![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What UDP-glucunorate derived from?
|
UDP-glucose
|
|
|
What UDP-glucuronate a precursor to (6 types of molecules)?
|
~proteoglycans & glucoprotein
UDP-xylose ~GLUCURONides ~iduRONATE ~bilirubin diGLUCURONide |
|
|
Where do glucuronidation reactions take place?
|
Mostly in liver and intestine
|
|
|
What is mutarotation?
|
spontaneously change at anomeric sugar between the α and β configurations, possible by opening of the ring structure
|
|
|
What 2 molecules does sucrose starts has?
|
O-α-D-Glucopyranosyl
(1—> 2)-β-D-Fructofuranoside |
|
|
Which enzyme cleaves sucrose?
|
Invertase
|
|
|
Why does muturotation need to occur after sucrose cleavage?
|
D-fructose is in the β-form, needs to change to α-conformation
|
|
|
Which enz initiates fruc metab in muscles if this enz is in LARGE qty?
What is 1st step? |
hexokinase
fructose --> F6P (direct glycolytic intermediate) |
|
|
Diff between liver vs. muscle fruct metabl?
|
predominance of glucokinase in liver which is gluc specific so diff enz needed vs. hexokinase in muscle which can phosph. fruct.
|
|
|
Fruct metabolized by which enz in liver? 1st reaction? 2nd reaction & enz?
|
fructokinase
1st: fru --> F1P (commited step) F1P aldolase 2nd: F1P ------->glycealdehyde |
|
|
Faith of gyceraldehyde in fructose metabolism?
|
->glycealdehyde-3-P (glyceyde Kase) --> glycolysis
--->glycerol(alcohol dehyoase) ->glycer3P(kinase)-->dihydroxyacertone--> glycolysis |
|
|
2 faith of glycehyldehyde in fruct metabolism?
|
1. phopho by glyceralhdehyde
2. Hydrolysed by alcohol dehydrogenase |
|
|
percent of lactose in cow's milk?
|
4-5%
|
|
|
What type of bond in lactose?
|
β-1,4 glycosidic bond
|
|
|
Since lactose is a heiacetal, what reaction can it undergo? What does this make it?
|
Mutorotation
Reducing sugar |
|
|
Which enz and product phosphorylase galactose?
|
Galactokinase
G1P |
|
|
Type of enzyme epimerizes UDP-glalactose to UDP-glucose?
What other products after that? |
isomerase
Gal1P --> G1P --> G6P --> glycolysis(tissues) or glucose in liver |
|
|
Which enzymes involved in Classic galactosemia and
non-classic galactosemia? |
Classic galactosemia: galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase.non-classic: galactokinase.
|
|
|
Whic 2 types of molecule require UDP-Galactose?
|
Glycoproteins
Glycolipids |
|
|
Where does lactose synthesis take place? Which enzyme, made of what?
|
only in mammary glands
ER enz: called lactase synthetase made of glalactosyltransferease + α-lactalbumin |
|
|
Which hormonal signal stimulates lactose synthesis?
Describe what happens: |
Prolactin following partution
lowers Km of α-lactalbumin from 1200 to 1 mM. |
|
|
What other role will galactotransferase take in the absebce of α-lactalbumin?
|
Function in the glycoprotein pathway
|
|
|
What 2 substate are needed for lactose synthesis?
|
UDP-glalactose
GLucose |
|
|
Which enz. and type of glycosydic bond link can be hydrolysed in month?
|
α-amylase
INTERNAL α-1,4 glycosidic bonds randomly hydrolyzed |
|
|
Where does complex CHO hydrolysis continue? what does it produce?
|
Small intestine: mix of disaccharide, trisaccharide, and sl oligosaccharides called limit dextrins, containing (1,6) branches
|
|
|
Final hydrolysis of alpha(1,6)bond are done by which type of enzyme?
|
glycosidases
|
|
|
2 ways to classify glycosidases?
|
1. By what part of polysacch. they cut:
endoglycosidase (middle) exo... (end) 2. if change alpha to beta (inverting) vs. not (returning) |
|
|
Where do you primarely find (1)glycolipids, (2)glycoprotein, (3)proteoglycans?
|
1.exoplasmic cell membrane
2. blood and cell membrane 3.ECM |
|
|
Where do 1.synthesis and 2.degradation of glycoconjugates occur?
|
1. endoplasmic reticulum and golgi.
2.lysosome |
|
|
Generalized Glycosyltransferase Reaction?
|
Nucleotide-Sugar + HO-Acceptor --> Sugar-O-Acceptor
enz. glycotransferase |
|
|
Define proteoglycans, decriscribing main componants:
|
GAG-GalGalXyl-O-CH2-protein
GAG:glycoaminoglycan (repeating dissach units GalNAc or GlcNAc + uronic acid (glucuronic or iduronic)) trissacharide (gal/gla/xyl) O-glycosidic bond to S residue of core protein |
|
|
Why are proteoglycans possess lg neg charge?
Advantage? |
1. residues are frequently sulfated
2. highly hydrated --> take large space in ECM (good as lubricant and molecule stucture |
|
|
Proteoglycans are componant of what? Name 4
|
ECM
joint fluid, humor of the eye, arterial walls bone and cartilage |
|
|
What are glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)?
|
long unbranched polysacc of repeating disacc(contain either of 2 modif. sugars (N-GalNAc or N-GlcNAc, and uronic acid (glucuronate or iduronate)
|
|
|
2 class of glycoprotein?
|
carbohydrate chains that are N-linked (via an Asn), O-linked (via Ser or Thr)
|
|
|
Name 3 GAGs
|
1. Heparin (lining the arteries of the lungs, liver and skin)
2. Hyaluronates (synovial fluid, vitreous humor, ECM) 3. Keratan sulfates (cornea, bone, cartilage) |
|
|
Name a common O-linked glycoprotein:
|
Mucins
|
|
|
Some mucins propreties:
|
-Found in gastro, resp. and resp. tract secretion
-Form protective physical barrier on skin, involv. cell-cell interactions, may mask or contain antigens -Extended stucture = high vicoelasticity -high in O-glycan chains |
|
|
Main features of O-glycolysation:
|
-enzymes are called: glycolyltransferase
-enz located in gogli apparatus -occurs pOst-translationally at Ser or Threonine residues |
|
|
N-linked transferred ____ translationally to protein
|
co-
|
|
|
In glycolipids what is CHO attached to?
|
Carbohydrates are attached to ceramide(a sphingolipid: sphingosineplus fatty acid).
|
|
|
A main funtion of glycolipids?
|
Involved in cell-cell contact/interactions
|
|
|
2 main classes of glycolipids and composition? And each are found where?
|
-CEREBROsides: single sugar group linked to ceramide, (gal or glu) high [ ] in brain
-Gangliosides–contain sialic acid residues, longer and branched vs. cerebrosides, in cell membrane |
|
|
What are sulfatides:
|
sulfated cerebosides
|
|
|
galactocerebroside has which 2 main:components
|
Galactose + ceramide
|
|
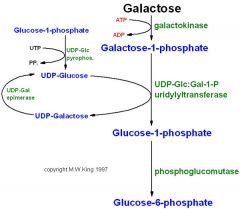
|
Galactose metabolism
|
|
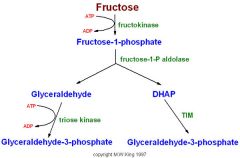
|
Fructose metabolism
|
|
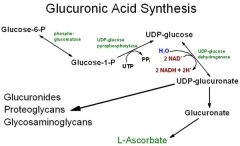
|
glucuronic metab
|

