![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the bones of the shoulder complex?
|
Sternum, Clavicle, Scapula, Humerus.
|
|
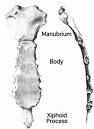
Name the parts of the Sternum ( Axial Skeleton)?
|
Manubrium, Body, Xiphoid
|
|
|
Name the articulations of the sternum?
|
Sternoclavicular joint, there are many articulations with ribs 1 - 7
|
|
|
What is sternoclavicular joint?
|
Synovial joint which links the upper extremity to the axial skeleton. it is a saddle shaped joint with a disc.
|
|
|
What is Manubrium?
|
superior part of the sternum, Jugular in superior midline, clavicular facets where the clavicles articulate with the sternum.
|
|
|
Sternum: The body?
|
majority of sternum, multicple facets for articulations with ribs.
|
|
|
What is the Xiphoid process?
|
Inferior tip of sternum.
|
|
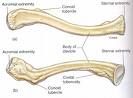
Shoulder complex: Describe the Clavicle?
|
Appendicular Skeleton,
S shaped bone located superior to the 1st rib, ligamentous attachments to the 1st ribs and 2 articulation surface. |
|
|
What are the Clavicle's articulation?
|
Sternoclavicular joint located medially and allows great mobility, Acromioclavicular joint: Synovial joint located laterally. it is considered a gliding joint. occasional disc.
|
|
|
Describe the Clavicles Posture?
|
In anatomical position, lateral end of the clavicle is 20 degrees posterior to the medial end.The clavicle is positioned such that the acromial end is slightly higher then the sternal end.
|
|
|
What is the Glenohumeral Joint?
|
Synovial ball and socket joint.
3 DOF, Concave fossa. Glenoid fossa and Head of humerus. |
|
|
What is Glenoid Labrum?
|
Fibrous connective tissue deepen the glenoid fossa. helps with stability of the joint.
|
|
|
Describe the head of humerus?
|
It is concave, and twice larger than glenoid fossa.
|
|
|
What muscles attach to the Greater tubercle?
|
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis muscle
|
|
|
Where is the Greater tubercle located?
|
It’s posterior laterally of the humerus
|
|
|
Where is the Lesser Tubercle located?
|
Anteriorly medial part of the humerus.
|
|
|
What muscle is attach to the Lesser Tubercle?
|
The Subscapularis muscle.
|
|
|
Where is Intertubercular ( bicepital) groove located?
|
It’s located between the greater and lesser tubercles
|
|
|
What tendon insert on the intertubercular groove?
|
The long head of the biceps tendon.
|
|
|
What is the position of the normal position of the glenohumeral joint?
|
The humerus is twisted 30 degree posterior. Epicondyles are in frontal plane, head angle is 135 degree relation to the shaft. shaft vertical with olecranon fossa facing posterior.
|
|
|
What are the joints of the shoulder complex?
|
Sternoclavicular SC
Scapulothoracic ST Acromiolavicular AC Glenohumeral GH |
|
|
What are the primary scapular elevators?
|
Upper trapezius
Levator scapula Rhomboids |
|
|
What are the primary scapular depressors?
|
Lower trapezius
Latissimus dorsi Pectoralis minor Subclavius |
|
|
What are the primary scapular upward rotators?
|
Serratus anterior
Upper trapezius Lower trapezius |
|
|
What are the primary scapular downward rotators?
|
Rhomboids
Pectoralis minor |
|
|
What are the primary scapular retractors?
|
Rhomboids
Middle trapezius |
|
|
What are the primary glenohumeral joint abductors?
|
Supraspinatus
Anterior deltoid Middle deltoid |
|
|
What are the primary glenohumeral joint flexors?
|
Anterior deltoid
Pectoralis major (clavicular head) Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii |
|
|
What are the primary glenohumeral joint adductors?
|
Teres major
Latissimus dorsi Pectoralis major |

