![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
spores
|
Are the product of meiosis
-alternation of generations: in plants the multicellular sporophyte (2n) and gametophyte (1n) |
|
|
sporophyte
|
(2n) produces spores
|
|
|
Spores
|
(n) grow into gametophytes
|
|
|
gametophyte
|
(n) produces gametes
|
|
|
gamete
|
(n) fusion results in zygote
|
|
|
zygote
|
(2n) grows into sporophyte
|
|
|
bryophytes
|
-non-vascular land plants
Example: mosses, hornworts, liverwurst -small, grow closely together to form mats/cushions -found of greet trunks, soil, rocks -spores require water to disperse, germinate -female and male gametophyte --archegonia --antheridia |
|
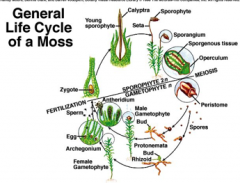
|
Life cycle of a moss
|
|
|
Pteridophytes
|
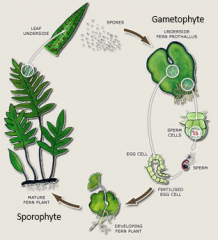
-vascular
-female and male gametophyte -spores require water to disperse, germinate |
|
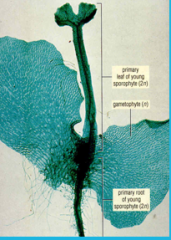
|
Sporophyte grows out of gametophyte
|
|
|
sorus
|
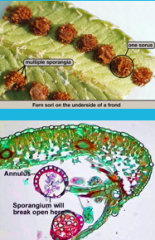
-cluster of sporangia (structures producing and containing spores)
-form a yellowish/brownish mass under a fern frond |
|
|
indusium
|
A film of tissue that protects a sours during development
|
|
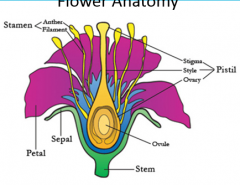
|
Flower anatomy
|
|
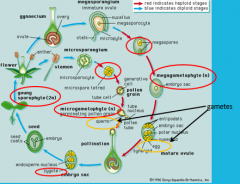
|
angiosperm life history
|
|
|
|
prepared sample of fern antheridia
|
|
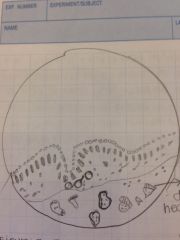
|
prepared sample of mature sporangia
|

