![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
138 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the following borders of the parotid gland?
Anterior - Posterior - Superior - Inferior - |
Anterior - masseter muscle
Posterior - tragal cartilage and SCM muscle Superior - zygomatic arch Inferior - tail is between the ramus of the mandible and SCM muscle, overlying the digastric muscle |
|
|
What divides the superficial and deep lobes of the parotid gland?
|
Facial nerve
|
|
|
What cervical space does the deep lobe lay in?
|
in the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space
|
|
|
The superficial lobe makes up ___% of the parotid gland.
|
80%
|
|
|
What's the name of the fascia overlying the parotid gland?
|
parotidomasseteric fascia
|
|
|
What is the arterial anatomy of the parotid gland?
|
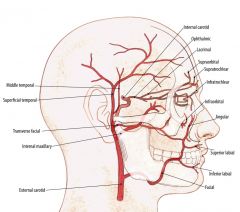
External carotid artery courses medial to the parotid gland dividing into the maxillary artery and the superficial temporal artery.
The superficial temporal artery gives off the transverse facial artery. |
|
|
What is the venous anatomy of the parotid gland?
|
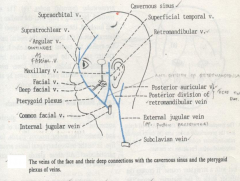
The maxillary and superficial temporal veins form the retromandibular vein.
Retromandibular vein joins the external jugular vein via the posterior facial vein. Retromandibular vein can give off an anterior facial vein that joins the internal jugular vein that is just deep to the marginal mandibularis branch of the facial nerve. |
|
|
What is the path of the Stensen's duct?
|
Tranverses over the masseter muscle
Pierces the oral mucosa adjacent to the 2nd upper molar |
|
|
The greater auricular nerve arises from where?
|
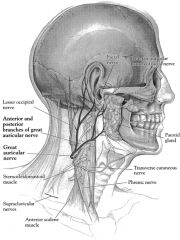
Arises from C2 and C3 cervical nerve branches.
Divides into anterior & posterior branches The posterior branch can occasionally be saved potentially reducing auricular numbness. |
|
|
What does the facial nerve form when it enters the parotid?
|
pes anserinus
|
|
|
Where is the tympano-mastoid suture in relation to the facial nerve?
|
about 2mm superior to the facial nerve
|
|
|
Where is the posterior belly of the digastric mucle in relation to the facial nerve?
|
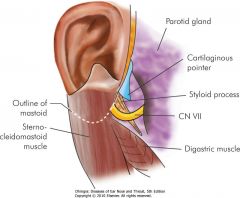
1cm inferior to the facial nerve
|
|
|
What is the sympathetic and parasymp innervation to the parotid gland?
|
SNS - superior cervical ganglion
PNS - glossopharyngeal nerve |
|
|
What are the boundaries of the parapharyngeal space?
Which compartment do deep parotid tumors present in? |
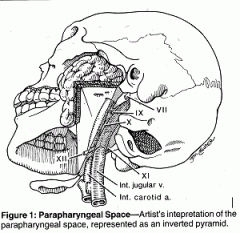
Inverted pyramid with the base at the petrous bone of the skull base
Medial boundary is the lateral pharyngeal wall Lateral boundary is the medial pterygoid muscle Posterior boundary is the carotid sheath and the anterior boundary is the pterygomandibular raphe. Prestyloid compartment - deep parotid tumors Poststyloid compartment - contains carotid sheath structures |
|
|
What are the following borders of the submandibular gland?
Superior - Inferior - |
Superior - inferior mandible
Inferior - anterior and posterior bellies of digastric muscle forming the submandibular triangle |
|
|
What is the arterial anatomy of the submandibular gland?
|
Facial artery courses deep tot he posterior belly of the digastric muscle
Facial vein lies lateral to the gland |
|
|
Where is the Wharton's duct in proximity to the lingual nerve?
|
It opens in the floor of the mouth and crosses deep to the lingual nerve
|
|
|
How are the submandibular and sinlingual glands innervated?
|
Facial nerve via the chorda tympani nerve provides secretomotor innervation for the submandibular and sublingual glands
|
|
|
Where does the lingual nerve lie proximity to the submandibular gland?
|
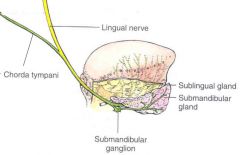
Lingual nerve (sensory nerve), traverses the floor of mouth and during submandibular gland surgery attaches to the deep superior surface of the submandibular gland via the submandibular ganglion
|
|
|
Where does the hypoglossal nerve lie proximity to the submandibular gland?
|
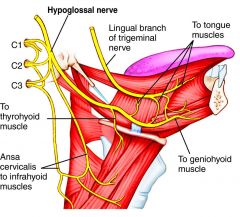
Hypoglossal nerve provides MOTOR function fo the tongue and is medial to the digastric muscle, which is medial to the submandibular gland
|
|
|
How do the sublingual glands drain?
|
Drain in the floor of mouth via Rivinus ducts or via the submandibualr duct via the Bartholin duct
|
|
|
What is the name of a mucocele of the sublingual gland?
|
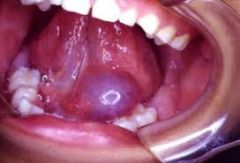
ranula
|
|
|
Almost all neoplasms are visualized as hyper or hypointense on T1 MRI imaging?
|
HYPOintense (dark)
|
|
|
What type of tumors are typically seen in pre-styloid space?
|
Deep lobe parotid tumors and minor salivary gland tumors
|
|
|
What type of tumors are typically seen in post-styloid space?
|
paragangliomas and schwannomas
|
|
|
Is sialography used in acute sialadenitis?
|
No, not used in acute setting
|
|
|
Bilateral parotid cysts in a patient suggest which systemic disease?
|
HIV
|
|
|
When does parotid development starts?
At what age does salivary secretion from the parotid start? |
7th embryonic week
Salivary secretion starts at birth |
|
|
Are there lymph nodes within any salivary glands?
|
Intraparotid lymph nodes form within the pseudocapsule of the parotid but nodes do not form within other salivary glands.
|
|
|
What is the makeup of saliva?
How much do humans secrete/day? |
99.5% water and otherwise proteins and electrolytes
~1 L/day |
|
|
Which gland produces mostly serous saliva?
Which gland produces most viscous saliva? |
Parotid gland
sublingual & minor salivary glands |
|
|
What is the most abundant protein in saliva?
|
amylase (40% of body amylase is produced by salivary glands)
|
|
|
What is the effect on ductal cells in pts with CF?
|
Results in abnormal chloride regulation with failure of reabsorption of NaCl in the ductal cells resulting in a more viscous saliva with decreased flow rates and sludging of saliva.
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of xerostomia?
|
Medications (mostly anticholinergic meds like antihistamines and antidepressants)
|
|
|
What is an adenomatoid hyperplasia?
|
Idiopathic assx nodule generally on the hard palate
Bx reveals normal minor salivary gland with excision being curative |
|
|
What is sialadenosis?
|
Painless enlargement of the salivary glands
Enlarged acinar cells Myoepithelial atrophy and degenerative changes in neural elements |
|
|
What is oncocytic metaplasia of the salivary glands?
|
Mitochondria are enlarged and more numerous.
Idiopathic and associated with aging and most common in the parotid. |
|
|
What is sebaceous metaplasia of the salivary glands?
What are fordyce granules? |
Sebaceous cells found in normal salivary glands, most commonly parotid.
Fordyce granules: sebaceous cells in the oral mucosa Metaplasia occurs with sebaceous cells replacing cells of the intercalated or striated duct. |
|
|
What is necrotizing sialometaplasia of the salivary glands?
|
Exuberant squamous metaplasia
Inflammatory response in minor salivary glands Can be misinterpreted as a malignant process |
|
|
What's the difference between accessory salivary gland tissue (SGT) and heterotopic SGT?
|
Accessory SGT are ectopic SGT with a DUCT system, most comonly located anterior to the main parotid gland (drain into the main parotid duct)
Heterotopic SGT has acini in an abnormal location WITHOUT a duct system, most commonly in cervical lymph nodes with rare examples in the middle ear, thyroid and pituitary |
|
|
Pt has painless salivary gland enlargement. Bx demonstrates positive Congo red staining. What is the dx?
|
amyloidosis
|
|
|
What is lipomatosis of the salivary gland?
|
Tumor-like accumulation of intraparenchymal fat tissue
Fibrous capsule, discreet mass Associated with ageing, DM, alcoholism, and malnutrition |
|
|
What is cheilitis glandularis?
|
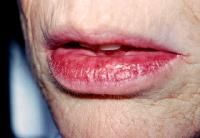
Nodular swollen lower lip of adult males
Can express saliva Nonspecific histologic finding, hyperplasia, fibrosis and ectasia |
|
|
What is the most common cause of acute suppurative sialadenitis?
|
Salivary stasis
Most common agent: S. aureus, followed by S. viridans & anaerobes. |
|
|
What are the typical sx of parotitis?
|
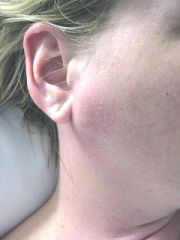
Parotitis - acute suppurative sialadenitis of the parotid gland
Unilateral painful swelling and pus from Stensen's duct |
|
|
What is the tx for acute suppurative sialadenitis?
|
Usually beta-lactemase and anaerobic sensitive antibiotics (unless case is mild)
Hydration Sialogogues |
|
|
What are the causes of chronic sialadenitis?
What are the tx? |
Sialolithiasis may result in scarred, stenotic ducts, and sialectasia leading to diminished secretory function of the gland.
Tx: Abx, hydration & sialagogues; possibly removal of sialolith |
|
|
What is a Kuttner's tumor?
|
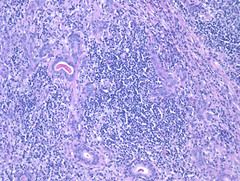
Kuttner's tumor = chronic sclerosing sialadenitis
Heavy lymphoid infiltrate submandibular gland |
|
|
What is the most common viral cause of parotitis?
|
Mumps (paramyxovirus)
Peaks at age 4-6yo Mostly bilateral involvement Also fevers, malaise, orchitis, encephalitis, or SNHL |
|
|
Why can HIV present with parotid enlargement?
|
Lymphoid hyperplasia, infection and lymphoma may all be factors in HIV
Parotid gland is the only salivary gland with lymphoepithelial cysts |
|
|
List some granulomatous diseases that can cause salivary gland enlargement
|
Tuberulosis
Atypical mycobacteria Actinomycosis Cat scratch dz Toxoplasmosis Sarcoidosis |
|
|
What will an atypical mycobacteria infection of the salivary gland present like? Tx?
|
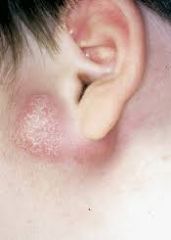
Violaceous hue of skin, sinus tracts
Rx: I&D, surgical excision of gland |
|
|
What are the risk factors of actinomycosis salivary gland dz and what is the presentation? Tx?
|
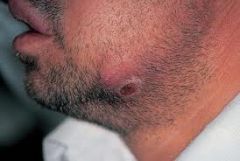
RF - poor oral hygiene, impaired immunity
Sinus tracts, multiloculated abscess Tx - penicillin G IV x 6 weeks, then PO erythromycin or clinda |
|
|
How is cat-scratch dz diagnosed? Tx?
|
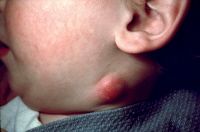
Bartonella henselae, rickettsial pathogen
Associated with lymphatics of parotid gland Dx: serology and PCR, lymphadenopathy, +Warthin-Starry stain reaction, pathologic features. Tx: observation & azithromycin |
|
|
How is toxoplasmosis diagnosed?
|
Toxoplasmosis gondii, protozoan parasite, increased incidence with HIV epidemic, under cooked meats, and cat feces
Dx: Cx, acute and convalescent titres Rx: Spiramycin, pyrimethamine, and sulfadiazine |
|
|
What is Heerfordt's syndrome? Tx?
|
aka uveoparotid fever
Triad of acute parotitis, uveitis and sarcoidosis Tx: steroids |
|
|
What are the diagnostic tests for Sjogren's syndrome?
|
+anti-Ro (SS-A) and anti-LA (SS-B) serologies
minor salivary gland Bx (ie. lip) associated with increased lymphocyte infiltration |
|
|
Sjogren's syndrome has a higher risk of lymphoma. Which type and why?
|
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
From prolonged stimulation of autoreactive B cells |
|
|
What is the tx for Sjogren syndrome?
|
Oral hygiene
Salivary substitutes Pilocarpine Cevimeline |
|
|
Quickly describe the intraoral sialolithotomy procedure
|
Incise floor of mouth mucosa
Remove stones Let heal by secondary intention or suture duct |
|
|
Where are stones typically located if they have come from the parotid or submandibular glands?
|
Parotid - in paranchyma
Submandibular - in Wharton's duct |
|
|
Stones larger than ____ are not able to be removed via sialendoscope
|
5mm
|
|
|
Is lithotripsy for salivary stones done?
|
Yes, but not FDA approved in the US
|
|
|
List the various etiologies of parotitis in pediatric population.
|
1) Neonatal suppuratiev parotitis - preterm, male, S. aureus
2) Recurrent parotitis of childhood - more common in boys, age 3-10yo, recurs weekly to monthly, no pus from duct, imaging shows ectasia of ducts. Rx: antibiotic for S. aureus, and dilation of Stensen's duct 3) Viral - mumps, HIV, CMV 4) Bacterial - S. aureus |
|
|
How do you differentiate a floor of mouth dermoid cyst vs ranula?
|
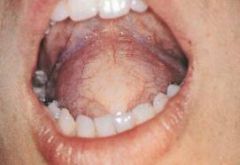
Dermoid cyst of floor of mouth is midline
Ranula's are unilateral |
|
|
List some congenital pediatric salivary gland cysts
|
1) Parotid dermoid-isolated cyst
2) Dermoid floor of mouth (midline) (ranula is unilateral) 3) Branchial cleft cyst 4) Polycystic parotid gland |
|
|
What procedure is done to reduce the recurrance of ranula's?
|
Excision of cyst with sublingual gland reduced recurrence
|
|
|
Where is the most common location for salivary mucocele's?
|
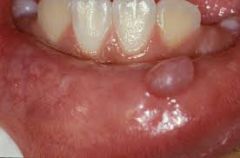
Lower lip (they are pseudocysts)
|
|
|
What is the most common salivary neoplasm of children?
|
Vascular neoplasm (20%)
|
|
|
What's the likelihood of involution of hemangioma's vs lymphangioma's in children/
|
Hemangioma's - usually involute between age 2-5
Lymphangioma's - rarely involute |
|
|
What is the most common BENIGN salivary tumor in kids
MC MALIGNANT salivary tumor in kids? |
Benign - benign mixed tumor
Malignant - mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|
|
Are solid salivary gland neoplasms less or more likely to be malignant in kids?
|
More likely - 50% of solid salivary gland neoplasms are malignant
|
|
|
What is the tx for sialorrhea?
|
Children w/ cognitive and physical disabilities, or metal poisoning
Conservative tx - glycopyrrolate, scopolamine, Botox Surgery - GOLD STANDARD - bilateral parotid duct ligation (risks: sialadenitis and fistulization) and submandibular gland excision. |
|
|
What are some surgical methods to correct aspiration?
|
-Parotid duct ligation and submandibular gland resection has some reports of success.
-Laryngotracheal separation is successful, theoretically reversible -Tracheotomy often unsuccessful in prevention -Tympanic neurectomy has lost favor. |
|
|
What is the most common salivary gland neoplasm in adults and children, and where does it typically present?
|
Benign mixed tumor
85% present in the parotid, most of these in the tail of parotid. |
|
|
What is the histology of a benign mixed tumor?
|
biphasic-benign epithelial cells and stromal cells
|
|
|
What is Frey syndrome?
|
gustatory sweating (complication of parotid tumor resection)
|
|
|
What is a technique of parotid surgery that does not dissect the facial nerve?
|
extracapsular dissection - in nonexpert hands can result in a higher rate of facial nerve dysfunction and recurrance
|
|
|
What are the two most widely accepted procedures for parotid surgery?
|
Partial superficial parotidectomy (with facial nerve dissection and a 2-cm cuff of normal parotid parenchyma around tumor)
Complete supfericial parotidectomy |
|
|
What is the rate of recurrance with facial nerve dissection procedures?
|
1 - 4% (usually multinodular)
|
|
|
Is the recurrence rate of enucleated parotid tumors low, mod or high?
|
unacceptably high recurrence rate with enucleation
|
|
|
A patient with recent enucleation of a parotid tumor has recurrence. What is the next procedure that should be performed?
|
Parotidectomy with facial nerve dissection
|
|
|
What is the incidence of myoepithelioma compared to all salivary gland neoplasms?
|
~1%; most present in the parotid gland
|
|
|
What's a more descriptive name for Warthin's tumor?
|
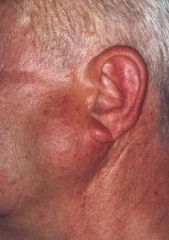
Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
- almost exclusively in the parotid gland |
|
|
What is the second most benign salivary gland neoplasm after benign mixed tumor?
|
Wharthin tumor
|
|
|
Wharthin tumor may not be a true neoplasm. Why?
|
It's associated with smoking and non clonal population by PCR, so may be an inflammatory reaction
|
|
|
What is the histology of Warthin's tumor?
|
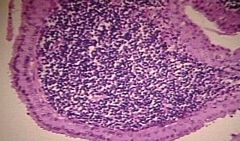
Oncocytic epithelium, papillary architecture, lymphoid stroma and cystic spaces
|
|
|
What is the tx for Warthin's tumor?
|
Partial superficial parotidectomy with facial nerve dissection or complete superficial parotidectomy most widely practiced
|
|
|
Basal cell adenoma can mimick which other salivary gland tumor?
|
solid subtype adenoid cystic carcinoma
|
|
|
Describe the location of canalicular adenoma and it's sx.
|
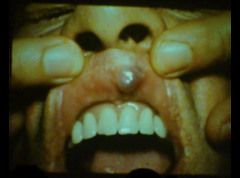
Usually in upper lip
Slow growing Asymptomatic |
|
|
What are oncocytoma's?
|
Proliferation of oncocytes - which are epithelial cells with accumulations of mitochondria
Oncocytic metaplasia - transformation of acinar and ductal cells to oncocytes -associated with aging Oncocytosis - proliferation of oncocytes in salivary glands. Minor salivary gland oncocytomas can be locally invasive |
|
|
What do Glands of Blandin-Nuhn refer to?
|
mucoceles of anterior lingual salivary glands
|
|
|
What's the frequency of salivary gland cysts?
|
About 5-10%
|
|
|
What's the incidence of malignant salivary gland tumors? Is there a relationship between them and smoking/alcohol use?
|
1-2 per 100,000
NO causative relationship with smoking and/or alcohol. (Radiation exposure may e a factor and genetic aberrations) |
|
|
There are multiple embryologic theories regarding malignant salivary gland tumors. Explain the:
-Reserve theory -Multicellular theory |
-Reserve theory - salivary gland neoplasms derived from stem cells
-Multicellular theory - all cells in the salivary unit are capable of replication |
|
|
Does imaging help distinguish between benign vs malignant salivary gland tumors?
|
It can, but generally does not
|
|
|
List surgical options for malignant salivary gland tumors
|
- Superficial parotidectomy with wide cuff of normal tissue may be adequate tx
- Total parotidectomy - deep lobe involved, high-grade tumor, +parotid nodes |
|
|
What are the tumor sizes for the following T grades?
T1 T2 T3 T4 |
T1 - 0-2cm
T2 - 2-4cm T3 - >4cm T4 - gross invasion |
|
|
There's a high chance of malignancy as you go from parotid -> lingual glands or lingual -> parotid?
|
High percent malignancy: lingual > minor > submandibular > parotid
|
|
|
In a pt with a malignant parotid tumor with a functioning facial nerve, what procedures need to be done to try and save the nerve?
If the facial nerve is grossly involved and has to be resected, what else do you do? |
surgical attempt coupled with planned postoperative XRT
if facial nerve is sacrificed, then immediate nerve grafting should be performed. |
|
|
How do you diagnose a submandibular gland mass?
|
Can do FNA to determine type of mass and if malignant, a planned zone 1 - 3 neck dissection along with gland excision.
|
|
|
Malignancy of the sublingual gland is rare, but if present, what must you do?
|
Dissection should include mucosa and a formal floor of mouth resection.
|
|
|
Where is the most common location for minor salivary gland malignant neoplasms?
|
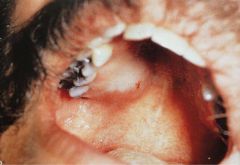
Hard palate
|
|
|
What are the typical neck disection zones for an N0 neck?
|
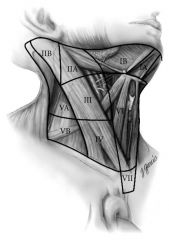
Zones 1-4 in N0, but 1-5 may be considered (with parotidectomy ofcourse) if high-grade histology, T3 or T4 (>4cm or invasive), extraglandular extension, and facial nerve dysfunction.
|
|
|
What is the overall rate of distant metastasis in malignant salivary gland tumors?
|
25%
|
|
|
Is chemotherapy effective in salivary gland tumors?
|
Not presently effective, but used for palliation
|
|
|
Gene methylation status may lead to targeted Tx. About 80% of parotid tumors express which factor?
Also, 90% of adenoid cystic cancers express which factor? |
Parotid tumors - epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
Adenoid cystic - c-KIT |
|
|
Are VEGF and p53 c-erbB markers have a favorable diagnosis?
|
No, poor prognosis
|
|
|
What is the most common malignant tumor of the salivary glands in adults and children?
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- low, intermediate and high-grade histology |
|
|
What is the surgical treatment for mucoepidermoid tumors?
|
complete superficial parotidectomy with total parotidectomy for deep lobe involvement.
Submandibular MEC more aggressive |
|
|
When should you use XRT for mucoepidermoid tumors?
|
high-grade tumor
perineural involvement positive margins cervical adenopathy |
|
|
What is the second most common OVERALL salivary gland neoplasm?
|
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (however, it is THE most common malignant tumor of minor salivary glands, submandibular and sublingual salivary glands)
|
|
|
Where is the most common site of adenoid cystic tumors?
|
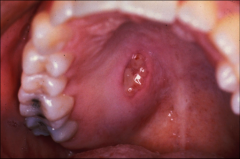
hard palate
|
|
|
Which salivary gland neoplasm has a propensity for perineural invasion?
|
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the best treatment for adenoid cystic ca?
|
surgery and postop XRT
|
|
|
What is the treatment for acinic cell carcinoma?
|
surgical with good margins
|
|
|
Which gland is epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma mostly found in?
|
Parotid gland
|
|
|
Explain salivary duct carcinoma. What is the tx?
|
High-grade tumor with resemblance to mammary ductal carcinoma
Early regional mets Tx: surgery, neck dissection to be considered in N0 neck, radiation therapy. |
|
|
What is the most common malignant MIXED tumor?
|
Carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma
Arises from long-standing mixed tumor |
|
|
What is the tx for carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma?
|
Surgery & XRT
- poor long-term survival |
|
|
In which salivary gland is lymphoma most likely to present?
|
parotid gland
|
|
|
What is the most common extranodal (primary) lymphoma? What is the tx?
|
MALT lymphoma
Tx for extranodal/primary lymphoma - resection and/or radiation (tx for secondary lymphoma is systemic) |
|
|
What are the two most common cancers that mets to the major salivary glands?
|
Squamous cell ca & Melanoma
(others include Merkel cell, eccrine, and sebaceous carcinoma) |
|
|
What percent of salivary gland malignancies are from mets?
|
10%
|
|
|
What are some risk factors of metastasis of cutaneous SCC?
|
Diameter >2cm
Thickness >4mm Local recurrence Peri-neural invasion Preauricular skin External ear index lesion |
|
|
Lip cancers can mets often to the ______ gland.
|
submandibular
|
|
|
Parotid mets from skin primary is associated with ___% rate of clinical neck mets and ___% rate of occult neck mets.
|
25%
35% |
|
|
Is mets from a cutaneous primary posterior to the external auditory canal likely or unlikely to involve the parotid gland?
|
unlikely
|
|
|
What is the tx for mets to parotid?
|
surgery + XRT
|
|
|
Regional mets rates for melanomas correlate with what?
|
Tumor thickeness
<1mm - <5% 1-4mm - 20% >4mm - 50% Mets to parotid - grim prognosis |
|
|
What is the histology of radiation-induced xerostomia?
|
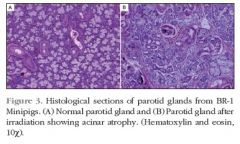
Acinar cell loss (with relative sparing of ductal cells)
|
|
|
Why is amifostine frequently used after XRT?
|
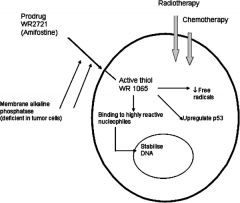
Amifostine is a radioprotector which acts intracellularly to scavenge and bind oxygen-free radicals and assist in DNA repair after radiation exposure
|
|
|
Explain submandibular salivary gland transfer
|
Gland released and repositioned in the submental space = shielded from radiation = less xerostomia
Retrograde blood flow to the transferred gland must be assured |
|
|
What is the sensitivity of FNA in distinguishing benign vs malignant salivary gland tumors?
|
90% (grade & tumor beter determined by frozen section)
|
|
|
What are the landmarks for identifying the facial nerve during parotid surgery?
|
1) Tympanomastoid suture (~ 6-8 mm lateral/distal to the stylomastoid foramen & CN7)
2) Tragal pointer (find nerve 10-15mm inferior, deep and slightly inferior to this) 3) Posterior belly of digastric muscle (nerve lies 10mm medial to this) |
|
|
How can you treat Frey syndrome?
|
Frey syndrome (rare) is gustatory sweating - tx with boulinum toxin
|
|
|
How many cm inferior to the mandible do you make an incision for submandibular gland resection? Why?
|
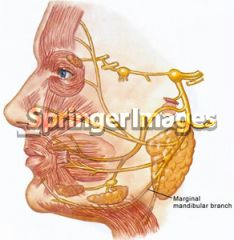
3cm, to preserve the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
The location of the hypoglossal nerve is ________ to the digastric muscle.
|
medial
|

