![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
connective tissues |
include blood, bone, cartilage, loose and other connective tissues that serve as packaging material for organs or other tissue. these tissues secrete an extracellular matrix that serves a specific function depending on the type of connective tissue; arise from mesoderm |
|
|
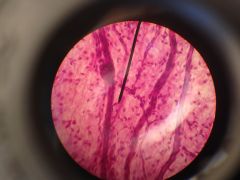
loose areolar tissue consists of collagen, elastic fibers, and various types of cells such as mast cells, fat cells, and fibroblast cells. serves as packaging material for organs or other tissues in the body collagen fibers stained pink and have a greater diameter than elastic fibers. fibroblasts are stained dark that produce these fibers. loose connective tissue |
|
|
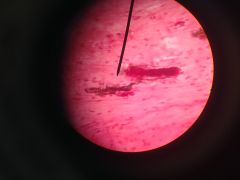
mammalian skin cross-section much of the tissue is dense irregular connective tissue; provides a cushion below the epidermis dense connective tissue |
|
|
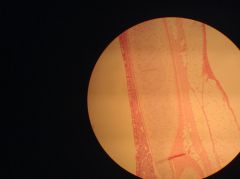
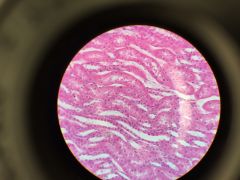
mammalian tendon longitudinal section connect skeletal muscle to bone and are composed primarily of dense regular fibrous connective tissue; fibroblasts are arranged in parallel with the collagen fibers dense connective tissue |
|
|
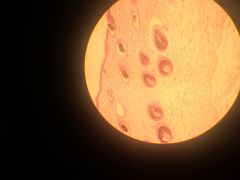
trachea longitudinal section supported by rings of hyaline cartilage tissue. Chondrocytes are cells in cartilage that secrete extracellular material such as collagen and elastic fibers that provide strength and durability to the tissue. Chondrocytes are found in small cavities within the matrix called lacunae. structural connective tissue |
|
|
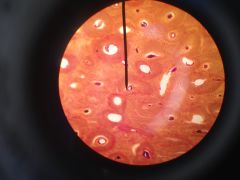
cross section of ground bone bone is a living tissue usually formed in layers called lamellae by parallel collagen fibers packed in together. structural unit of bone called osteon or Haversian system. Lamellae encircle a central canal that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues. osteocytes, the actual living bone cells, are found in small lacunae, the small dark cavities that form the concentric circles between lamellae structural connective tissue |
|
|
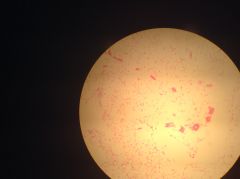
white adipose tissue a bunch of fat cells, or adipocytes. collagen fibers, other connective tissue cells surrounding bunches of adipocytes; important for storing energy loose connective tissue |
|
|
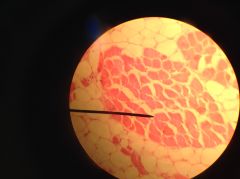
Skeletal Muscle Cross Section - nuclei located peripherally just under each plasma membrane - multinucleate (possess multiple nuclei) - red of the muscle cells are packed with bundles of myofibrils, which consist of actin and myosin filaments |
|
|
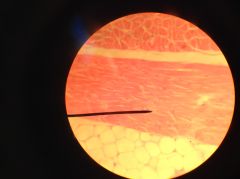
Skeletal Muscle Longitudinal Section - myofibrils arranged in parallel, with striations (dark and light alternate bands) evident - narrower dark lines are the "A-bands" and the thicker, lighter lines are the "I-bands". |
|
|
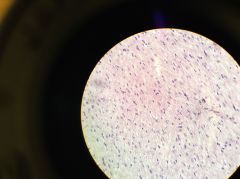
Cardiac Muscle - striated -contain their single nuclei in the middle of the cell - cells are branched, not in parallel - possess intercalated disks (junctions that connect two muscle cells allowing fast, direct cell-cell communication |
|
|
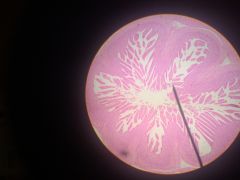
Smooth Muscle Cross Section - smooth muscle lines many tubular organs, such as those of the digestive system, aiding in peristaltic movement of food through the tract - uninucleate - not striated |
|
|
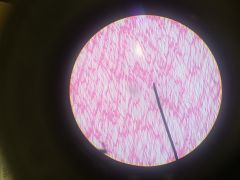
Smooth Muscle Longitudinal Section |
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium - outermost cells appear flattened and only about one cell-layer thick - lines the outer and inner surfaces of most of your organs |
|

|
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Cortex of the Mammalian Kidney - lined with simple cuboidal epithelium - cells look like little boxes with a circle (the nucleus) in the middle |
|
|
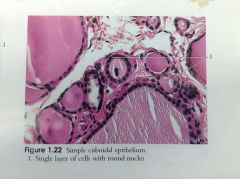
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
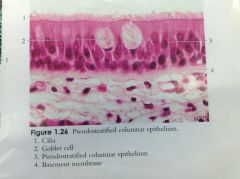
Trachea - lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium - tissue is actually one cell layer thick, but because the nuclei of the cells reside at different levels, the tissue appears to be multiple layers - surface of cells lined with cilia, hair-like projections that aid in moving foreign bodies through the respiratory tract and help prevent infection or obstruction - white, oval or cup-shaped "goblet cells" secrete mucus into the respiratory tract for lubrication and in helping trap bacteria or dust |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
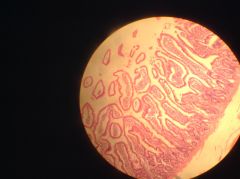
Human Ileum (small intestine) - lined with simple columnar epithelium - possessed microvilli (not cilia) to increase surface area and thus increase absorption - goblet cells present |
|
|
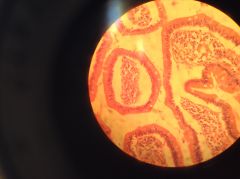
Human Ileum (small intestine) - lined with simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
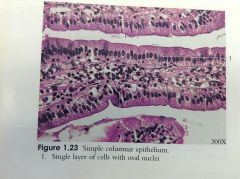
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
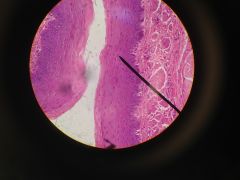
Esophagus Cross Section - stratified squamous |
|
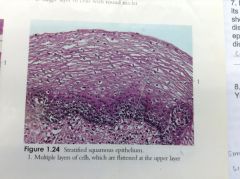
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
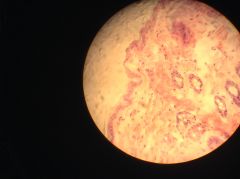
|
Mammalian skin - at outermost levels (epidermis), stratified squamous epithelium is keratinized, meaning that a protective protein is manufactured by these cells - below them is a connective tissue that makes up the dermis and hypodermis |
|
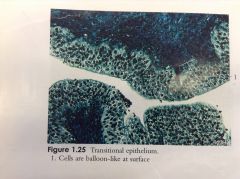
|
Transitional Epithelium - cells are balloon-like at surface |
|
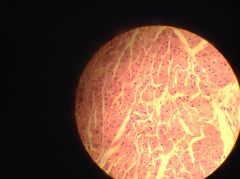
|
Contracted Bladder - when empty epithelium is contracted - transitional |
|
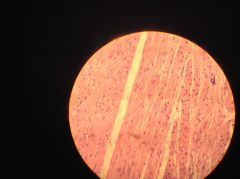
|
Distended Bladder - when full of urine epithelial lining is distended, or stretched |
|
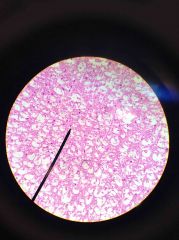
|
Mammal Spinal Cord Smear |
|
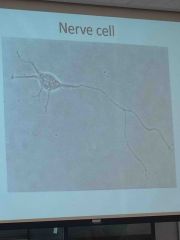
|
Neuron |

