduodenal arteries.
The hepatic branch off of the hepatic artery supplies blood to the liver. Off of the hepatic branch comes the cystic artery which goes to the gall bladder. The right gastric artery supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach and the right side of the lesser omentum. The gastroduodenal artery becomes the right gastroepiploic and cranial pancreaticoduodenal arteries. The right gastroepiploic artery supplies the greater curvature of the stomach and the great omentum on the right side. The cranial pancreaticoduodenal artery supplies the initial portion of the duodenum and adjacent right lobe of the pancreas. |
|
|
What does the celiac a.branch and supply blood to?
|
It branches to the left gastric artery and then to the esophageal branches.
The left gastric artery supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach on the left side. The esophageal branches of the left gastric artery supplies the esophagus. |
|
|
What branches come from the splenic artery and where do they supply blood?
|
The splenic artery branches into the pancreatic branches, splenic branches, short gastric arteries, and left gastroepiploic artery.
The left lobe is supplied by the pancreatic artery. The splenic branches supply the spleen. The fundus of the stomach is supplied by the short gastric arteries. The left gastroepiploic artery supplies the greater curvature of the stomach and the greater omentum, both on the left side. |
|
|
Clinically, what branch off of the celiac artery will we deal with the most?
|
The splenic artery.
|
|
|
Why are splenectomies so tricky?
|
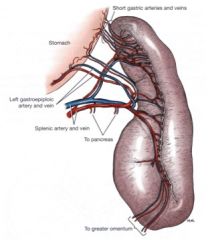
As the picture shows, you can't ligate the splenic artery and vein before they serve the stomach, so must ligate all of the branches.
|
|
|
What structures are supplied by the celiac artery? It was a Jeopardy question!
|
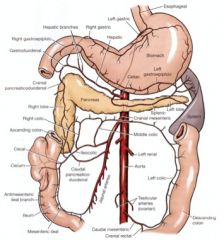
A crap storm. The nine organs are:
spleen, pancreas, stomach, esophagus, liver, gall bladder, duodenum, lesser omentum, greater omentum |
|
|
What are the four branches of the cranial mesenteric artery?
Which one supplies blood to the distal part of the duodenum? |
The common colic, caudal pancreaticoduodenal, jejunal, and ileal arteries.
The caudal pancreaticoduodenal artery supplies blood to the distal part of the duodeunum and the pancreas. |
|
|
What's the difference between the ilium and the ileum?
|
Ilium - pelvis
Ileum - enteric or intestines |
|
|
What does the common colic artery branch into and what do the branches supply?
|
The common colic artery, or common trunk, branches into the ileocolic a. (which branches into the colic and mesenteric ileal branches and the cecal artery), right colic a. and middle colic a.
The colic branch of the ileocolic artery supplies the initial ascending colon. The cecal artery gives rise to the antimesenteric ileal branch supplying the ileum. Also supplying the ileum is the mesenteric ileal branch of the ileocolic artery. The right colic artery supplies blood to the distal ascending colon, the right colic flexure, and the initial transverse colon. The middle colic artery supplies blood to the distal transverse colon, the left colic flexure and the initial descending colon. |
|
|
What does the caudal pancreaticoduodenal artery supply blood to?
|
The distal descending duodenum and right lobe of the pancreas.
|
|
|
What does the ileal arteries anastomose with?
|
The mesenteric ileal arteries.
|
|
|
What are the two branches from the caudal mesenteric artery?
What areas do these arteries supply? |
The left colic artery and cranial rectal artery.
The left colic artery supplies the distal descending colon. The cranial rectal artery supplies the initial rectum. |
|
|
What supplies blood to lesser and greater curvature of the stomach?
|
The lesser curvature is supplied by the left gastric a. from the celiac a. and the right gastric a. from the hepatic a.
The greater curvature is supplied by the left gastroepiploic artery from the splenic a. and the right gastroepiploic artery from the gastroduodenal a. off of the hepatic a. |
|
|
What supplies blood to the proximal and distal duodenum?
|
Proximally, the duodenum is supplied by the cranial pancreaticoduodenal artery from the hepatic artery.
Distally, the duodenum is supplied by the caudal pancreaticoduodenal artery from the cranial mesenteric artery. |
|
|
Where does the celiac artery stop and the cranial mesenteric artery pick up for it?
|
The mid-duodenum. The proximal part is served from the celiac a. and the distal part from the cranial mesenteric a.
|
|
|
What supplies blood to the ileum?
|
The ileal, mesenteric ileal branches and antimesenteric ilieal branches.
|
|
|
What supplies blood to the colon?
|
The initial ascending colon is supplied by the colic branches of the ileocolic a.
The distal ascending colon, right colic flexure and the initial transverse colon are supplied by the right colic artery. The distal transverse colon, the left colic flexure, and the initial descending colon are supplied by the middle colic a. The distal descending colon is awash in blood from the left colic artery. The initial rectum is supplied by blood from the cranial rectal artery. |
|
|
What is the portal vein joined from?
|
The cranial and caudal mesenteric veins.
|
|
|
Why do structures deliver blood to the hepatic portal veins?
|
The structures draining to the portal vein make sense because they contain blood that needs to be filtered for toxins and nutrients.
The cranial mesenteric vein drains blood from the jejunum, ileum, duodenum, and pancreas. The caudal mesenteric vein drains blood from the cecum and colon. The gastroduodenal vein drains the pancreas, stomach, duodenum, and greater omentum. The splenic vein drains the spleen, stomach, pancreas and greater omentum. |
|
|
What veins deliver blood to the hepatic portal vein?
|
the cranial and caudal mesenteric veins, the gastroduodenal vein and the splenic vein.
|
|
|
What veins drain into the caudal vena cava?
|
The lumbar, hepatic, phrenicoabdominal, renal, right testicular and ovarian, deep circumflex iliac and common iliac veins all drain to the caudal vena cava.
|

