![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 major cell type classification based on energy requirements ? Describe them |
Photoautotrophs, energy from light and CO2 as carbon source. Photoheterotrophs, energy from light and organic compounds as C source. Chemoautotrophs, energy from reduced organic molecules and CO2 as carbon source. Chemoheterotrophs, energy from reduced organic molecules and organic compounds as C source. |
|
|
5 major cell type classification based on Oxygen requirements? Describe them |
Obligate aerobes, require oxygen to live Facultative anaerobes, do not require oxygen but use it if available (better wiht oxygen) Obligate anaerobes, die in presence of oxygen Aerotolerant, do not mind oxygen, no advantage if in oxygen Microaerophiles, require oxygen only at low levels (0.2 atm or less if more then they die) |
|
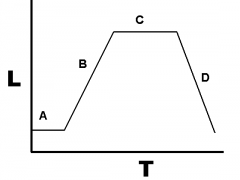
- Name each phase (A, B, ...) - What causes C, and D? (hint: what are they running out off?) - When are they more susceptible to antibiotics? |
A: Lag phase B: growth phase C: stationary phase D: decline phase - the plateau is caused by close to 1 ratio of growth and cell death. ( [nutrient]~[waste] ) and the decline when cells die due to poor growth. - B: more susceptible due to increased growth and synthesis. |
|
|
Describe psychrophiles, mesophiles and thermophiles. |
psychrophiles, grow between -10C and 20C mesophiles, (most baceria) grow between 10C and 50C thermophiles, growth between 40C and 70C. |
|
|
Examples of acid tolerants? (name 2 general ones) Extreme halophiles? define |
acid tolerants: fermenters and yeast. extreme halophiles: can survive extremely hypertonic environments |
|
|
Define the following types of growth medium: - minimal essential growth medium - Complex growth medium - Differential growth medium - Selective growth medium |
Minimal essential: consist of primary precursors compounds essential for growth. Bacteria needs to synthesize most organic compounds Complex: contains most organic compounds building blocks necessary for growth. Differential: contains nutrients and pH indicators to allow visual distinction between different bacteria Selective: contains compounds that prevent the growth of unwanted bacteria while allowing others to grow |
|
|
Define antisepsis, disinfection and sterilization. |
antisepsis: kill or prevent growth (can be used on body) (i.e. EtOH, iodophor, etc) disinfection: kill bacterial and some eukaryotic cells (not too safe for body parts). (i.e Formaldehyde, some alcohols, H2O2) sterilization: total inactivation of all living things (UV and iodizing radiation, filtration, autoclaving) |
|
|
McConkey Agar, what is it used for ? (in terms of bacteria species we have discussed in class) |
Used to identify Enteric gram(-) cells (Ecoli, salmonella, shigella) It's a differential and selective growth medium. Contains pH indicator and inhibits growth of gram(+) bacteria. |
|
|
Identify. Process by which cells duplicate their DNA and form a hard coat around themselves that can resist extreme heat and desiccation when environment is unfavorable. |
Sporogenesis, formation of spores that allow bacteria to remain dormant and be almost indestructible. Can germinate back when environment is favorable. |

