![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The Endocrine glands |
Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland, Thyroid Gland, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads, Thymus, Pineal |
|
|
Hypothalamus produces |
ADH and Oxytocin |
|
|
Anterior Pituitary hormones |
FSH, LH,ACTH, TSH, GH, Prolactin
|
|
|
Posterior Pituitary hormones |
ADH, Oxytocin |
|
|
General Function and feedback mechanism for FSH |
Follicle stimulating hormone. GnRH gonadotropin releasing hormone causes release. Targets Ovaries and Testes. Stimulates ovarian follicle maturation, estrogen production, and sperm production. Negative feedback.Tropic hormone |
|
|
General Function of LH
|
Luteinizing Hormone. stimulated by: GnRH. Targets Ovaries and Testes. F: trigger ovulation. Stimulates estrogen and progesterone production. M: stimulates testosterone production. Tropic Hormone |
|
|
ACTH |
Adrenocorticotropic hormone. Stimulated by CRH. Targets Adrenal Cortex. Stimulates release of glucocorticoids and androgens. Tropic hormone. |
|
|
TSH
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone. stimulated by TRH. Targets thyroid gland. stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones. T3 and T4. Tropic hormone. |
|
|
GH |
Not tropic, Growth hormone. stimulated by GHRH. Targets liver, muscles, bone, and cartilage. Stimulates body growth and protein synthesis, mobilizes fat and conserves glucose. |
|
|
PRL |
Prolactin. not tropic. Stimulated by decrease in PIH prolactin inhibiting hormone. Targets mammary glands in the breasts. Stimulates milk production. (lactation) |
|
|
Posterior pituitary hormones |
ADH, Oxytocin. Produced in the hypothalamus. |
|
|
ADH |
Antidiuretic hormone. stimulus for release is nerve impulses. increased blood solute concentration or decreased blood volume. targets kidneys. tells kidneys to reabsorb more water. |
|
|
Oxytocin
|
responde to cnerve impulses. ervical/uterine stretching or suckling of an infant. target uterus and mammary glands. stimulate powerful contractions. |
|
|
Hormones of the thyroid gland |
Thyroxine t4, and triiodothyronine t3 and calcitonin |
|
|
T4, T3 |
Thyroxine, Triiodothyronine. S4R = TSH. target = most cells of the body. Effects = increase BMR, regulate tissue growth and development |
|
|
Calcitonin
|
S4R = high levels of calcium in the blood. humoral. Targets bones. No known physiological role in humans. |
|
|
Parathyroid hormone |
PH. S4R = low levels of calcium in the blood. Targets bones and kidneys. effects = increases blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts and stim kidneys to resorb more calcium. |
|
|
Adrenal glands |
medulla and the cortex |
|
|
adrenal medulla cells and hormones |
chromaffin cells. hormones: catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine
|
|
|
catecholamines: epinephrine and norepinephrine |
S4R = nerve impulses from preganglionic sympathetic fibers.
Target cells = most body cells. Effects = mimics sympathetic NS fight or flight response. |
|
|
Adrenal Cortex |
Corticosteroids: mineralocorticoids - aldosterone glucocorticoids - cortisone Gonadocorticoids - androgens |
|
|
mineralcorticoids - aldosterone |
s$R = increased potassium in the blood. target = kidneys. effects = ^ of reabsoption of sodium and water by the kidneys. increase secretion of potassium in the urine. |
|
|
Glucocorticoids mostly cortisol |
S4R = ACTH. Target = most body cells. Effects = promotes breakdown of fat and protein. promotes stress resistance, inhibits the immune response |
|
|
Gonadocorticoids - androgens |
S4R = ACTH Target= bone, muscle, integument, and other tissues. Effects = body groeth, pubic & axillary hair, sex drive. insignificant effects in males. |
|
|
Pancreas hormones |
insulin and glucagon |
|
|
Insulin |
S$R = increase blood glucose levels. Target = most cells. Effects = accelerates transport of glucose into body cells.glycogen, fat, and protein synthesis |
|
|
Glucagon |
S4R = decrease blood glucose levels. Target cells = liver and adipose Effects = breakdown of glycogen to glucose, conversion of lactic acid into glucose. |
|
|
Female Gonads |
Estrogens and E and progesterone together |
|
|
Estrogen |
S4R = LH and FSH Targets = most cells. Effects = promote matuartion of female reproductive organs. and secondary sex characteristics. |
|
|
Estrogen and progesterone together |
S4R = LH and FSH. Target = uterus and mammary glands. Effects = regulate menstrual cycle and breast development. |
|
|
Testosterone |
S4R = LH and FSH Targets = most cells. Effects = maturation of male reproductive organs. |
|
|
Approximately ______ liters of blood in the adult body |
5-6 males 4-5 females |
|
|
2 major components of blood |
plasma - non-;iving 55% of blood and formed elements (cells) - living 45% of blood |
|
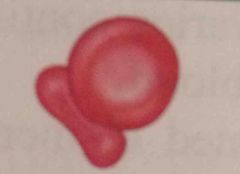
RBC |
RBC. Erythrocytes. sacs of hemoglobin molecules. transport oxygens. 4-6 million/mm3 |
|
|
WBC |
Leukocytes. Spherical. 4800-10800, 2 major groups granulocytes and agranulocytes |
|
|
granulocytes |
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
|
|
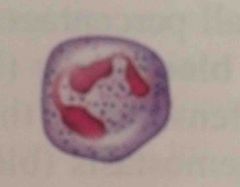
neutrophils |
Neutrophils. Most numerous. Multilobed nucleus. Pale red and blue granules. . phagocytize pathogens or debris. 3000-7000 |
|
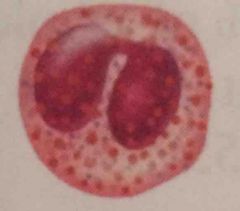
|
Eosinophils. bi lobed nucleus, dark red dots. kill parasitic worms. Phacocytic. 100-400 |
|
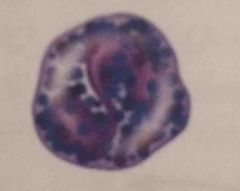
Basophils
|
Basophils. vary dark purple dots. 20 - 50. Release histamines and other mediators of inflammation. anticoagulant. |
|
|
Aranulocytes |
lymphocytes and monocytes |
|
|
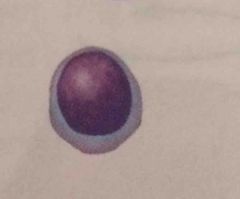
Lymphocytes. smaller cells little cytoplasm. mount inmmune response by direct cell attack. 1500-3000. |
|
|
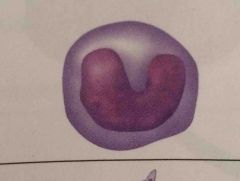
Monocytes. huge cells hazyblue no dots. U shaped nucleus. 100-700. develop into macrophages in tissues and phagocytize pathogens or debris. |
|
|
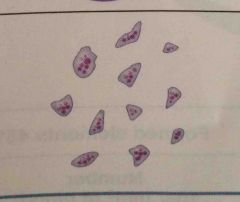
Platelets. smaller than RBC. look like specs of dust. 150000-400000. seal tears in blood vessels. instrumental in blood clotting. Not cells. |
|
|
Heart APex |
the inferior point |
|
|
hearts base |
mainly left ventricle, flat, superior region. |
|
|
serous membrane inclosing heart |
visceral pericardium or epicardium - on the surface of the heart. parietal pericardium not part of the heart |
|
|
Layers of the heart wall |
epicardium or visceral pericardium - outer layer. Myocardium - middle layer, muscle. endocaridium - very thin inner layer. |
|
|
Atrium "atria" |
2 superior chambers. auricle - out growth for more space. receive blood R sid from sup and inf vena cava. left side from pulmoary veins. contract slightly.
|
|
|
Ventricles |
2 inferior chambers. the pumps. left pumps to body. right pumps to lungs. |
|
|
blood supply to the myocardium |
R & L coronary atries branch from aorta and supply to myocardium. then passes through capillaries, collected by the veins and drained into the coronary sinus > the R atrium. |
|
|
Atrioventricular valves |
AV, between R and L atrium and R & L ventricles. |
|
|
Right and Left AV valves |
Right = tricuspid Left = mitral or bi cuspid |
|
|
Semilunar valves |
between ventricles and arteries, made up of 3 pocket cusps |
|
|
pulmonary and aortic semiluner valves |
Pulmonary = from right V to Lungs Aortic = Left V to body. |
|
|
Chordae tendonae |
anchor tips of heart valves to ventricular walls |
|
|
papillary muscles |
cardiac muscle that anchor chordae tendonae |
|
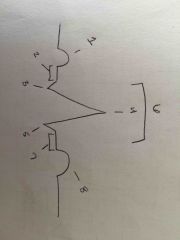
What happens at each |
1 - p wave - A depolarization + 2 - atrial contraction 3, 4, 5, 6 - QRS Complex - V depolarization + (also repolarization of atria -) 7 - ventricle contraction 8 - T wave repolarization of ventricles. |
|
|
flow of conduction in the heart |
Sinoatrial node - pace maker
Atrioventriclular node - RA septum AV bundle of his - more in V septum. R & L bundle branches - down the septum Perkunje fibers - up the walls |
|
|
Tackycardia / brady cardia |
>100 / < 60 Normal = 75 |
|
|
fibrillation |
rapid uncoordinated heart contractions |
|
|
how to find pulse pressure |
Sys BP - Dia BP = pp |
|
|
how to find MAP |
Dia bp + (1/3 X PP) = mean arterial pressure |
|
|
Systole / diastole |
ventricular contraction / ventricular relaxation |
|
|
cardiac cycle |
1 heart beat |
|
|
AVg HR, avg length of 1 cardiac cycle. |
75, .8 |
|
|
1st heart sound "lub" = 2nd heart sound "dub" = |
1 = S1, AV closure 2 = S2 SL closure |

