![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
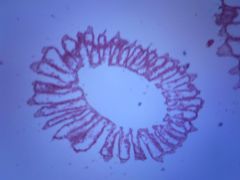
what phyla and phylum
what common name |
Phyla Parazoa
phylum Porifera the sponges |
|

what are these?
|
Phyla parazoa
Phylum porifera |
|
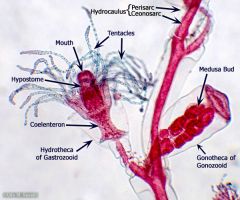
what phyla
what phylum what class what life stage do they posess? Habitat and how are they found? |
Eumetazoa
Cnidaria Hydrozoans the medusa( which are in the buds) housed inside the repriductive polyp. there are also the feeding polyp polyp they are marine and are colonial |
|
|
what does the term radiates mean?
to what group does this term belong? |
that they posess more than one form of symmetry
the Cnidarians of the Diploblastic Eumetazoa |
|
|
What is a planula? to what group?
explain this groups body plan |
it is a ciliated larval stage of the phylum eumetazoan diploblasts and the cnidaria
Diploblast, outer body wall called an Epidermis and an inner layer which is the lining of the Digestive system (gastrodermis) |
|
|
what is the mesoglea
|
it is the gelatinous mixture between the epidermis and gastrodermis of the diploblast eumetazoan cnidarians
|
|
|
how is the nervous system arranged in the cnidarian
|
they lack a central nervous system, instead it is arranged in a nerve net
|
|

What phylum
explain what is occuring which life stages? habitat? |
Eumetazoan Cnidarian class hydrazoan.
Asexual reprduction, this budding will produce a clone of the parent. Polyp and medusa stages Most marine and colonial Common examples: Portuguese man-of-war and freshwater hydra |
|

what phylum? how can you tell? what are the defining characteristics?
|
Eumetazoa Cnidarians class schyphozoa
these are the true jellies it has the medusa morphology moves be undulating Possess epitheliomuscular cells that form a ring around bell |
|

what class? what phylum? and what defining characteristic?
|
Diploblastic Eumetazoan Cindarian class Cubazoa
the four edges that resemble a box form where the tentacles tend to cluster |
|
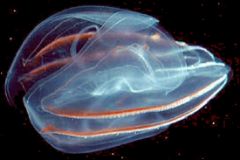
What phylum? or class? is there a class?
what are the defining characteristics? what body plan? |
diploblastic eumetazoan
phylum ctenophora once thought to be cnidarians commonly called comb jellies however not true jellies basic body plan medusa posess an anal pore to remove waster 2 long tentacles for feeding lack nematocysts instead have colloblast cells along the 2 long tentacles some also have a mesodermal layer and are considered triploblastic. |
|

2 long tentacles with combs. what is this?
|
Eumetazoan-ctenophore
|
|

what class phylum?
what body plan? |
Eumetazoan Cnidaria Anthazoa
these are reduced to the polyp morphology like the corals these are colonial calcium carbonate skeleton |
|

what is this
what common name |
Eumetazoan Cnidaria Class Anthazoa
known as the flower animals |
|
|
If you see the suffix -Zoan, what does this tell you
|
it is an animal
|
|
|
If something is said to be 'Amorphous', what does this mean?
|
No defined shape, and no symmetry
|
|
|
What is the Lumen referring to usually?
|
The central cavity of a tubular or other hollow structure in an organism or cell.
|
|
|
Why is a stomach not a true body cavity?
and what is the suffix -coel mean? |
There is no tissure seperating it
coel means stomach |
|
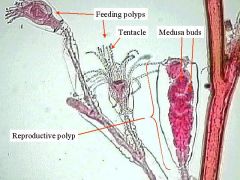
what phyla
|
Eumetazoan Cnidarian Hydrozoa
|
|
|
What groups the animal kingdom together?
hint, 7 main things |
All chemoheterotrophs
All multicellular Distinctive embryonic stage: the blastula No cell walls Almost exclusively sexually reproductive Active movement Diverse in form |
|

What is this? Describe it
what Grouping? |
It is a Lophophore; a ring of tentacle like structures nea the mouth. primarily function in feeding.
the Lophotrochozoans |
|
|
what morphologies are covered in the Lophotrochozoans?
|
They are triploblastic ranging from acoelomate to pseudocoelomate to eucoelomate
|
|
|
Coelom
|
a body cavity which seperates an animals digestive system from its outer body wall
|
|
|
describe the symmetry of the Lophotrochozoans
what does this this entail about a central organ? |
radial symmetry is now reduced to bilateral symmetry. one plane of symmetry giving it a posterior and anterior end, this is good for locomotion
Encephalization. the bilateral morphology now supports a head which is the primary source of sensory |
|
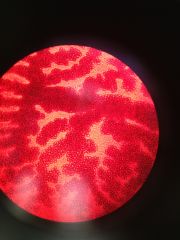
what phylum and what class
|
Phylum Platyhelminthes (the flatworms)
this is a dendrocoelom of the class Turbellaria |
|
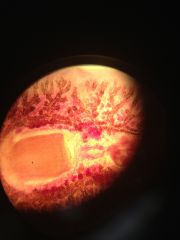
what is this?
|
this is the Pharynx of a Platyelminthes class turbellaria (free living flatworm
|
|
|
specify the circulatory system of the mollusca
|
either an open circulatory where the blood enters a hemoceol or its closed where it never leaves the circulatory system
|
|
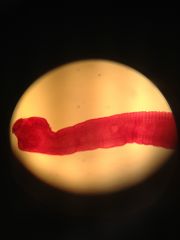
what class? and phylum?
what is on the left? the thing that looks like suckers |
class cestoda phylum platyhelminthes
a scolex is one of 3 parts of the body plan and it is the attachment part. notice the hooks on the left |
|

these look like segments. what are they called?
what phylum and class? |
proglottids
phylum Platyhelminthes class cestoda |
|
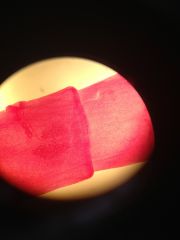
each segment contains a self contained reproductive system with gonads
what is this segment called? |
a proglottid and it is of the phylum Platyhelminthes class cestoda
|
|

what is this?
|
another proglottid segment Platyhelminthes class cestoda
|
|
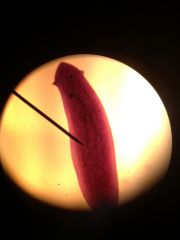
notice the probuscus in the center, this tells us...
|
its a phyrynx/mouth
Planaria Phylum Platyhelminthes class turbellaria |
|
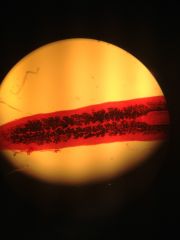
notice the folded digestive cavity. why is it positioned this way?
|
to maximize surface area
this is a turbellaria of the platyhelminthes phylum |
|
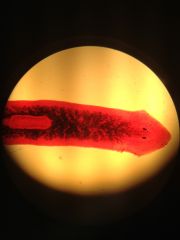
center notice the probuscus
|
mouth/pharynx turbellaria
|
|
|
all platyelminthes are what
|
aceolomates
|
|
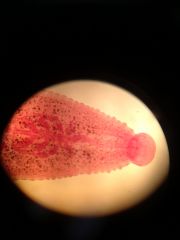
posterior sucker
aboral |
Phylum Annelida class hirudinea
|
|
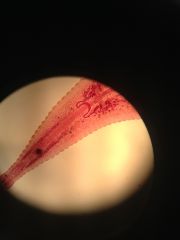
anterior sucker
oral |
Phylum Annelida Class Hirudinea
|
|
clonorchis sinensis
|
phylum platyhelminthes
class trematoda. the flukes |
|
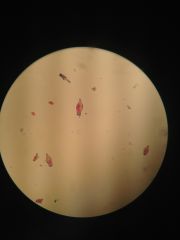
100x Pseudocoelomates
|
phylum rotifer
|
|
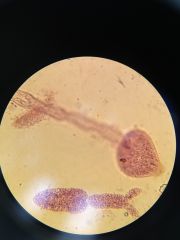
the flukes
|
class trematoda phylum platyhelminthes
|
|
Microscopic, comprised on only a few hundred cells (smaller than some protists)
Generally FW aquatic Related to flatworms (flame cells) Usually separate sexes Complete DT (alimentary canal) Parthenogenesis |
Phylum Rotifera
|
|
|
Lack organs for gas exchange and circulation
Triploblastic Nitrogen wastes diffuse through body wall Ciliated cells (flame cells) help maintain osmotic balance Dorso-ventrally flattened Bilateral symmetry 20,000 species Marine, FW, damp terrestrial, parasitic Microscopic to > 20 m long Incomplete digestive system (gastrovascular cavity) Paired lateral nerves and simple brain Acoelomate 4 classes |
Platyhelminthes the flatworms
|
|
|
what are the lophophorates?
|
the ectoprocts(colonial marine animals) and the brachiprocts(the lampshells)
|
|
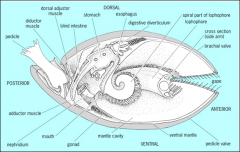
Phylum? hint... the lampshells
|
Phylum Brachiopods
the lophophorates |
|

the branchy things are for feeding, they have well develped feeding lophophore
|
Phylum Ectoprocta
|
|
Most marine, carnivorous
Some 30 m long Possess complete DT Proboscis (some with stylet) held within a rhynchocoel (everts when feeding) Blood vessels/closed circulatory system Lack a true coelom Uncertain taxonomy |
The Phylum Nemertea Ribbon worms
|
|
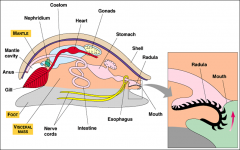
the radula is a specialized feeding mouthpeice
True coelomic cavity Lophotrochozoa 110,000 species Snails, slugs, clams, oysters, scallops, octopus, and squid Marine origins Possess a radula and a mantle Trocophore and veliger larvae |
the euceolomate phyla phylum mollusca
|
|
|
all platyhelminthes are what
|
aceolomates
|
|
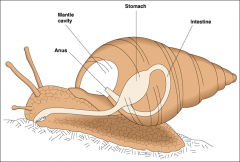
phylum mollusca
an example of what |
torsion
|
|

what is this
the terrestrialized what |
class gastropoda
molluscs |
|

notice 8 segments of what
|
chiton
class polyplachophora of the phylum mollusca |
|
|
all molusca are what
|
euceolomates
|
|
|
Lophotrochozoan
Segmentation (metamerism) along body providing greater local control of functions (repeated and specialized segments) and localizes damage Hydrostatic ‘skeleton’ 11,000 species (most marine) Closed circulatory system |
phylum annelida
|
|

Clitellum for reproduction
|
class oligocheata the earthworms
|

