![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the biological functions of lipids? |
1. Components of cellmembranes(phospholipids & cholesterol) 2. Precursors of hormonescholesterol steroid hormonesarachidonic acid prostaglandins 3. Long term fuels(triglycerides) |
|
|
Where are triglycerides stored? |
Compact storage - triglyceridesstored as large fat droplets inthe fat cells of adipose tissue • Large body stores -70 kg adult has: 11 kg fat (as TG) 120 g glycogen in liver 10 g glucose |
|
|
What is the efficiency of fats on a weight basis? |
Efficiency on weight basis –1 g fat yields 38 kJ 1 g protein 21 kJ 1 g carbohydrate 17 kJ |
|
|
What are some common fatty acids? |
palmitic acid C 16:0 stearic acid C 18:0 oleic acid C 18:1 linoleic acid C 18:2 linolenic acid C 18:3 |
|
|
What is lipase activated by? |
Lipaseactivated byadrenaline& glucagon |
|
|
How do free fatty acids travel in the plasma? |
Free fatty acidstravel in plasmabound to albumin |
|
|
What do the fatty acids act as? |
Act as fuelsfor muscles,heart & liver |
|
|
What happens to the glycerol in the breakdown of triacylglycerides? |
Glyceroldiffuses inblood streamto all tissues |
|
|
How are triglycerides broken down? |
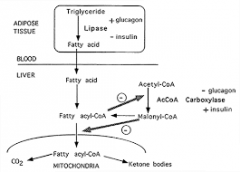
|
|
|
Why can glycerol be taken up by all cells? |
Glycerol is water soluble & is taken up by alltissues |
|
|
What happens to glycerol in most tissues? |
Enters glycolysispathway for conversionto pyruvate, theninto TCA cycle foroxidation to CO2 |
|
|
What happens to the glycerol in liver or in starvation? |
Enters glycolysispathway and isconverted to glucose bygluconeogenesis |
|
|
Where does Fatty acid metabolismby B-oxidation pathway take place? |
all reactions occur in the mitochondrial matrix(* transport across membrane) |
|
|
What are the intermediates in this pathway? |
intermediates present as CoA thioesters |
|
|
How is the biological energy of fatty acids conserved? |
biological energy of fatty acid molecule isconserved as the transfer of 2 H atoms to thecofactors NAD+ and FAD to form NADH & FADH2(no direct ATP synthesis) |
|
|
How is acetyl CoA removed? |
series of four enzyme reactions results in removalof two carbon unit as acetyl CoA |
|
|
What happens when the fatty acid is activated? |
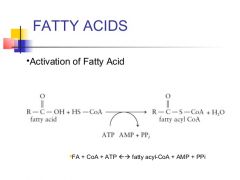
Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase(cytosol) Coenzyme A forms thioesterbonds with carboxylic acids |
|
|
How are fatty acids Transported intomitochondria? |
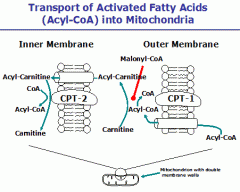
|
|
|
What moves the carnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane? |
Translocase |
|
|
What happens in reaction 1? |
Reaction 1 - Removal of 2 H atoms acyl-CoAdehydrogenase |
|
|
What are the 4 reactions in B-oxidation of fatty acids? |
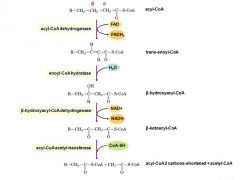
|
|
|
What happens in reaction 2? |
Reaction 2 – Addition of water Enoyl-CoA hydratase |
|
|
What happens in reaction 3? |
Reaction 3 – Removal of 2 H atoms Hydroxyacyl-CoAdehydrogenase |
|
|
What happens in reaction 4? |
Reaction 4 - Removal of 2 C units B-Ketoacyl-CoA thiolase |
|
|
What happens to the shorter fatty acid? |
Shorter fatty acid re entersreactions 1 - 4 |
|
|
what is a summary of the B-oxidation pathway? |
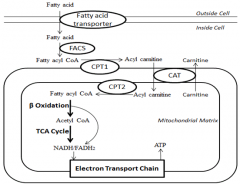
Fatty acid with 16 C atomswill pass through 7 repeatsof B-oxidation pathwayproducing 7 NADH& 7 FADH2 |
|
|
How many acetyl CoA will a fatty acid with 16 C atoms give rise to? |
Fatty acid with 16 Catoms will give riseto 8 acetyl CoA whichenter the TCA cycle |
|
|
What is the Energy yield from fatty acid oxidation? |
Fatty acid with 16 C atoms goes through 7 repeats of-oxidation producing 7 NADH & 7 FADH2 ATP yield = 7 x 2.5 + 7 x 1.5 = 28 Fatty acid with 16 C atoms produces 8 acetyl CoAATP yield from complete oxidation of acetyl CoAby TCA cycle = 8 x 10 ATP = 80 TOTAL = 80 + 28 = 108 – 1 = 107 |
|
|
What activates lipase enzyme? |
Release of fatty acids from adipose tissueadrenaline & glucagon activate lipase enzyme |
|
|
What determines the rate of entry of fatty acid into mitochondria? |
Rate of entry into mitochondria via carnitineshuttle |
|
|
What determines the rate of reoxidation of cofactors NADH and FADH2? |
Rate of reoxidation of cofactors NADH & FADH2by cytochrome chain |
|
|
What happens in the metabolism of odd numbered fats? |
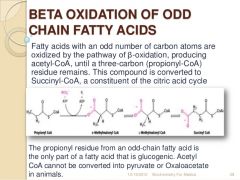
|
|
|
When does ketogenesis occur? |
Ketogenesis occurs when fat metabolism is the main sourceof energy: – in starvation – in Type I diabetes |
|
|
What does fatty acid oxidation in hepatocytes lead to? |
Fatty acid oxidation in hepatocytes leads to highconcentrations of Acetyl Co A - exceeds capacity of the TCAcycle. |
|
|
What happens to the excess Acetyl CoA? |
Excess Acetyl CoA is converted into ‘ketone bodies’ in liver |
|
|
What are the ketone body compounds? |
Acetoacetate B-Hydroxybutyrate |
|
|
What are the ketone bodies used for? |
Ketone bodies can be utilised for energy bymost (but not all) tissues |
|
|
What happens to the acetoacetate and β hydroxybutyrate? |
acetoacetate and β hydroxybutyrate are released into thebloodstream. |
|
|
What happens in most tissues? |
In most cell types they can be converted back into TCA cycleintermediates (acetyl CoA and succinate). Most tissues oxidise a mixture of fatty acids and ketonebodies |
|
|
Liver cannot utilise ketone bodies – WHY? |
Ketone bodies cannot be used as fuel by the liver, because the liver lacks the enzyme β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, also called thiophorase. |
|
|
Brain cannot utilise fatty acids – WHY? |
Cannot pass through Blood-Brain barrier – uses glucose and small amount of ketone bodies (‘emergency fuel’) |
|
|
Red blood cells cannot utilise fatty acids or ketone bodies, useglucose only – WHY? |
No mitochondria |

