![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
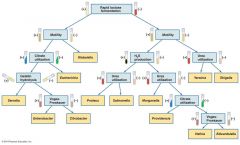
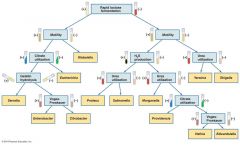
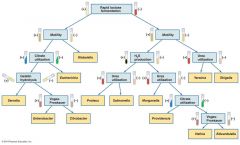
Pathogenic Gram Negative Bacteria: Enterobacteriaceae |
•Escherichia •Enterobacter •Salmonella •Serratia •Proteus |
|
|
|
Pathogenic Gram Negative Bacteria: Enterobacteriaceae - multi-drug resistance |
•2nd class Carbapenem resistant |
|
|
|
Coliform Bacteria (within Enterobacteriaceae) |
•Facultative anaerobe •Gram negative bacteria |
|
|
|
Escherichia |
•Facultative anaerobic, non-spores •Serotype (strains) cause disease •Enterohemorrhagic. coli •Enteroinvasive E. coli •Enterotoxigenic E. coli •Enteroaggregative E. coli •Enteropathogenic E. coli |
|
|
|
Enterohemorrhagic E.Coli EHC - Coliform Bacteria |
•Shiga-like toxin •Acts on vascular endothelium •Causes inhibition in protein synthesis •Kills vascular endothelial cells •Bloody diarrhea, little to no fever •Leads to hemorrhage •Complication: Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome |
|
|
|
Enteroinvasive E.Coli EIC - Coliform Bacteria |
•No Shiga-like toxins •Use surface protein, adhesin, attach to cells of intestines •Invade & destruction of intestinal cells •Self-limiting; run course; if serious antibiotics |
Goes into cell don't produce toxins |
|
|
Enteroaggregative E.Coli EAC - Coliform Bacteria |
•Aggregate w/each other after attaching to intestinal cells •Mucous blanket promote (bioform characteristic) •Produce enterotoxins & cytotoxins induce inflammation •Watery or mucoid diarrhea, low-grade fever |
•Travelers diarrhea • No clean water • Newest class |
|
|
Enterotoxigenic E.Coli ETEC - Coliform Bacteria |
•Activate intestinal cells to hypersecrete water & chloride into the lumen (loses water) •Antibodies produced for heat labile toxins •Run course |
Common traverlers diarrhea |
|
|
Enterotoxigenic E. Coli ETEC - Coliform Bacteria What are 2 types of toxin? |
•Heat labile toxins |
|
|
|
Enteropathogenic E.Coli EPEC - Coliform Bacteria |
•No shiga-like toxin •Attachment of organism to intestinal cells cause the destruction •Water diarrhea, develop dysentery |
|
|
|
Treatment for Escherichia Coli |
•Meningitis (serious disease) |
|
|
|
Klebsiella |
•Facultative anaerobe •Encapsulated •Klebsiella pneumoniae |
|
|
|
Klebsiella causes |
•Immunodeficient patients •Meningitis •Pneumonia •UTI •URTI |
•Alcoholics •Drug addicts •Steroid uses |
|
|
Klebsiella treatment |
•Intrinsic antibiotic resistance •Molecular mimicry implicated in autoimmune diseases (host cell immune attack body) •Sensitive study |
|
|
|
Serratia |
•Facultative anaerobic, ferments lactose •S. Marcescens •Nosocomial infections (elderly care homes; hospitals) |
|
|
|
Serratia Causes |
•Endocarditis (heart) •Meningitis •URTI •UTI |
|
|
|
Serratia antibiotic resistance |
•Ampicillin •Early generation Cephalosporin •Macrolides •Sensitive study |
|
|
|
Enterobacter |
•Facultative anaerobic •E.aerogenes, E. cloacae •Opportunistic & nosocomial infections |
|
|
|
Enterobacter causes |
•CNS infections (meningitis, encephalitis) •Endocarditis •Respiratory tract infections (pneumonia) •Tissue infections (cutaneous) •UTI |
|
|
|
Enterobacter treatments |
•Aminoglycosides, Carbapenems, Fluoroquinolones |
|
|
|
Enterobacter infections risk factor |
ICU care |
|
|
|
Proteus |
•Facultative Anaerobe, •Breaks down urea (kills bacteria) •Community acquired infections •P. Mirabilis, P. Penneri, P. Vulgaris, |
|
|
|
Proteus causes |
•Endotoxin induced sepsis (gram -) •SIRS (can't locate issue - 50% death) •Struvite stones (collect in clumps) •UTI (cathers) |
|
|
|
Proteus treatments |
•Cephalosporin •Fluoroquinolone •Vancomycin |
|
|
|
Morganella |
•Facultative anaerobe, oxidase-negative, catalase •Endophthalmitis (fluids in eye) •Meningitis •Sepsis •Septic arthritis |
|
|
|
Morganella treatments |
•Cephalosporin •Extended spectrum β - lactam •Fluoroquinolone •Sensitive study (48-72) |
|
|
|
Providencia |
•Facultative anaerobic, catalase & urease positive •P.stuartii, P. rettgeri •Found in urine, & other bodily fluids •UTI - long dwelling catheters (month) |
|
|
|
Providencia treatments |
•Carbapenem •Cephalosporin •Extended spectrum β - lactam •Sensitive study (48-72) |
|
|
|
Providencia infections of the eye? |
•Conjunctivitis •Keratitis |
|

