![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common odontogenic cyst of the jaw?
|
Periapical cysts aka Radicular cyst
- associated with a nonvital tooth or trauma, not always symptomatic - necrotic dental pulp creates inflammatory response at apex leading to granuloma formation, a fistula to the gingival or even through cheek/jaw skin can occur |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of a periapical/radicular cyst?
|
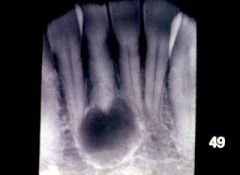
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular Surrounding apex of tooth |
|
|
What is the tx of periapical/radicular cysts?
|
Removal of underlying inflammatory process through endodontic tx (root canal) or tooth extraction with enucleation and curettage;
Abx and drainage of any soft tissue abscess |
|
|
What is a residual periapical cyst?
|
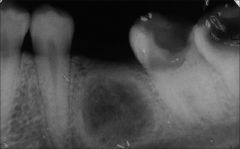
Cyst at the site of previous tooth extraction
Remnant of process that led to tooth loss versus insufficient curettage during tooth extraction versus continuation of epithelial rest inflammatory response after tooth extraction Generally assx |
|
|
What is the second most common odontogenic cyst of the jaws?
|
Dentigerous cyst
|
|
|
Describe the clinic features of a dentigerous cyst
|
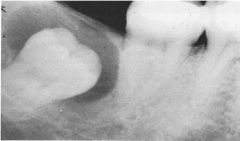
Associated with the crown of UNERUPTED tooth
Most commonly arises from mandibular 3rd molar or maxillary canines, altough can occur at any unerupted tooth Can grown very large, associated with painless expansion of bone 18G needle aspiration can yield STRAW-COLORED FLUID |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of a dentigerous cyst?
|
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular Associated with crown of UNERUPTED tooth |
|
|
Tx of dentigerous cyst?
|
Extraction of affected tooth with enucleation and curettage
If larger cyst, may consider two-stage approach with prolonged decompression with drain prior to formal treatment |
|
|
Describe the clinical features of an eryption cyst
|
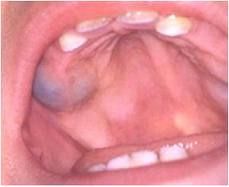
Occurs during tooth eruptions process in children less than 10yo
BLUISH CYST appears under the gingiva, can sometimes be painful |
|
|
What is the tx of an eruption cyst?
|
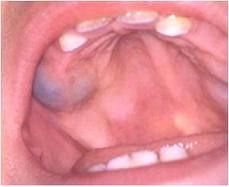
Usually not needed, resolves when tooth erupts through it; if fails to occur, then simple excision
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of a lateral periodontal cyst?
|
Assx, only found on radiographs
Occurs in age of 40-70yo, rare in less than 30yo About 80% occur in mandibular premolar/canine/lateral incisor area |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of a lateral periodontal cyst?
|
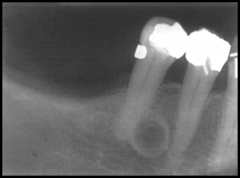
Radiolucent
SIngle lesion Well-demarcated unilocular LATERAL to roots of vital teeth Usually less than 1cm in size |
|
|
What is the tx of a lateral periodontal cyst?
|
Enucleation with preservation of tooth
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of a glandular odontogenic cyst?
|
Middle age adults
About 80% occur in mandible, generally anterior Small cysts can be assx, but larger ones can expand to produce pain/paresthesias |
|
|
What are the readiographical features of a glandular odontogenic cyst?
|
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular (Histopathalogically there are mucous cells present) |
|
|
What are the clinical features of Gorlin's cyst?
|
Gorlin's cyst = calcifying odontogenic cyst
Variable clinical behavior Variable age, infant to elderly Variable location, intraosseous vs extraosseous |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of Gorlin's cyst?
|
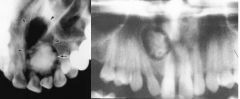
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular Irregular calcifications can be present |
|
|
What is the tx of a Gorlin's cyst?
|
Enucleation and curettage for intraosseous
Excision for extraosseus |
|
|
What is the most common NONodontogenic cyst of the jaw?
|
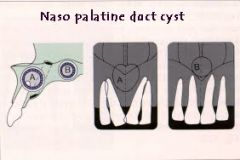
Nasopalatine duct cyst/incisive canal cyst
- forms during fusion of primary and secondary palate - male predominance |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
HEART SHAPED radiolucent lesion
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular Above roots of central incisors |
|
|
What are the tx of nasopalatine duct cyst?
|
Enucleation
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of nasolabial cysts?
|
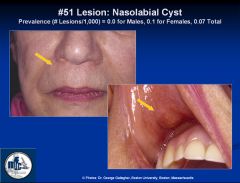
Soft tissue cyst, occurs between ala and lip from trapped epithelium during embryologic fusion; remnants of nasolacrimal duct
Female predominance, 30-50yo Generally assx |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of nasolabial cysts?
|
Due to origin in soft tissues, NO radiographic changes usually present, however can sometimes saucerize adjacent bone of maxilla
|
|
|
What is the tx of nasolabial cysts?
|
Surgical excision
|
|
|
Name 3 pseudocysts of the jaw
|
Traumatic bone cyst
Aneurysmal bone cyst Stafne bone cyst ALL have a cystic appearance, but DO NOT have a true epithelial lining |
|
|
What are the clinical features of a traumatic bone cyst?
|
Doe NOT necessarily have traumatic hx
Most common between ages 10-20yo Male predominance Affects mandible more than maxilla 18G needle aspiration yields nothing or scant blood |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of a traumatic bone cyst?
|
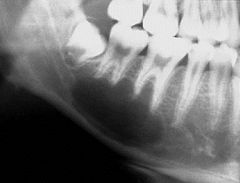
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcate multilocular Can scallop roots of adjacent teeth |
|
|
What is the tx of a traumatic bone cyst?
|
Surgical exploration of cyst alone will often induce healing process
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of an aneurysmal bone cyst?
|
Affects mandible > maxilla
Rapid swelling of jaw can occur 18G needle aspiration can yield blood |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of an aneurysmal bone cyst?
|
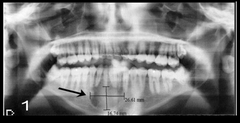
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular Can have "soap bubble" appearance |
|
|
What is the tx of an aneurysmal bone cyst?
|
Generally curettage, possible cryosurgery; resection in severe cases
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of a Stafne bone cyst?
|
Assx, radiographic finding
Thought to be developmental, may occur due to submandibular gland developing close to lingual surface leading to thinner bone formation Inferior to mandibular canal where inferior alveolar nerve runs in posterior mandible Most commonly unilateral Strong male predominance |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of a Stafne bone cyst?
|
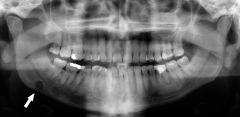
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular |
|
|
What is the tx of a Stafne bone cyst?
|
None required
|
|
|
What is the most common odontogenic tumor?
|
Ameloblastoma - a benign, locally aggressive neoplasm
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of solid or multicystic (intraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
Generally occurs after 20yo
About 85% occur in the mandible, most commonly in molar/ramus regions Slow-painless expansion of jaw |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of solid or multicystic (intraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
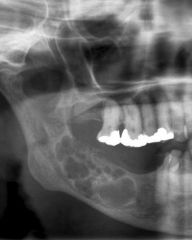
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular Resorption of tooth roots Cortical bone expansion |
|
|
What are the tx options for solid or multicystic (intraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
Optimal method has been controversial
Most favor resection with 1cm past radiographic extent of tumor |
|
|
What are the clinical features of unicystic (intraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
Majority occur int he mandibule, generally molar/ramus region
Painless swelling of the jaws |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of uncystic (intraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
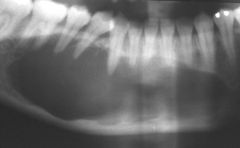
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular |
|
|
What are the clinical features of peripheral (extraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
Middle age adult
Sessile pr pedunculated gingival mass, not ulcerated, usually posterior location |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of peripheral (extraosseous) ameloblastoma?
|
Limited utility since extraosseous
|
|
|
How are malignant ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma differentiated?
|
Mainly based on histopathological features
- malignant ameloblastoma - no cytologic changes from benign ameloblastoma other than the fact that it is metastatic - ameloblastic carcinoma - has malignant cytologic changes in both the primary and mets sites |
|
|
How are radiogaphical features of malignant ameloblastoma and ameloblastic carcinoma?
|
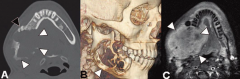
Malignant ameloblastoma - radiolucent, single lesion, well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular
Ameloblastic carcinoma: radiolucent, single lesion, poorly defined margins (image) |
|
|
What are clinical features of keratocystic odontogenic tumors?
|
Formerly known as odontogenic keratocyst (reclassified by WHO in 2005 based on genetic and histologic findings)
Majority involve the posterior body and ramuso of mandible 18G needle aspiration can yield a white/yellow, cheese-like materal |
|
|
How are radiogaphical features of keratocystic odontogenic tumors?
|
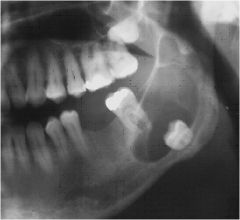
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular |
|
|
If there are MULTIPLE keratocystic odontogenic tumors, what syndrome does the pt need to be worked up for?
|
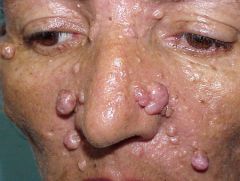
Gorlin's syndrome = Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS)
- autosomal dominant - multiple basal cell carcinomas - multiple keratocystic odontogenic tumors - skin cysts, palmar/plantar pits - calcified falx cerebri, increased head circumference - rib/vertebral malformations - hypertelorism - spino bifida |
|
|
What are clinical features of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
|
Most coommonly below 20yo
Female predominance Majority occur in the anterior maxilla Slow growing, relatively assx |
|
|
What are radiographical features of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
|
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular May contain small calcifications which helps differentiate from dentigerous cysts |
|
|
What are clinical features of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors?
|
Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors aka Pindborg Tumors
Generally occur between 30-50yo More common in mandible than maxilla Painless, slowly progressive swelling |
|
|
What are radiographic features of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors?
|
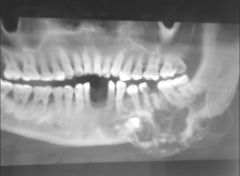
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated multilobular |
|
|
What are the clinical and radiographical features of squamous odontogenic tumors?
|
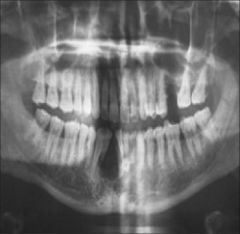
Variable age and location
Radiolucent Single Poorly defined margins |
|
|
What are the clinical features of ameloblastic fibroma?
|
Generally occur less than 30yo
Male predominance Most common in posterior mandible |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of ameloblastic fibroma?
|
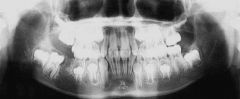
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular |
|
|
What are the tx options for ameloblastic fibroma?
|
Initial: enucleation and curettage
Recurrence: en block resection |
|
|
What are the clinical features of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma?
|
Most common in children
Posterior mandible |
|
|
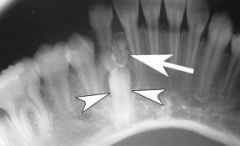
What are the radiographical features of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma?
|
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular with flecks of calcification |
|
|
What are the clinical features of ameloblastic fibrosarcoma?
|
ameloblastic fibrosarcoma = malignant
generally occur in young adults Majority occur in the mandible Pain, swelling, rapid growth Poor prognosis |
|
|
What are the radiological features of ameloblastic fibrosarcoma?
|
Radiolucent
SIngle lesion Poorly defined margins |
|
|
What is the tx for ameloblastic fibrosarcoma?
|
Radical resection
|
|
|
What are clinical features of odontoma?
|
Commonly occurs during 10-30yo
Assx, found on routine dental radiographical screening |
|
|
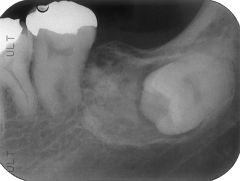
What are radiographical features of odontoma?
|
ReadiOPAQUE
Single lesion Well-demarcated Two types: 1) compound - appears as small tooth-like structure (image) 2) complex - enamel and dentin, no resemblance of tooth |
|
|
What is the tx of odontoma?
|
Enucleation
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of central, intraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
More common after age of 40yo
Most commonly located in posterior mandible, anterior maxilla Generally assx, may cause bony expansion or loose teeth |
|
|
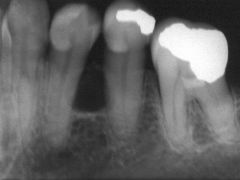
What are the radiographical features of central, intraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular (when small) or multilocular (when large) |
|
|
What is the tx of central, intraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
Enucleation and curettage
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of peripheral, extraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
More commonly occurs in mandible
Painless expansion of bone (when large) |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of peripheral, extraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
Radiolucent
Single Well-demarcated Unilocular or multilocular "Soap-bubble" pattern Appears similar to ameloblastoma |
|
|
What is the tx of peripheral, extraosseous odontogenic fibroma?
|
resection as often locally aggressive
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of cementoblastoma?
|
Majority occur in molar/premolar region of mandible
Most common under 30yo |
|
|
What are the radiographical features of cementoblastoma?
|
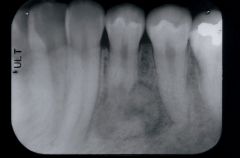
Radiopaque
Single lesion Well-demarcated Associated with root |
|
|
What is the tx of cementoblastoma?
|
Extraction of tooth with attached mass
|
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of osteoma's? |
Young adults
Assx, slowly growing Usually found at angle of mandible Gardner syndrome = Autosomal dominant, colonic polyposis, multiple osteomas of the jaw, skin fibromas and impacted teeth; Need close surveillance with colonoscopy as there is a high rate of malignant transformation of colonic polyps |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of osteoma's? |
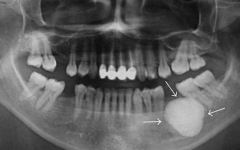
Radiopaque
Single lesion (can have multiple lesions of Gardner syndrome) Well-demarcated |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What is the tx of osteoma's? |
Observation or surgical excision
|
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of osteoblastoma? |
Commonly PAINFUL
Majority occur under age of 30yo |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of osteoblastoma? |
Radiopaque
Single lesion Well-demarcated or poorly defined |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of osteosarcoma's? |
Most common between ages 10-20yo
Equal incidence in both mandible and maxilla Swelling, pain, loosening of teeth |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of osteosarcoma's? |
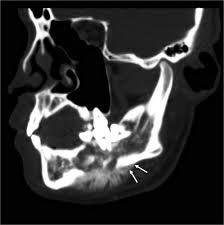
Radiolucent
Single lesion Poorly defined margins or radiopaque "SUNBURST" appearance Widening of periodontal ligament around teeth |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of chondroma's? |
Most common between ages 30-50yo
Most commonly located in anterior maxilla or condyle Painless, slow growing |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of chondroma's? |
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular with central area of radiopacity |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of chondrosarcoma's? |
Occurs in older adults
More common in maxilla than mandible Painless swelling |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of chondrosarcoma's? |
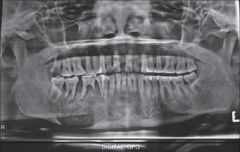
Radiopaque
Single lesion Poorly defined |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of fibrous dysplasia? |
Generally assx
May cease or "burn out" after puberty Two subtypes - Monostotic, 80% - Polyostotic (McCube-Albright syndrome: polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cafe au lait skin lesions, endocrinopathies such as precocious puberty, pituitary or thyroid abnormalities) |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of fibrous dysplasia? |
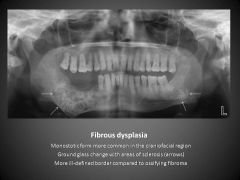
Radiopaque
Single lesion Poorly defined "Ground glass" appearance |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What is the tx of fibrous dysplasia? |
Observation or surgical excision
Dependent on size, location and sx severity |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of ossifying fibroma? |
Most common between ages 20-40yo
Female predominance More common in premolar/molar region of mandible Painless swelling |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of ossifying fibroma? |
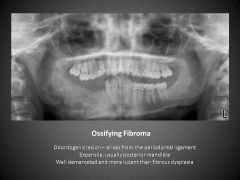
Radiolucent or radiopaque (can be mixed)
Well-demarcated unilocular |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of cemento-osseous dysplasia? |
Strong female predominance
More common in African Americans Middle age Three subtypes: 1) Focal: posterior mandible 2) Periapical: anterior mandible, around tooth root 3) Florid: diffuse involvement |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of cemento-osseous dysplasia? |
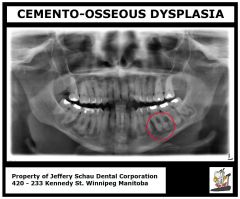
Radiopaque
Single Lesion Well demarcated or poorly defined Extent depends on subtype as florid can have multiple lesions |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What is the tx of cemento-osseous dysplasia? |
Generally, none needed
|
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of central giant cell granuloma? |
Majority occur less than 30yo
Majority occur in the mandible Can cross midline in anterior maxilla |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical of central giant cell granuloma? |
Radiolucent
Single lesion Well-demarcated unilocular or multilocular lesions or ill defined (histologically: multinucleated giant cells) |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the medical and surgical tx of central giant cell granuloma? |
Closely resembles brown tumor and hyperparathyroidism should be ruled out in all cases
Medical: intralesional steroids, calcitonin, interferon Surgical: aggressive curettage (usually treated surgically) |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of Langerhans cell histiocytosis? |
Most common in CHILDREN
Males > females Dull pain common |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of Langerhans cell histiocytosis? |
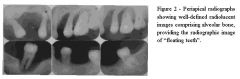
Radiolucent
Single or multiple lesions Poorly defined Teeth appear to be "floating in air" |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the tx options for Langerhans cell histiocytosis? |
Radiation or chemotherapy
(poor prognosis) |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of cherubism? |
Autosomal dominant
Most common during 2-5yo, can enlarge with growth and become stable by puberty Painless, bilateral cheek swelling due to expansion of posterior mandible |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the radiographical features of cherubism? |
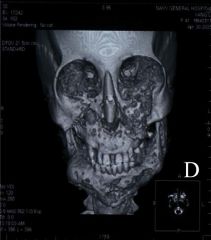
Radiolucent
Multiple lesions Upper and lower jaws involved (Histo: vascualr fibrous tissue containing giant cells) |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What is the tx of cherubism? |
Observation vs surgical excision depending on sx severity
|
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What are the clinical features of Paget Dz? |
Male predominance
More common in Caucasions than African Americans Usually occurs after 50yo Chronic, slowly progressive Can have cranial neuropathies if foramina are involved |
|
|
Nondontogenic Tumors
What is the tx for Paget Dz? |
Bisphosphonates
Calcitonin (slows bone turnover) |
|
|
What are the clinical features of osteomyelitis of the jaw?
|
More common in mandible than maxilla
Fever, leukocytosis, swelling, lymphadenopathy |
|
|
What are the clinical features of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw?
|
Complication from head & neck radiation, leaving bone hypocellular and hypoxic
Can be very painful |
|
|
What are the tx for osteoradionecrosis of the jaw?
|
If mild, good oral hygiene, hyperbacric oxygen therapy, debridement as needed.
If severe, may require surgical resection with vascularized flap reconstruction |
|
|
What are the clinical features of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ)?
|
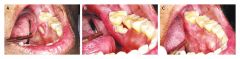
Occurs in pts undergoing dental procedures after receiving PO/IV bisphosphonate therapy
No hx of radiation therapy Can be very painful |

