![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
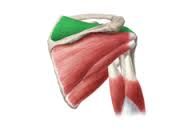
Supraspinatus
O: supraspinous fossa I: superior facets of greater tubercle of humerus A: initiates roll N: suprascapular nerve |
|
|
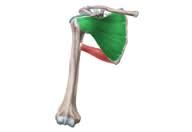
Infraspinatus
O: infraspinous fossa I: middle facets of greater tubercle of humerus A: lateral rotator and horizontal abduction of shoulder N: suprascapular nerve |
|
|
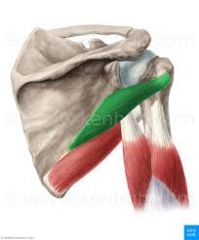
Teres Minor
O: axillary border of scapula I: inferior facets of greater tubercle of humerus A: lateral rotator and horizontal abduction of shoulder N: axillary nerve |
|
|
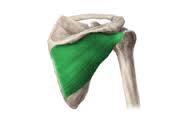
Subscapularis
O: subscapular fossa I: lesser tubercle of humerus A: medial rotator of shoulder N: subscapular nerve |
|
|
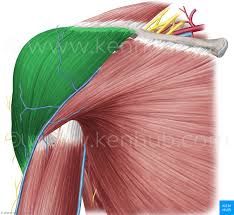
Anterior Deltoid
O: inferior aspect of 1/3 of clavicle I: deltoid tuberosity A: shoulder abduction, flexion, medial rotation, and horizontal abduction N: axillary nerve |
|
|
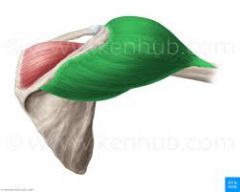
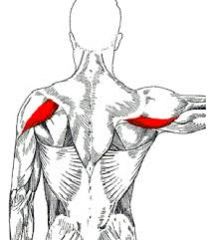
Middle deltoid
O: acromian I: deltoid tuberosity A: shoulder abduction N: axillary nerve |
|
|
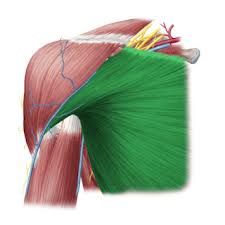
Posterior Deltoid
O: spine of scapula I: deltoid tuberosity A: shoulder abduction, extension,lateral rotation, horizontal abduction N: axillary nerve |
|
|
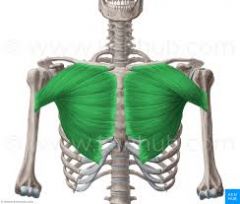
Pectoralis Major (clavicular portion)
O: inferior aspect of medial 2/3 of clavicle I: lateral lip of the bicipital groove A: shoulder adduction, horizontal ADD, internal rotation and flexion 0-60% N: lateral and medial pectoral nerve |
|
|
Pectoralis Major (sternal portion)
O: sternum, costal cartilage of first 6 ribs I: lateral lip of bicipital groove A: shoulder adduction, horizontal ADD, internal rotation and full flexion minus 60% N: lateral and medial pectoral nerve |
|
|
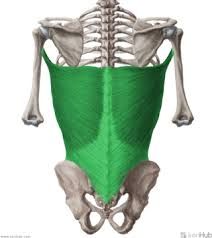
Latissimus Dorsi
O: SP T7-L5, posterior surface of sacrum, iliac crest, lower 3 ribs, and thoracolumbar fascia I: floor of bicipital groove and inferior angle of scapula A: primary shoulder extension, internal rotation of humerus, scapula depression N: thoracodorsal nerve |
|
|
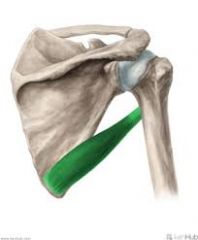
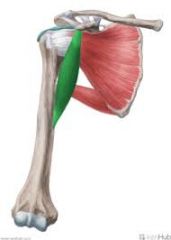
Teres Major
O: inferior angle of scapula I: medial lip of bicipital groove A: internal rotation of shoulder , shoulder extension and adduction N: subscapular nerve |
|
|
Coracobrachialis
O: coracoid process I: medial aspect of mid shaft of humerus A: shoulder adduction, and assist in shoulder flexion N: musculocutaneous nerve |
|
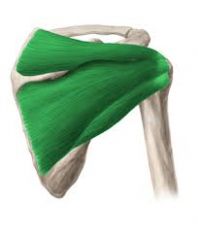
4 muscles of the rotator cuff (SITS)
|
- supraspinatus
- infraspinatus - teres minor - subscapularis |
|
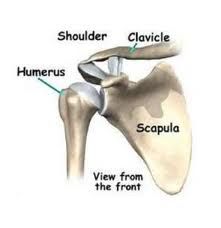
glenohumeral joint
|
faces anterior lateral, with superior rotation, this allows the humerus to rest in the glenoid cavity. The humerus must be able to passively sit in the glenoid cavity.
-MUST SIT PASSIVELY |
|
|
POS- plane of the scapula
|
pos-45 degrees
scaption |
|
|
joint motions/ degrees
|
flexion/ext : 0-180 degrees
ab/ad duction: 0-180 degrees medial/ internal rot: 0-70 degrees lateral/ internal rot: 0-90 degrees horizontal adduction: 0-30 degrees horizontal abduction: 0-120 degrees |
|
|
reversal movement of the lats
|
hip hiker
|
|
|
contractions for glenohumeral movement
|
1. brain signal
2.supraspinatus roll 3.deltoids lift arm 4.infraspinatus and teres minor take humerus and pull in posterior/inferior 5.trapezius upwardly rotate the scapula 6.serratus anterior, assist in elevation and protract to reach. |
|
poor resting posture of the scapula could be described as...
|
slightly protracted position
|
|
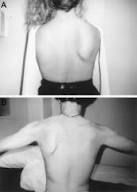
traction ischemia of the rot. cuff
|
cutting off blood , because arm is to close to the body
especially in supraspinatus |
|
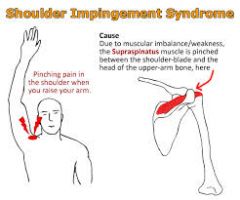
impingment syndrome
|
activities that require forceful overhead actions.
fixed position exercises like military presses. these actions do not allow proper rolling of the humerul head |

