![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pulmonary ventilation |
Nose / mouth <--air--> Lungs. Invloves the exhange of air between the atmosphere and the alveoli of the lungs. |
|
|
External respiration |
Lungs --O2--> Blood --CO2--> RPT |
|
|
Internal Respiration |
Blood --O2--> Cells --CO2--> RPT |
|
|
Respiratory Muscles |
STM, External intercostals, diaphragm, internal intercostals, external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis, recus abdominis, |
|
|
Inhalation: Eupnea (unlaboured breathing) |
Diaphragm 75% responsible, External Intercostals 25% responsible. |
|
|
Inhalation: Strenuous Breathing |
STM raises sternum, scalene pull up ribs 1 and 2, pectoralis minor pull up ribs 3-5 |
|
|
Exhalation: Eupnea (unlaboured breathing) |
Passive recoil of lungs and chest wall. Relaxation of the diaphragm and external intercostals |
|
|
Exhalation: Strenuous Breathing |
Abdominals, internal intercostals |
|
|
Respiratory Centers |
Medulla oblongoata (breathing frequency, innervation of accessory breathing muscles. Pons (influence breathing frequency) |
|
|
Spirometer |
Measure of volume of air ventilated and respiratory rate |
|
|
Forced vital capacity |
Total amount of air exhaled during test forecully. |
|
|
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second |
Amount of air exhaled forcefully within the first second. |
|
|
Alveoli, Respiratory Bronchiole, Alveolar Sac |
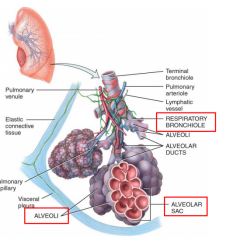
|
|
|
Respiratory Membrane |
Membrane of the alveous. |
|
|
External Respiration Process |
Oxygen binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, Carbon Dioxide diffuses from blood plasma into alveolus. |
|
|
Internal Respiration Process |
Oxygen diffuses into body cells, CO2 diffuses into blood. |
|
|
Transport of Oxygen |
Plasma responsible for 1.5% of Oxyge, but hemoglobin in RBCs responsible for 98.5% of Oxygen. Each hemoglobin (Hb) can maximally carry four Oxygen molecules. |
|
|
Transport of Carbon Dioxide |
7% dissolved in blood plasma, 23% carbaminohemoglobin (Hb-CO2), 70% Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) |
|
|
Asthma |
Chronic airway inflammation condition. |
|
|
COPD |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (usually bronchitis or emphysema). |
|
|
Empysema |
Destruction of alveolar walls, permanent elargement of alveoli, loss total surface area for gas exchange. Usually from smoking |

