![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Syphilis is caused by what agent?
What's its shape? |
Treponema pallidum
Spirochete |
|
|
Syphilis types?
|
Infectious
endemic congenital |
|
|
Syphilis clinical types?
|
primary
secondary tertiary quaternary latent congenital |
|
|
Orofacial menifestations of primary syphilis?
|
chancres 4-12%
males: upper lip females: lower lip tongue, gingivae, fauces cervical lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Orofacial menifestations of secondary syphilis?
|
ulcer (painless/grey)
snail tract ulcers maculopapular eruptions lymphadenopathy sialadenitis |
|
|
Orofacial menifestations of tertiary syphilis?
|
gummata
|
|
|
Early features of congenital syphilis?
|
Condylomata lata at mucocutaneous junctions
radiating rhagades at angle of mouth, nose, eyes, severe mucosal ulceration |
|
|
Late features of congenital syphilis?
|
Hutchinson's permanent incisors
Moon's permanent molars Frontl and parietal bossing saddle shape nose deep palatal vault mandibular prognathism cranial neuropathies |
|
|
What methods to verify it's syphilis?
|
veneral disease reference laboratory (VDRL)
rapid plasma reagin card test (RPR) T. pallidum haemaglutination assay (TPHA)** fluorescent treponema antibody absorption test (FTA Abs) |
|
|
Oral manifestations of tuberculosis?
|
It's rare:
oral ulceration (painless on tongue, gingivae, lip) cervical lymphadenopathy osteomyelitis (maxilla > mandible) parotid swelling, parotitis, fistula CN VII palsy TMJ involvement |
|
|
How to verify TB?
|
Mantoux test
followed by PCR for confirmation |
|
|
Tuberculosis is caused by which organism?
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
Name two other mycobacteria
|
M. avium (oral ulcer)
M. leprae (leprosy) |
|
|
actinomyces is caused by gram ___ aerobic/anaerobic bacteria
|
positive
anaerobic |
|
|
Actinomycosis
clinical features: site |
cervicofacial region, thoracic, abdominal, cutaneous, genital
|
|
|
Actinomycosis
clinical features: appearance |
Suppurative yellow, sulphur granules
Fistula on the skin |
|
|
Actinomycosis
Management? |
High doeses of antibiotics
penicilin for 3-6 weeks Excision of sinus tracts |
|
|
ANUG
Predisposing factors? |
psycholgic stress
smlking local trauma poor nutrition oral hygiene |
|
|
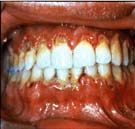
ANUG
Clinical: Appearance? |
inflamed and edematous interdental papillae with punched out crater like necrosis
Grey psudomembranous covering Bad odour Exquisite pain |
|
|
Noma/Cancrum oris or ANUG are caused by what organisms?
|
fusobacterium nucleatum
Borrelia vincenti Staph. aureus Streptococcus |
|
|
Management of ANUG?
|
thorough cleaning of teeth
metronidazole |
|
|
List all HHV from 1 to 8
Name them and name the associated disease |
HHV1: or HSV1 Herpes labialis
HHV2: or HSV2 Genital herpes HHV3: varicella zoster: chicken pox/ herpes zoster HHV4 (Epstein-Barr): Hairy leukoplakia, infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever), lymphomas, nasopharyngeal carcinoma HHV5 (cytomegalovirus) HHV8 |
|
|
Mode of transmission for HSV1?
Mode of transmission for HSV2? |
HSV1: oral/saliva
HSV2: genital/sexual |
|
|
Herpes simplex incubation period?
|
3-9 days
|
|
|
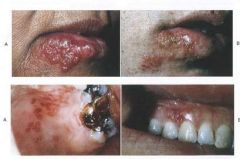
Herpes Simplex:
for primary exposures, early exposure leads to what disease? |
gingivostomatitis
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex:
for primary exposures, late exposure leads to what disease? |
early:gingivostomatitis
late:pharyngotonsilitis |
|
|
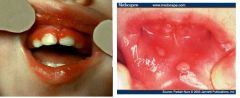
Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis:
age? |
6months to 5 yrs
|
|
|
Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis:
signs and symptoms? |
cervical lymphadenopathy
fever anorexia irritability soreness |
|
|
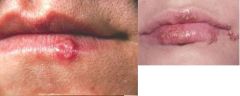
Herpes labialis
AKA? |
cold sore
fever blister |
|
|
Herpes labialis
site? |
vermillion border
|
|
|
Herpes labialis:
Prodrome? |
pain
burning itching tingling localised warm sensation erythema |
|
|
Herpes labialis:
When does is re-emerge? Healing time? |
when immunocompromised
7 to 10 days |
|
|
Herpes labialis:
most common appearance? |
3mm vesicle
|
|
|
Herpes virus infection in the finger is called?
|
Herpetic whitlow
|
|
|
Hand Foot and mouth disease caused by ....
|
enterovirus
|
|
|
Hand Foot and mouth disease :
presentation? |
skin 1 - 100 lesions
resemble herpangina Vesicles |
|
|
Hand Foot and mouth disease
Diagnosis? |
Serology enteroviral IgM
|
|
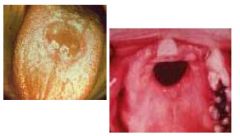
|
gummata (tertiary syphilis)
|
|
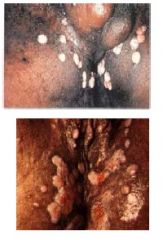
|
Congential syphilis
|
|
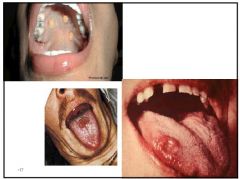
|
Congential syphilis
|
|
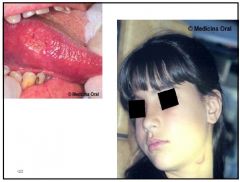
|
Tuberculosis
|
|
|
anug
|
|
|
Herpes Simplex Infection
|
|
|
Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis
|
|
|
Herpes labialis
|
|
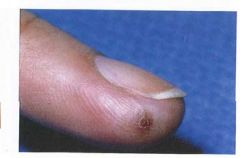
|
Herpetic whitlow
|
|
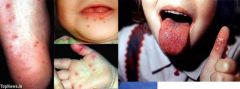
|
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease
|
|
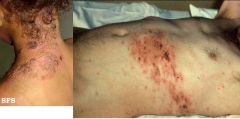
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
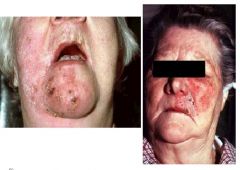
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
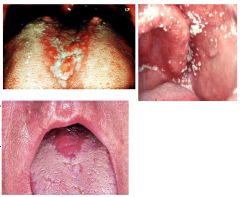
|
Candidiasis
|
|
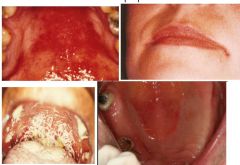
|
Candidiasis
|
|
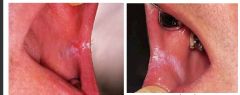
|
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
|
|
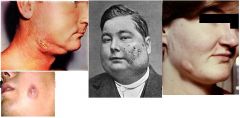
|
actinomycosis
|
|
|
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease
duration? |
resolves in a week
|
|
|
Herpes zoster
virus is dormant in which area? |
sensory nerves
dorsal root ganglia |
|
|
Herpes zoster
Predisposing factors |
old age,
immunosuppression, radiation, cytotoxic drugs, dental manipulation, malignancies |
|
|
Herpes zoster
clinical features? |
Prodromal pain over the skin of affected nerve, may be accompanied by fever, malaise, headache: 1 - 4 days
Pain may masquerade as sensitive teeth, otitis media, migraine headache, myocardial infraction, appendicitis Skin vesicles (cluster) on an erythematous base 3 - 4 days: pustular, ulcerate 7 - 10 days: crusting 2 - 3 weeks: exanthem resolves |
|
|
Herpes zoster
if pain lasts for more than a month and continues it is termed? |
Post-herpetic neuralgia
|
|
|
Herpes zoster
Management? |
Acyclovir/aciclovir
Corticosteroids |
|
|
Candidiasis
Predisposing factors? Local and systemic |
Local: smoking, xerostomia, corticosteroids,
broad-spectrum antibiotics, cytotoxics, irradiation, malnutrition, dental prosthesis Systemic: immune defects by malnutrition, chemotherapy |
|
|
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
frequency? |
uncommon
|
|
|
Chronic hyperplastic Candidiasis
age and sex? |
Middle aged/elderly with no sex predilection
|
|
|
Chronic hyperplastic Candidiasis
Management? |
stop habit, anti-fungals and, surgery
|

