![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
An essential ingredient for the multiple chemical reactions that take place within the cells of the body (large protein molecules). |
Enzymes |
|
|
Enzymes are large protein molecules that act as ____________ in biochemical reaction's, they speed up chemical reactions or allow them to take place under conditions that are otherwise not favorable to the reactions without their help. most of the chemical reactions necessary for life would either proceed to slowly to become affective or not proceed at all without them. |
Catalysts |
|
|
What speeds up the chemical reaction process without itself being changed? |
Enzymes or catalysts |
|
|
Enzymes or catalysts are usually in the form of... |
Proteins |
|
|
An enzyme works by lowering the... |
Energy of activation |
|
|
Prior to the chemical reaction that results in products a specific site on the enzyme molecule called the active site binds with the substrate to produce an _______ __________ ______ |
Enzyme substrate complex |
|

This diagram is called the... |
Lock and key model |
|
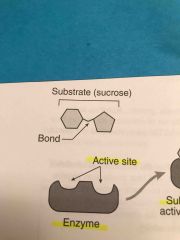
This substrate at the beginning of the reaction is called The... |
Reactant |
|
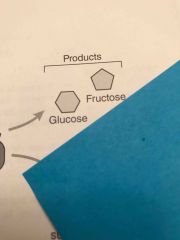
The substrate at the end of the reaction is called... |
The products |
|
What are the arrows pointing to |
The active site |
|
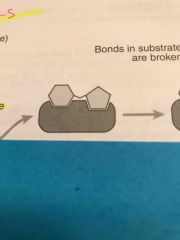
What are the shapes that are bonding to the active site? |
Substrate |
|
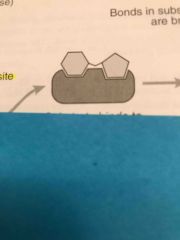
What is it called when the substrate binds to the active site? |
Enzyme substrate complex |
|
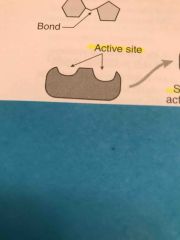
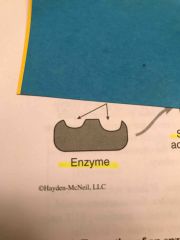
What is the gray shape called? |
Enzyme |
|
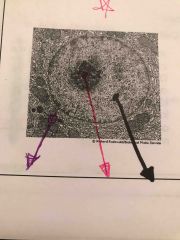
What do these three lines represent |
Purple cytoplasm pink nucleolus black nucleus |
|
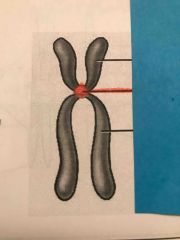
What does the red area represent? |
centromere |
|
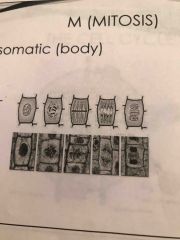
Name the phases of mitosis in order |
Interphase (technically not part of mitosis) prophase metaphase anaphase telophase |
|
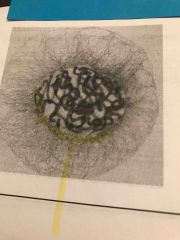
What type of cell in what phase of mitosis |
Animal prophase |
|

What type of cell in what phase of mitosis |
Plant prophase |
|
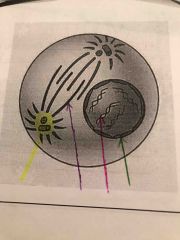
What phase of mitosis and what are the lines pointing to |
Prophase Yellow Centrosome purple spindle fiber pink chromosomes green cell membrane |
|

What type of cell in What phase of mitosis is this and what are the lines pointing to ? |
Animal Metaphase Blue spindle fibers Yellow metaphase plate Red centrosome |
|

What type of cell in what phase of mitosis? |
Plant metaphase |
|
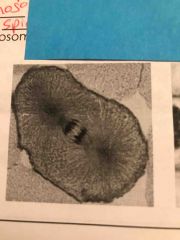
What type of cell in what phase of mitosis? |
Animal anaphase |
|

What type of cell in what phase of mitosis? |
Plant anaphase |
|
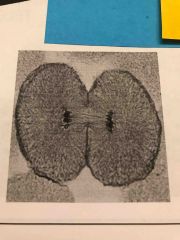
What type of cell in what phase of mitosis? What phase of the cell cycle also starts?... |
Animal Telophase cytokinesis |
|
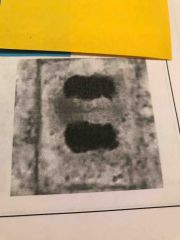
What type of cell in what phase of mitosis? |
Plant telophase |
|
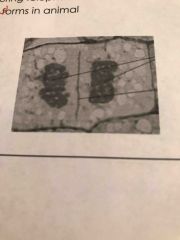
What type of cell is this in what phase what is starting to form... |
Plant telophase cell plate |
|
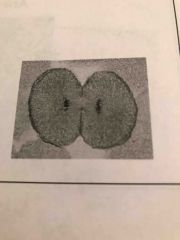
What type of cell in what phase and what is starting to form? |
Animal Telophase cleavage Furrow |
|
|
Nuclear membrane begins to break down duplicated centrosome begins to migrate toward opposite poles spindle apparatus begins to form chromosomes shorten and thicken and become distinguishable within the cytoplasm chromosomes migrate toward the center spindle fibers connect centromere's to centrosomes nucleolus disappears |
ProPhase |
|
|
Daughter chromosomes have reached opposite poles nuclear membrane is beginning to form chromosomes elongate and become indistinguishable from other chromosomes cell plate or cleavage Furrough begins to form |
Telophase |
|
|
Centromere's of the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell |
Metaphase |
|
|
Centromere's duplicate daughter chromosomes are pulled toward opposite poles by the contracting spindle fibers which remain fixed at the centrosomes |
Anaphase |
|
|
A part of the cell cycle where cytoplasm divides resulting into daughter cells |
Cytokinesis |
|
|
When hydrogen peroxide is added to the cells catalase activity can be noted by the production of |
Bubbles of oxygen |
|
|
Cells use the enzyme called _________to catalyze reactions in our experiment with hydrogen peroxide |
Catalase |
|
|
What specific enzyme is used to breakdown hydrogen peroxide into water and carbon dioxide? |
Catalase |
|
|
What specific enzyme is used to breakdown hydrogen peroxide into water and carbon dioxide? |
Catalase |
|
|
Catalase is used to breakdown hydrogen peroxide into what two components |
Water and carbon dioxide |
|
|
When hydrogen peroxide is mixed with the enzyme the production of bubbles tells you that the catalase is working it represents the production of_____________. |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
What four things in this experiment affect the rate of enzyme activity? |
Temperature pH concentration substrate concentration |
|
|
A majority of ATP energy is found where? |
Between the second and third phosphate groups |
|
|
The metaphase plate is found upon the invisible line called... |
Equator |
|
|
Seeds contain food storage as... |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
What two chemical reactions proceed with out the input of outside energy? |
Spontaneous reaction exergonic reaction |
|
|
What organelle is responsible for ribosome production? |
Nucleolus |
|
|
What organelle is present during interphase that disappears in prophase? |
Nucleolus |
|
|
What is it called when you have multiple spindle fibers all together |
Spindle apparatus |
|
|
If you place a bean seed into a cup of water what process takes place? |
Osmosis |
|
|
If you place a bean seed into a cup of water what process takes place? |
Osmosis |
|
|
When you place a seed into water the water will activate the _______ causing the breakdown of carbohydrates into _______ and the seed will swell.  |
Enzymes glucose aka: monosaccharide |
|
|
After placing a seed into water cellular respiration starts and the plant begins to grow early growth of the plant is called |
Germination |
|
What is the little white part sticking out of the seed? |
Root |
|

What does the yellow line represent |
Stem |
|
|
When carbon dioxide and water is formed what is the result? |
Carbonic acid |
|
|
What color does phenyl red turn in the presence of what... |
Phenyl red turns yellow in the presence of acid |
|
|
Phenol red is the chemical that showed_________ was present and being produced by turning yellow |
Acid |
|
|
Glycolysis the Krebs cycle aerobic anaerobic fermentation electron transport ...are all a part of... |
Cellular respiration |
|
|
What part of cellular respiration is the most efficient at producing ATP? |
Electron transport chain |
|
|
Why was the boiled seed not activated by the phenol red? |
The boiled seed was denatured so that's why it didn't work phenyl red didn't change to yellow carbon dioxide was not produced |
|
|
What process is common to aerobic anaerobic and fermentation? |
Glycolysis is common to all three because it can take place without oxygen |
|
|
With a pond full of animals the pH drops causing it to become more _________ and the aladia has __________ bubbles |
Acidic oxygen |
|
|
In a punnets square the capital letter is _______ and the lower case letter is _________ |
Dominant recessive |
|
|
Rr is an example of |
A heterozygous pair |
|
|
Rr is an example of |
A heterozygous pair |
|
|
RR Is an example of |
A homozygous pair |
|
|
RR rr Rr |
Homozygous dominant Homozygous recessive Heterozygous dominant |
|
|
Blood type could be considered as a... |
Phenotype |
|
|
The only way to have blood type O is... |
OO genotype |

