![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
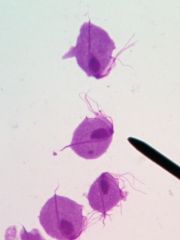
|
Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
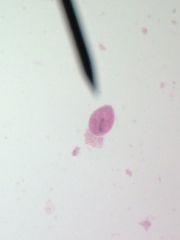
|
Balantidium coli |
|
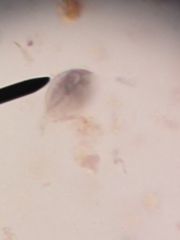
|
Giardia lamblialambkins |
|
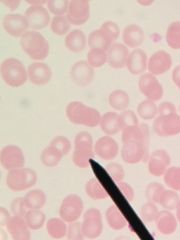
|
Plasmodium SPP |
|

|
Clonorchis sinensis |
|
|
Schistosoma mansoni |
|
|
Entromoeba hystolytics |
|
|
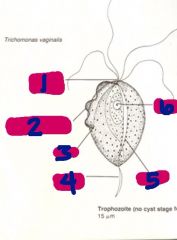
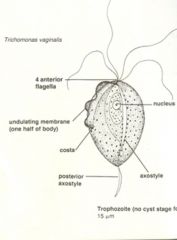
Trichomonas vaginalis |
-Protozoan parasite -Most common sexual transmitted disease in US -Can be both asymptomatic in both male and females -s/s include burning and itching within the urethra for both sexes. Females may also have painful intercourse, redness, edema, and vaginal discharge with odor
|
|
|
Life cycle of Trichomonas vaginalis |
1) Trophozoite (Urethra, vagina, epididymus, prostate)
2) Infectious stage multiply by longitudinal fission (no cyst)
3) method of infecton Sexual transmitted disease |
|
|
|
|
|
Balantidium coli |
-Protozoan parasite -endemic to tropical areas -transmitted by oral/fecal route -cysts ingested and trophozoites colonized in intestinal tract -reproduced by binary fission -pigs can be the resevoir -s/s are cramping and diahrrea and most severe bowel perforation
|
|
|
Life cycle of Balantidium coli |
1) Trophozoite in large intestine; multipy asexually by binary fission 2) Infective stage; cysts passed in feces 3) Method of infection; man ingests infective cyst; transmitted by feces, fingers, food, formites, and flies |
|
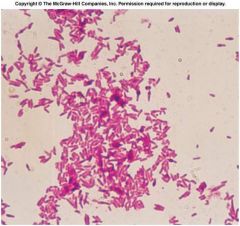
|
simple stain |
|
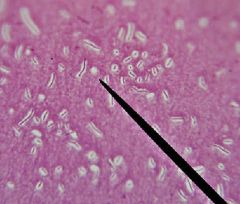
|
negative stain |
|
|
do you heat fix a negative stain |
No. It will interfere with the dye/cell interaction |
|
|
What are the negative stains |
ACIDIC -India Ink -Nigrosin |
|
|
What are the positive stains |
BASIC -Methylene Blue -Crystal violet -Safranin3 |
|
|
What can be determined with a simple stain |
-size -shape -arrangement
|
|
|
what color do negative stained bacteria take |
they are colorless |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE when performing the simple stain one decolorizes for 30 seconds |
FALSE simple stains dont have a decolorizer |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE |
FALSE |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE When performing a negative stain th slide is heat fixed after th dye has been added |
False |
|
|
Define pure culture |
One type of specimen in a media |
|
|
Briefly explain why it is important toobserve aseptic technique when performing a negative stain |
Because you don't wnt your specimen to be contaminated and alter your view and conclusion of your specimen |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE When preparing a smear from a liquid broth you should not add water to your slide |
TRUE |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE When preparing a smear from a solid media you should not add water to your slide |
FALSE Adding DI water allows the bacteria to spread out so you can observe the bacteria properly |
|
|
What is the reason for heat fixing a smear |
To adhere te bacteria to the slide To kill th bacteria without altering the bacteria chemical properties |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE Parfocal is a characteristic of a microsope that allows one to adjust the working distance once andthen use the fine adjutment knob to focus on the specimen |
True |
|
|
What is the total magnificatin of a scan power lens |
40 x
Objective lens magnification -4x Ocular magnification - 10x |
|
|
What is the total magnification of a low power |
100x
objective lens magnification - 10x Ocular magnification - 10x
|
|
|
What is the total magnifcation of a high power |
400x
Objective lens magnification - 40x Ocular magnification - 10x
|
|
|
What is the total magnification of oil immersion |
1000x
Objective lens magnification - 100x Ocular magnificaton - 10x |
|
|
What is resolution |
the ability to discern the different aspects of a specimen from each other |
|
|
There are two aspects of resolving power that must be considered when calculating the resolving power of a particular lens |
1) Wavelength of light used to illuminate the specimen 2) The refractive index of the lens (Refraction is the bending of a ray of light as it passes through any material and th refractive index is related to the degree by which it is bent) |
|
|
What is the formula for resolving power |
Wavelength of light (nm) __________________________ 2 x Numerical Aperture
example: 500 nm ________ = 200 nm 2x1.25 |
|
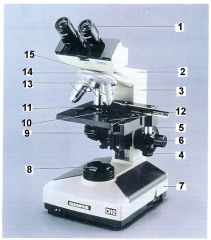
|
1) Ocular lens 2) Arm 3) Body 4) dont have to know 5) Course Adjustment knob 6) Fine Adjustment knob 7) base 8) Lamp 9) Diaphragm and Condensor 10) dont have to know 11) Stage clips 12) Mechanical stage 13) Objective lens 14) Revolving Nosepiece 15) dont have to know |
|
|
Who invented the Gram Stain |
Christian Gram |
|
|
What kind of stain is a Gram Stain |
Differential |
|
|
What does it mean by a differential stain on a Gram stain |
Because it separates bacteria into tow groups based on cell wall structure |
|
|
what are the exceptions that you won't use a Gram stain |
Spirochaetes, Mycobacteria, and Actinomycetes because they do not respond to the Gram staining in a consistant manner |
|
|
What manuel is the definitive resource for bacterial identification, is divided based on Gram reaction |
Bergey's Manuel |
|
|
What are the reagents used in a Gram Stain |
Crystal violet- Primary Stain Gram's Iodine- Mordant Ethanol- decolorizer Safranin- Seconday stain (counterstain) |
|
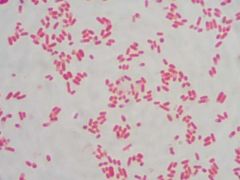
What Gram stain is this |
Gram negative
|
|
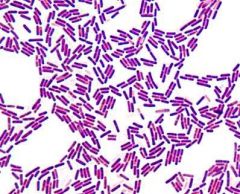
What Gram stain is this |
Gram positive |
|
|
Define staph |
clusters of bacterial cells |
|
|
Define strep |
a line of bacterial cells |
|
|
List the possible shapes that bacteria may take |
Coccus Bacillus Spirochete/spirillum |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE Gram positive bacteria stain red |
False Gram positive stain purple |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE Gram positive bacteria stain purple |
TRUE |
|
|
List one factor that may affect the outcome of the Gram stain |
overuse of te decolorizer (Alcohol) |
|
|
What type of staining techniqu is the Gram stain |
Differential |
|
|
Name the secondary stain used in the Gram stain |
Safranin |
|
|
What can be determined with the Gram stain |
Gram reaction morphology arrangement |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE It is not necessary to heat fix slides that are Gram stained |
FALSE must heat fix slides to see bacteria if not they will wash away |
|
|
What color are Gram negative bacteria after staining |
pink |
|
|
Briefly explain why Gram positive bacteria stain the way they do |
Because they have a thick cellular wall (made up of peptidoglycan) that absorbs the dye with the help with the mordant (Iodine) which binds to the crystal violet allowing it to keep the dye intact |
|
|
Name the primary stain used in the Gram stain |
Crystal violet |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE Acid fast bacteria stain red |
True |
|
|
What type of staining technique is the acid fast stain |
differential
because it distinquishes bacteria that has mycolic acid |
|
|
Briefly explain why acid fast bacteria resist staining using conventional staining techniques |
Because it has a mycolic layer tha does not allow dyes to penetrate. Its protectant |
|
|
Name the primary stain used in the acid fast |
Carbolfusion |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE Non-acid fast bacteria stain red |
False
Non acid fast stain blue |
|
|
TRUE/FALSE The primary stain is steamed in the acid fast stain |
True
|
|
|
Name the secondary stain used in the acid fast stain |
Methlene Blue |
|
|
Name the steps for an Acid-Fast stain |
1) make a smear on a slide and lay bibulous paper on the slide and saturate with carbolfuchsin (primary stain) 2) place slide on boiling water and allow it to steam (mordant) 3)Remove blotting paper and rince with DI water, Add the acid-alcohal (decolorizer) and rinse with DI water 4) Add methylene blue (counterstain) to the smear for 1 min and rinse with DI water
|
|
|
What is the a positive and a negative result in an Acid-Fast stain |
Positive- Red Negative- Blue |
|
|
What is the pH indicater solution in a Carbohydrate fermentation test |
Bromocresol purple |
|

What test is this? What result is #1? What result is #2B? What result is #3A? |
Carbohydrate fermentation test negative reaction positive reaction (acidic) positive reaction with production of gas |
|
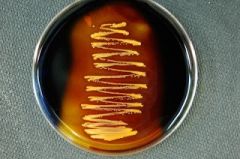
What kind of test is this?
Is this positive or negative?
What is added to the plate?
What are you looking for in this test? |
Starch Digestion test
Positive ( contains enzyme amylase)
Iodine
If bacteria contains amylase to break down starch |
|
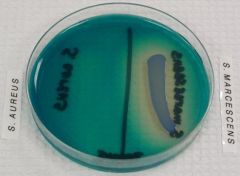
What test is this?
Which is a positive result?
What are you looking for?
What does this agar contain? |
DNA Digestion Test
S. Marcescens
Looking to see if bacteria contains DNAse for breaking DNA down to nucleotides
methyl green |
|

What test is this
What is a positive test
What are you looking for? |
Catalase test
A bubbly top
To see if hydrogen peroxide will break down into water and oxygen by the enzyme catalase |
|
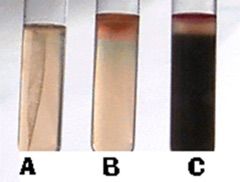
What test is this?
Explain A Explain B Explain C
What reagent do you use for indole? |
SIMs Test (Sulfur, Indole, Motility)
A- No motility, no indole, and no hydrogen sulfide
B- Motility, Indole (amino acid tryptophan will degrade and produce indole by the enzyme tryptophanase), no hydrogen sulfide
C- motility, indole production, hydrogen sulfide production (amino acid Cysteine is degraded by the enzyme Cysteine Desulfurase and produces hydrogen sulfide) |

