![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
muscle movement uses what specialized cells for contraction? |
muscle fibers |
|
|
muscle movement depends on interaction of which two proteins? |
actin and myosin |
|
|
three types of vertebrate muscle tissue |
skeletal, cardiac, smooth |
|
|
T/F: muscles can only actively shorten |
true |
|
|
muscle fiber consists of |
myofibril and filaments |
|
|
what is the thick portion of filaments |
myosin |
|
|
what is the thin portion of filaments |
actin |
|
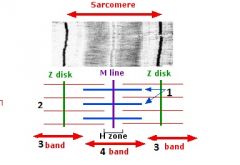
type of filament and actin or myosin for 1 |
thick, myosin
|
|
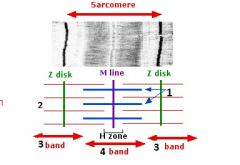
type of filament and actin or myosin for 2 |
thin filament, actin |
|
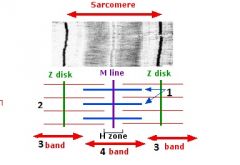
3 |
I band |
|
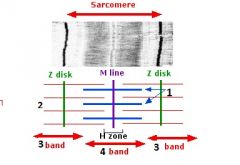
4 |
A band |
|
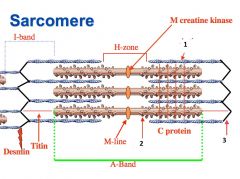
1 actin or myosin |
actin |
|
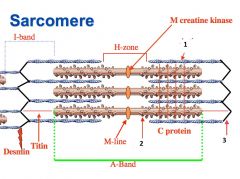
2 actin or myosin |
myosin |
|
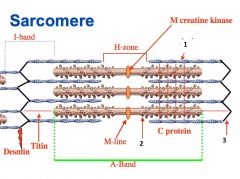
3 |
Z line |
|
|
what forms the cross bridges |
myosin heads |
|
|
what are the cross bridges used for in muscle contraction |
bind active sites on actin filaments |
|
|
what is required to contract muscle |
ATP |
|
|
what is the neuromuscular junction |
place where motor axon terminates on muscle fiber |
|
|
How does nerve stimulate muscle to contract? |
1. nerve impulse travels to neuromuscular junction, 2.neurotransmitter is released and binds to receptors, 3. excitation of muscle membrane |
|
|
how does muscle excitation cause contraction? |
1. excitation of muscle cell membrane travels into cell along t-tubule 2. calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum 3. calcium binds to troponin which causes tropomyosin to uncover active sites |
|
|
awhich type of respiration requires oxygen |
aerobic |
|
|
in what form is extra energy stored in muscles |
glycogen and creatine phosphate |
|
|
where is elastic energy stored |
tendons and cuticle |
|
|
to who does homeostasis go back to? |
Walter B. Cannon |
|
|
isosmotic means |
animal has same concentration as surroundings |
|
|
hypoosmotic means |
animals has lower concentration than surroundings |
|
|
herposmotic |
animal has higher concentration than surroundings |
|
|
what is the process of diffusion |
concentration going from high to low |
|
|
what is osmosis |
diffusion of water |
|
|
what is an isotonic solution |
same concentration as cytoplasm |
|
|
what is a hypertonic solution and what happens (bursting/shrivelling) |
more concentrated than cytoplasm; shrivelling |
|
|
what is a hypootonic solution and what happens (bursting/shrivelling) |
less concentrated than cytoplasm; bursting |
|
|
what are osmoconformers |
animals thatmaintain an internal environment that is isosmotic to their external environment |
|
|
what is being stenohaline |
restricted to living in narrow salinity range |
|
|
what is being an osmoregulator |
able to regulate or keep the solutes or salts o body fluid at a higher or lower concentration than the concentration of solutes in surroundings
|
|
|
is a shore crab an osmoregulator or osmoconformer |
osmoregulator |
|
|
marine fishes are (hypo/hyper)-osmotic regulators |
hypo |
|
|
osmoregulators excrete _______ and absorb salts through ______ __________ |
water; active transport |
|
|
freshwater animals are (hyper/hypo)-osmotic regulators |
hyper |
|
|
what do freshwater fishes have to do constantly to hyperregulate? |
pee constantly |
|
|
what do marine fishes have to do to hyporegulate? |
drink constantly |
|
|
marine sharks and ray maintain _____ to (raise/lower) osmolarity which makes them isosmotic |
urea; raise |
|
|
how do terrestrial animals lose water |
evaporation, excretion of wastes |
|
|
how do terrestrial animals conserve water |
concentrated urine, behavioral strategies |
|
|
what are the three possible forms of nitrogeneous waste |
smmonia, urea, uric acid |
|
|
what animals excrete ammonia |
fishes |
|
|
what animals excrete urea |
mammals |
|
|
what animals excrete uric acid, amphibians |
insects, land snails, birds |
|
|
what is the invertebrate excretory system |
nephridia |
|
|
excretory system for arthropods |
antennal |
|
|
excretory system for vertebrates |
kidney |
|
|
what is it called when fluid is filtered from blood into bowman's capsule |
glomerular filtration |
|
|
are cells and proteins included in glomerular filtration |
no |
|
|
what is absorbed during tubular reabsorption? |
amino acids, glucose, ions, water |
|
|
what is absorbed in tubular secretion |
ions |
|
|
what is the main idea of diabetes |
not enough insulin, so glucose builds up in blood and body cells can't take it in and glucose appears in urine |
|
|
where in the kidney is there a high concentration of salts and urea |
medulla |
|
|
what controls the permability of collecting duct |
ADH |
|
|
what does mammalian urine concentration depend on |
osmolarity of renal medulla |
|
|
an animal that lives in the desert has a (long/short) loop of Henle and produces (high/low) concentrated urine |
long; high |

