![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The basic living unit of structure and function of any living organism is the |
D. cell
|
|
|
Crenation of a red blood cell may occur when it is placed in a(n) __________ solution.
A. neutral B. isotonic C. hypertonic D. hypotonic |
C. hypertonic
|
|
|
Phagocytic vesicles form by inward folding of the __________ .
A. lysosomal membrane B. nuclear membrane C. plasma membrane D. endoplasmic reticulum |
C. plasma membrane
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the structural arrangement of cellular membranes?
A. a solid, rigid layer of phospholipid with loosely bound protein molecules B. a fluid bilayer of phospholipid molecules in which protein molecules are floating C. strong layers of protein molecules where carbohydrate molecules freely float D. three layers: lipid on the inside, protein in the middle, and carbohydrates (and polysaccharides) on the outside |
B. a fluid bilayer of phospholipid molecules in which protein molecules are floating
|
|
|
Ribosomes are assembled in the
A. cytoplasm B. Golgi complex C. rough ER D. nucleolus |
D. nucleolus
|
|
|
Which of the following is a function of ribosomes on the rough ER?
A. produce steroids B. package hydrolytic enzymes C. store calcium D. synthesis of proteins |
D. synthesis of proteins
|
|
|
Which of the following processes do not require use of cellular energy?
A. phagocytosis B. phagocytosis C. cellular pumps D. diffusion |
D. diffusion
|
|
|
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell because their main function is
A. generating ATP B. homeostasis C. hydrolysis D. motility |
A. generating ATP
|
|
|
Proteins are packaged for secretion by the
A. golgi complex B. nucleoli C. ribosomes D. nucleosomes |
A. golgi complex
|
|
|
If the concentration of solutes in the fluid outside a cell is lower than the concentration
inside A. water will tend to enter the cell by active transport B. water will tend to leave the cell by osmosis C. glucose will tend to enter the cell by osmosis D. water will tend to enter the cell by osmosis |
D. water will tend to enter the cell by osmosis
|
|
|
A transport process that does not require the expenditure of cellular energy is
A. facilitated diffusion B. phagocytosis C. receptor mediated endocytosis D. active transport |
A. facilitated diffusion
|
|
|
DNA replicates during
A. prophase B. telophase C. interphase D. metaphase |
C. interphase
|
|
|
Glucose crosses the plasma membrane by
A. facilitated diffusion B. osmosis C. filtration D. pinocytosis |
A. facilitated diffusion
|
|
|
Ribosomes, mRNA, and tRNA all have one thing in common. They all
A. are found in the nucleus B. are produced by nucleoli C. function in translation D. move through ion channels |
C. function in translation
|
|
|
Which of the following functions as part of the cytoskeleton, cell identity markers, receptors, and enzymes?
A. glycolipids B. membrane proteins C. carbohydrates D. DNA |
B. membrane proteins
|
|
|
The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration is called
A. diffusion B. osmosis C. endocytosis D. facilitated diffusion |
B. osmosis
|
|
|
Which of the following would be most likely to enter a cell by endocytosis?
A. fatty acids B. lipid-soluble hormones such as estrogen C. calcium ions D. viruses such as HIV |
D. viruses such as HIV
|
|
|
Microtubules are located in the
A. endoplasmic reticulum B. cytoplasm and cilia C. Golgi complex D. nucleus |
B. cytoplasm and cilia
|
|
|
Channels (pores) and transporters in the cytoplasmic membrane are made up of
A. integral proteins B. lipids C. cholesterol D. peripheral proteins |
A. integral proteins
|
|
|
The molecules that make up most of the plasma membrane are
A. proteins B. cholesterol C. glycoproteins D. phospholipids |
D. phospholipids
|
|
|
The hydrophobic phospholipid tails in the plasma membrane bilayer point toward
A. the extracellular fluid B. each other C. the cytosol D. the integral proteins |
B. each other
|
|
|
Which type of membrane protein attaches to specific hormones such as insulin?
A. ligand B. receptor C. channel D. anchor |
B. receptor
|
|
|
The membrane potential is caused by
A. the diffusion of amino acids across the plasma membrane B. osmosis of water into the cell C. enzymes on the outer surface of the cell D. a separation of ions by the cell membrane |
D. a separation of ions by the cell membrane
|
|
|
Inside the cell (cytosol) the main cations are
A. negatively charged amino acids, proteins and phosphates B. chloride ions C. potassium ions D. phospholipids |
C. potassium ions
|
|
|
A red blood cell is placed into a beaker containing pure water, what occurs?
A. the number of water molecules leaving and entering the sac is equal B. the sugar molecules move into and out of the bag at an equal rate C. the sugar molecules diffuse into the pure water D. the water moves into the red blood cell via osmosis |
D. the water moves into the red blood cell via osmosis
|
|
|
In primary active transport
A. glucose is moved across membranes with sodium ions B. energy derived from ATP directly moves a substance across a membrane C. symports and antiports are involved D. sodium ions leak across the membrane because of a diffusion gradient |
B. energy derived from ATP directly moves a substance across a membrane
|
|
|
Calcium concentration in the cytosol (inside the cell) is kept low by action of
A. sodium/calcium antiporters B. primary active transport of calcium ions C. excess permeability of calcium ions D. symport of calcium and glucose |
A. sodium/calcium antiporters
|
|
|
A pump protein moves sodium and potassium ions across the membrane by
A. changing shape B. rotating C. flip-flopping D. breaking down into a smaller molecule |
A. changing shape
|
|
|
The function of ATP in the operation of the Na+/K+ pump is to
A. add a phosphate to the pump protein, changing its shape B. activate the pump, which then attaches to K+ C. release energy which pushes the ion through the membrane D. open a hole in the phospholipid bilayer, where sodium passes through |
A. add a phosphate to the pump protein, changing its shape
|
|
|
Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves
A. ligands and specific proteins on the cell surface B. osmosis C. movement of tiny droplets of water out of the cell D. active transport of glucose |
A. ligands and specific proteins on the cell surface
|
|
|
In exocytosis, __________ unite with the plasma membrane and release their contents to the
outside of the cell. A. phagosomes B. secretory vesicles C. endosomes D. pinocytic vesicles |
B. secretory vesicles
|
|
|
Chemically, the cytosol is 75 - 90 percent __________ .
A. water B. protein C. phospholipid D. sodium ions |
A. water
|
|
|
Some endoplasmic reticulum appears rough because
A. large proteins are attached to the surface B. it is still in the process of formation C. ribosomes are attached to the surface D. it is digesting molecules |
C. ribosomes are attached to the surface
|
|
|
In mitochondria the enzymes that carry out the reactions of aerobic cellular respiration are located
A. on the smooth outer surface B. on the inner folds, called cristae C. between the two membranes D. within the central cavity, called the matrix |
B. on the inner folds, called cristae
|
|
|
Mitochondria are more numerous in cells that
A. protect the body B. are located in the intestines C. communicate with the external environment D. have a high rate of ATP utilization |
D. have a high rate of ATP utilization
|
|
|
Numerous short projections from the surface of cells of the respiratory tract are called
A. flagella B. microtubules C. cilia D. hydrophilic head |
C. cilia
|
|
|
Continuous destruction of unneeded, damaged, or faulty cytosolic proteins is the function of
__________ A. peroxisomes B. proteasomes C. lysosomes D. mitochondria |
B. proteasomes
|
|
|
The process of translation terminates when
A. the large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit B. the stop codon of the mRNA enters the ribosome C. ATP is no longer available D. DNA no longer produces mRNA |
B. the stop codon of the mRNA enters the ribosome
|
|
|
Somatic cell division involves the nuclear division called
A. cytokinesis B. mitosis C. meiosis D. fission |
B. mitosis
|
|
|
During interphase of cell division
A. cleavage furrow develops B. the DNA replicates C. the nuclear membrane disappears D. the centrioles separate |
B. the DNA replicates
|
|
|
When cytokinesis is complete __________ begins
A. interphase B. prophase C. metaphase D. anaphase |
A. interphase
|
|
|
In active transport across a plasma membrane
A. a substance is moved from where it is less concentrated to where it is more concentrated B. a substance is moved from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated C. there is net movement of a solvent through the membrane D. the energy source is kinetic (thermal) energy |
A. a substance is moved from where it is less concentrated to where it is more concentrated
|
|
|
Gametes are most different from other cells of the body because of
A. their size B. their shape C. the method of metabolism D. the number of chromosomes in their nuclei |
D. the number of chromosomes in their nuclei
|
|
|
The organelle that packages proteins, such as the hormone insulin, into secretory vesicles that can undergo exocytosis is the
A. lysosome B. smooth endoplasmic reticulum C. nucleolus D. Golgi complex |
D. Golgi complex
|
|
|
Which of the following cross the plasma membrane by diffusing through the lipid bilayer?
A. carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules B. water molecules and proteins C. glucose and amino acids D. glucose and digestive enzymes |
A. carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules
|
|
|
Apoptosis is
A. a process in which free radicals are produced during normal aging B. an abnormal type of cell division in which cdc2 proteins and cyclin promote proliferation of cells C. a normal type of cell death that helps maintain an appropriate number of cells in each tissue D. a pathological type of cell death that results from injury of a tissue |
C. a normal type of cell death that helps maintain an appropriate number of cells in each tissue
|
|
|
A neoplasm that does not metastasize is called a
A. malignant tumor B. benign tumor C. carcinogen D. carcinoma |
B. benign tumor
|
|
|
A carcinogen is
A. a virus B. an oncogene C. a chemical agent or radiation that causes cancer D. a mutation |
C. a chemical agent or radiation that causes cancer
|
|
|
In the process of aging, tissues stiffen and lose their elasticity because
A. certain proteins break down in cells B. ozone causes elastic fibers to become brittle C. we gradually lose our ability to metabolize glucose D. irreversible glucose cross-links form between adjacent protein molecules |
D. irreversible glucose cross-links form between adjacent protein molecules
|
|
|
Substances in our diet such as vitamin E, vitamin C, and beta-carotene may slow the process of aging by
A. reducing the rate of mutation B. stimulating cell division of nerve cells C. inhibiting free radical formation D. reducing UV damage of the skin cells |
C. inhibiting free radical formation
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of the proteins associated with the cell membrane?
A. regulates the passage of ions in and out of the cell B. acts as a carrier molecule for various compounds C. acts as a receptor of certain hormones D. produces energy for the cell |
D. produces energy for the cell
|
|
|
Which of the following does NOT require the cell to expend its own ATP?
A. facilitated diffusion B. phagocytosis C. endocytosis D. pinocytosis |
A. facilitated diffusion
|
|
|
A 0.89% saline solution is isotonic for RBCs. If a RBC is placed in a 10% saline solution, it will undergo:
A. hemolysis B. crenaton C. bursting D. lyses |
B. crenaton
|
|
|
What structures are absolutely necessary if a cell is to reproduce?
A. lysosomes and peroxisomes B. cilia and flagella C. centrosomes and nucleus D. ribosomes and RER |
C. centrosomes and nucleus
|
|
|
Which of the following transport mechanisms involves vesicle formation?
A. sodium-potassium pump B. facilitated diffusion C. osmosis D. receptor-mediated endocytosis |
D. receptor-mediated endocytosis
|
|
|
Which of the following events occurs during anaphase of mitosis?
A. cytokinesis B. chromatid pairs line up at equatorial plane C. chromosomes move to opposite poles of cell D. chromatin shortens into chromosomes |
C. chromosomes move to opposite poles of cell
|
|
|
Integral proteins are part of the:
A. cytoplasm B. nucleolus C. plasma membrane D. cytosol |
C. plasma membrane
|
|
|
Which organelle inactivates or detoxifies drugs in liver cells?
A. rough endoplasmic reticulum B. smooth endoplasmic reticulum C. mitochondrion D. ribosome |
B. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
What controls the movement of substances between the nucleus and the cytoplasm?
A. DNA B. mitochondria C. nuclear pores D. protein synthesis |
C. nuclear pores
|
|
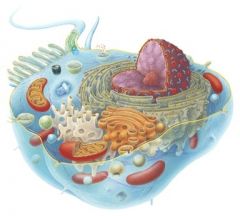
Which organelle on the diagram is responsible for digesting worn out cells?
|
lysosome
|
|
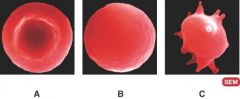
Cell B is in which type of solution?
A. isotonic B. hypotonic C. hypotonic |
B. hypotonic
|
|
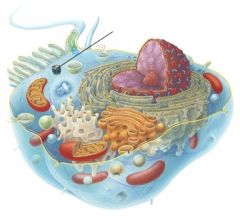
What is the function of this organelle?
A. protein synthesis B. ATP production C. degrade unneeded, damaged, or faulty proteins D. control movement of substances between the nucleus and the cytoplasm |
C. degrade unneeded, damaged, or faulty proteins
|
|
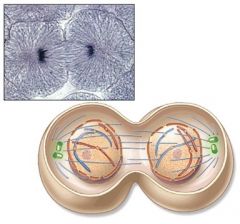
Which stage of the cell life cycle is shown in this diagram?
|
Telophase
|
|
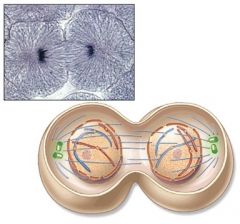
What event completes the mitotic phase of cell division?
|
Cytokinesis
|

