![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the 3 isotopes of carbon? |
12, 13 and 14 |
They're in the teens |
|
|
Who developed the radiocarbon method? |
Willard Libby |
Initials W.L. |
|
|
When/where was radiocarbon developed? |
University of Chicago, 1949 |
Think of BP 1950 |
|
|
What is the half-life of radiocarbon? |
5700yrs |
5--- yrs |
|
|
Explain what 'half life' means |
The time it takes for half of the radiocarbon to disappear |
|
|
|
What is the time limit for radiocarbon dating? |
40,000-50,000 yrs |
|
|
|
How does radiocarbon enter the marine and terrestrial biospheres? |
Marine: Carbon dissolves in water Terrestrial: Plants absorb carbon through photosynthesis |
Absorption |
|
|
What is the meaning of the designation 'BP'? |
Before Present |
Think of year radiocarbon was developed |
|
|
List three materials from archaeological sites that can be dated with radiocarbon. |
Plant matter, bone, charcoal |
Anything organic |
|
|
List three sources of variation or errors in radiocarbon dating. |
- Contamination with old/new carbon (from different stratigraphic layers) - Statistical variability - Changes in atmosphere |
|
|
|
What are the 3 statistical confidence levels assc. with radiocarbon dates? |
Sigma 1 = 68% Sigma 2 = 95% Sigma 3 = 99% |
Sigma |
|
|
Calculate the age ranges for the radiocarbon date 5000+-100yrs for each of the three statistical confidence levels (sigmas) |
1: 5000+-100 = 4900-5100 2: 5000+-200 = 4800-5200 3: 5000+-300 = 4700-5300 |
Sigma 2 is double Sigma 1 Sigma 3 is triple Sigma 1 |
|
|
How do you turn BP ages into calendar year dates? |
Subtract 1950 from BP date if older than 1950 years. |
|
|
|
Why are luminescence methods (allowing longer time limits) important to Australian prehistoric Archaeology? |
Because many Aboriginal sites in Australia are as old or older than the radiocarbon time limit (40,000-50,000) |
|
|
|
Define isotope |
An element that has the same amount of protons but different amounts of neutrons |
|
|
|
What are the stable isotopes of carbon? |
c12 c13 |
|
|
|
What are the stable isotopes of nitrogen? |
n14 n15 |
|
|
|
How do stable carbon isotopes enter the marine and terrestrial biosphere? |
Marine: Biocarbonate gas dissolves in ocean Terrestrial: Carbon absorbed by plants during photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Define isotopic fractionation |
Changes in isotopic ratios, associated with chemical and physical reactions (Any process that prefers one isotope over another due to differences in mass) |
|
|
|
What does a more positive sigma value mean? |
More positive = heavier |
|
|
|
Isotope values are measured in 'per mil' which is parts per... |
Thousand |
|
|
|
c3 plants are dominant in which Australian geographic region? |
Temperate (south of Aus.) |
|
|
|
c4 plants are dominant in which Australian geographic region? |
Tropical (Nth of Aus.) |
|
|
|
What are the two main dietary types recorded in bone and tooth stable carbon isotopes? |
Marine and Terrestrial |
|
|
|
What are the two dietary types recorded in bone and tooth stable nitrogen isotopes? |
Marine and Terrestrial |
|
|
|
Apes were dominant during the Miocene geological period. What are the dates for this period? |
25-5 million years BP |
|
|
|
Why was the global diversity of apes reduced significantly after 5 million years ago? |
Changes in climate, habitats lost |
|
|
|
What is the foramen magnum? |
The big hole in the base of a skull that connects it to the neck |
|
|
|
Why does the foramen magnum sit towards the back of the skull in apes? |
Because they're quadripeds and not bipeds. They primarily walk on all fours meaning that their head is further forward, not in the centre. |
|
|
|
Muscle attachments produce large bony processes on the crania of apes. Name three of these bony processes. |
Sagittal crest (Across top of skull) Nuchal Crest (At the back of the skull) Supra Orbital Ridges (Brow ridges) |
|
|
|
What is a Sagittal Crest? |
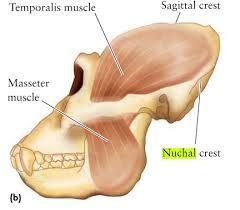
A ridge of bone running across the top of the skull (front to back) |
|
|
|
What is a Nuchal Crest? |
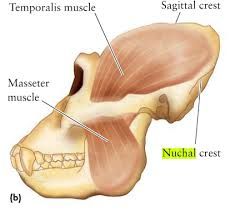
A lump of bone in the back of the cranium, close to where it meets the neck |
|
|
|
What is a Supra-orbital Ridge? |
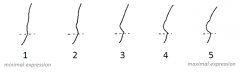
A ridge of bone across the brows |
|
|
|
Why do apes have larger canines and incisors than humans? |
1. For processing tougher foods for longer periods of time 2. Competition for mates/dominance |
|
|
|
Why do apes have larger molar surfaces than humans? |
For more extensive chewing |
|
|
|
What is the dental arcade? |
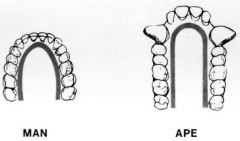
The shape of the bite from above/below |
|
|
|
The dental arcade shape in apes is... |
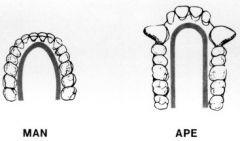
Parallel |
|
|
|
The dental arcade shape in humans is... |
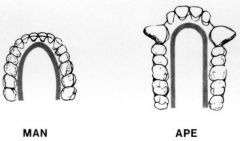
Parabolic |
|
|
|
What is the pubic symphyses? |
A gap at the front of the pelvis connected by cartilage |
|
|
|
Describe the general changes observed with the erosion of pubic symphyses over time. |
At Stage 1, (20-24yrs) the symphyses has grooves and ridges on the surface. The grooves and ridges become smooth over time. By Stage 6 (45-49yrs) the smoothed surface begins to develop pits and notches. |
|
|
|
You can identify a male skeleton through which features? |
- More prominent brow ridges - Larger nuchal crest - Smaller pelvic opening - Smaller sciatic notch |
|
|
|
You can identify a female skeleton through which features? |
- Larger pelvic opening - Larger sciatic notch - Smaller brow ridges and nuchal crest |
|
|
|
What is a sciatic notch? |
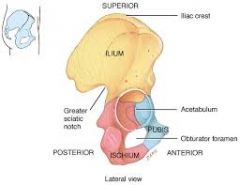
An angle in the pelvic bone |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When was the Pliocene? |
5-2.5mya |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When was the Pliocene? |
5-2.5mya |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pliocene? |
Woodland, Savannah & primates |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When was the Pliocene? |
5-2.5mya |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pliocene? |
Woodland, Savannah & primates |
|
|
|
When is the Pleistocene? |
2.5mya-10ka BP |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When was the Pliocene? |
5-2.5mya |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pliocene? |
Woodland, Savannah & primates |
|
|
|
When is the Pleistocene? |
2.5mya-10ka BP |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pleistocene? |
Woodlands, savannahs, cooling climates, hominids. |
|
|
|
When is the Miocene? |
25-5mya |
|
|
|
What is the Miocene characterised by? |
Tropical forests and fossil apes |
|
|
|
When was the Pliocene? |
5-2.5mya |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pliocene? |
Woodland, Savannah & primates |
|
|
|
When is the Pleistocene? |
2.5mya-10ka BP |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the Pleistocene? |
Woodlands, savannahs, cooling climates, hominids. |
|
|
|
When is the Holocene? |
10ka-Present |
|
|
|
What is the term for the fusion of post-cranial bones? |
Epiphyseal Closure |
|
|
|
What is the term for the fusion of post-cranial bones? |
Epiphyseal Closure |
|
|
|
When to babies develop their deciduous teeth? |
From 8 months |
|
|
|
What is the term for the fusion of post-cranial bones? |
Epiphyseal Closure |
|
|
|
When to babies develop their deciduous teeth? |
From 8 months |
|
|
|
When to humans begin to develop their adult teeth? |
From 6 years |
|
|
|
What is glass commonly made of? |
Silica, lime, soda |
|
|
|
What is glass commonly made of? |
Silica, lime, soda |
|
|
|
What is Frit? |
Early, low quality glass. Crushed, ground silica mixed with alkali, lower heating temperature. Looks like clumped sand or sandstone. |
|
|
|
What is glass commonly made of? |
Silica, lime, soda |
|
|
|
What is Frit? |
Early, low quality glass. Crushed, ground silica mixed with alkali, lower heating temperature. Looks like clumped sand or sandstone. |
|
|
|
What is Faience? |
Ancient glass like frit, higher heat temperature gives it a glossy appearance on outside. |
|
|
|
What is glass commonly made of? |
Silica, lime, soda |
|
|
|
What is Frit? |
Early, low quality glass. Crushed, ground silica mixed with alkali, lower heating temperature. Looks like clumped sand or sandstone. |
|
|
|
What is Faience? |
Ancient glass like frit, higher heat temperature gives it a glossy appearance on outside. |
|

