![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
|
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
|
|
|
Staphylococcus saprophyticus |
|
|
|
Micrococcus luteus |
|
|
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
|
Streptococcus agalactiae |
|
|
|
Streptococcus gallolyticus |
|
|
|
Enterococcus fecalis |
|
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|
|
|
Streptococcus sanguinus (Viridans group) |
|
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
|
|
|
Neisseria meningitidis |
|
|
|
Neisseria lactamica |
|
|
|
Neisseria sicca |
|
|
|
Moraxella catarrhalis |
|
|
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
|
|
|
Corynebacterium jeikeium |
|
|
|
Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum |
|
|
|
Bacillus cereus |
|
|
|
Listeria monocytogenes |
|
|
|
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae |
|
|
|
Lactobacillus |
|
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
|
|
|
Haemophilus parainfluenzae |
|
|
|
Bordetella bronchiseptica |
|
|
|
Pasteurella multocida |
|
|
|
Escherichia coli |
|
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
|
|
|
Enterococcus aerogenes |
|
|
|
Yersinia enterocolitica |
|
|
|
Proteus mirabilis |
|
|
|
Proteus vulgaris |
|
|
|
Morganella morganii |
|
|
|
Providencia rettgeri |
|
|
|
Providencia stuartii |
|
|
|
Serratia marcescens |
|
|
|
Serratia rubidaea |
|
|
|
Citrobacter diversus |
|
|
|
Citrobacter freundii |
|
|
|
Salmonella Typhimurium |
|
|
|
Shigella sonnei |
|
|
|
S. flexneri |
|
|
|
Salmonella Typhi |
|
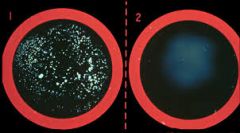
|
|
|

|
Top: Positive; S. aureus Bottom: Negative; S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, M. luteus
Enzyme clots plasma Cell bound: slide Extracellular free coagulase: test |
|

|
Left: Positive Right: Negative
2H20--->2H20+O2 |
|
|
Produces bound coagulase but not free coagulase |
Staphylococcus lugdunensis |
|
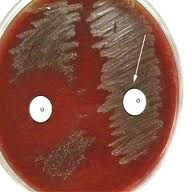
Bacitracin |
Left: Susceptible >10mm M. luteus, S. pyogenes Right: Resistant <10mm S. agalactiae |
|
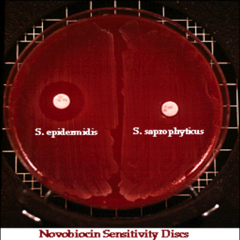
|
Left: susceptible >16mm Right: resistant <16mm |
|
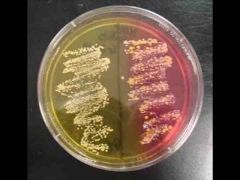
MSA |
|
|

PYR |
|
|
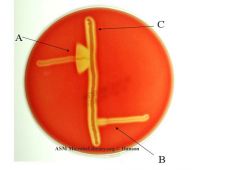
CAMP test |
A: Positive S. agalactiae B: Negative: S. pyogenes C: S. aureus |
|

Sodium Hippurate |
Left: Positive; S. agalactiae Right: Negative S. pyogenes Ninhydrin added |
|
|
SXT |
Group C streptococci SXT susceptible S. pyogenes: SXT disk resistant |
|

|
Left: Positive; Enterococcus fecalis Right: negative |
|
|
6.5% NaCl |
Cloudy: Positive; E. fecalis |
|

Bile solubility |
|
|

Optochin |
|
|
|
Chocolate Agar |
Enriched growth medium Contained lysed RBC which has: X and V |
|
|
phenol red indicator If sugar is oxidized; yellow |
|
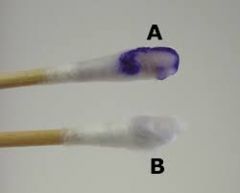
|
A: Positive B: Negative Presence of enzyme cytochrome oxidase |
|
|
MTM; modified thayer martin |
Selective for N. gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis Colistin: Inhibits gram negative bacteria other than Neisseria Vancomycin: inhibit most gram positive bacteria Nystatin or anisomycin: inhibit yeast Trimethoprim: inhibit Proteus |
|
|
Nitrate reduction |
NO3-->NO2-->N2 Red after addition of alpha-naphthylamine, sulfanic acid Zn detects nitrate not reduce Red is positive |
|

Urease |
Left: negative acidic Right: Positive alkaline Produce urease (hydrolysesammonia) |
|

|
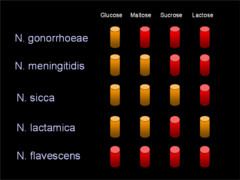
carbohydrate fermentor (lactose (1%), glucose (0.1%), sucrose(1%))
|
|
|
Eosin Methylene Blue |
|
|
|
MacConkey |
|
|

Indole |
|
|

|
|
|

Voges Proskauer |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Bordet-Gengou Agar |
|
|
|
CA |
|
|
|
Malonate |
|
|
|
Phenylalanine Deaminase |
|
|
|
Shigella Serotypes |
|
|
|
Hektoen Enteric Agar (HE) |
|
|
|
Xylose Lysine Desoxycholate (XLD) |
|
|
|
Cefsulodin-Irgasan-Novobiocin (CIN) |
|
|
|
Fermentation of L-arabinose |
S. marcescens is the only Enterobacteriaceae that does not ferment L-arabinose Pos: Yellow |
|
|
ONPG |
Differentiates between lactose and non-lactose fermentors ONPG: is an analog of Lactose Hydrolzyed by Beta-galactosidase |
|
|
DNase |
Dnase degrades extracellular DNA Serratia: + Enterobacteriaceae: = |

