![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the bones of the upper extremity
|
-shoulder -thumb -upper arm -scapula -elbow -clavicle -forearm -sternum -wrist -ribcage -hand -humerus -digits -ulna -forefingers -radius |
|
|
What is the function of the upper extremity and shoulder
|
-UE is not a weight bearing limb -allow movement of the entire UE -shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the body |
|
|
Describe the shoulder complex
|
-all the structures involved with movement of the shoulder, scapula, clavicle, sternum, humerus, and ribcage.
|
|
|
What joints comprise the shoulder complex
|
-sternoclavicular joint -arcomicalcalvicular joint -glenohumeral joint -scapulothoracic articulation |
|
|
Describe the shoulder joint
|
-glenohumeral joint -articulation between the scapula and the humerus |
|
|
Describe the shoulder girdle
|
-scapula, clavicle, sternum -sternoclavicular joint and the aromialcalviuclar joint |
|
|
When at rest where does the scapula lay?
|
-between T2 and T7
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following on a diagram -superior angle -inferior angle -vertebral border -axillary border -spine -coracoid process -acromion process -glenoid fossa -supraspinous fossa -subscapular fossa -infraglenoid tubercle -supraglenoid tubercle -glenoid labrum |
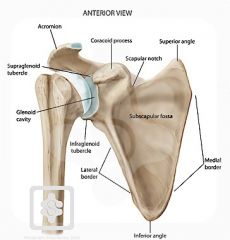
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following on a diagram-superior angle -inferior angle-vertebral border -axillary border-spine -coracoid process-acromion process -glenoid fossa-supraspinous fossa -subscapular fossa-infraglenoid tubercle -supraglenoid tubercle-glenoid labrum
|
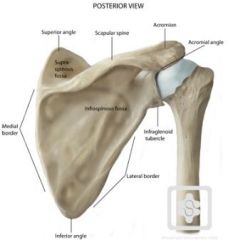
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following on a diagram -sternal end -acromial end -body |
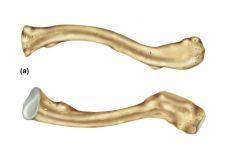
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following on a diagram -manubrium -body -xiphoid process |
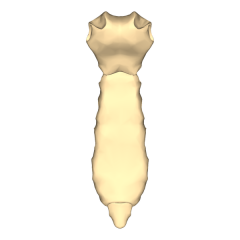
|
|
|
Define and be able to identify the following: -sternoclavicular joint |
-articulation between the sternum and the clavicle -classified as synovial joint, plane joint -motion is gliding -three planes of motion |
|
|
Identify the ligaments of the sternoclavicular joint
|
-articular disc -sternoclavicular ligament -costoclavicular ligament -interclavicular ligament |
|
|
Describe the articular disc
|
-freedom of movement there -primarily there for shock absorption -promotes movement |
|
|
Describe the sternoclavicular ligament
|
-ligament where the sternum meets the clavicle
|
|
|
Describe the costoclavicular ligament
|
-ligament that runs from the clavicle down to the first rib
|
|
|
Describe the interclavicular ligament
|
-ligament that is between the two clavicles over the top of the sternum
|
|
|
Define and be able to identify the following: -acromioclavicular joint |
-articulation between the scapula and the clavicle -classified as synovial joint, plane joint -motion is gliding -motion in all three planes |
|
|
What are the ligaments of the acromioclavicular joint
|
-acromioclavicular ligament -coracoclavicular ligament -coracoaromial ligament |
|
|
Describe the acromioclavicular ligament
|
-ligament that goes over the articulation of the acromion process and the lateral end of the clavicle
|
|
|
Describe the coracoclavicular ligament
|
-ligament that runs from the coracoid process of the scapula to the clavicle
|
|
|
Describe the coracoaromial ligament
|
-ligament that runs from the coracoid process of the scapula to the acromion process of the scapula
|
|
|
Describe the movement that occurs in the shoulder girdle in the movement of elevation and depression
|
-scapula goes up and down (linear movement) -can be performed without any movement of the humerus |
|
|
Describe the movement that occurs in the shoulder girdle in the movement of protraction and retraction
|
-shoulder and scapula goes forward and backward -scapular abduction and adduction -linear movement |
|
|
Describe the movement that occurs in the shoulder girdle in the movement of upward and downward rotation
|
-inferior angle of scapula moving up and away for upward rotation -inferior angle of scapula moving down and in for downward rotation -rotary movement |
|
|
Define scapulahumeral rhythm
|
-relationship between the shoulder joint and shoulder girdle -first 30 degrees is pure glenohumeral joint motion -past 30 degrees there is a 2 to 1 ratio the scapula must upwardly rotate 1 degree for every 2 degrees of shoulder abduction/flexion |
|
|
What are the muscles that move the scapula
|
-trapezius -levator scapulae -rhomboids -serratus anterior -pectoralis minor |
|
|
What is the origin of the upper trapezius
|
-occipital bone
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the upper trapezius
|
-outer third of clavicle, acromion process
|
|
|
What is the action of the upper trapezius
|
-scapular elevation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the upper trapezius
|
-spinal accessory (cranial nerve XI)
|
|
|
What is the origin of the middle trapezius
|
-spinous processes of C7 through T3
|
|
|
What is the action of the middle trapezius
|
-scapular retration
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the middle trapezius
|
-spinal accessory (cranial nerve XI)
|
|
|
What is the origin of the lower trapezius
|
-spinous processes of the middle and lower thoracic vertebrae
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the lower trapezius
|
-base of the scapular spine
|
|
|
What is the action of the lower trapezius
|
-scapular depression and upward rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the lower trapezius
|
-spinal accessory (cranial nerve XI)
|
|
|
What is the origin of the levator scapulae
|
-transverse processes of first four cervical vertebrae
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the levator scapulae
|
-vertebral border of scapula between the superior angle and the spine
|
|
|
What is the action of the levator scapulae
|
-scapular elevation and downward rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the levator scapulae
|
-third and fourth spinal nerves and dorsal scapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the rhomboids
|
-spinous processes of C7 through T5
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the rhomboids
|
-vertebral border of scapula between the spine and inferior angle
|
|
|
What is the action of the rhomboids
|
-scapular retraction, elevation, and downward rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the rhomboids
|
- dorsal scapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the serratus anterior
|
-lateral surface of the upper eight ribs
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the serratus anterior
|
-vertebral border of the scapula, anterior surface
|
|
|
What is the action of the serratus anterior
|
-scapular protraction and upward rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the serratus anterior
|
-long thoracic nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the pectoralis minor
|
-anterior surface, third through fifth ribs
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the pectoralis minor
|
-coracoid process of the scapula
|
|
|
What is the action of the pectoralis minor
|
-scapular depression, protraction, downward rotation, and tilt
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the pectoralis minor
|
-medial pectoral nerve
|
|
|
Be able to identify on a diagram the following: -head -neck -shaft -grater tubercle -lesser tubercle -deltoid tuberosity -bicipital groove |
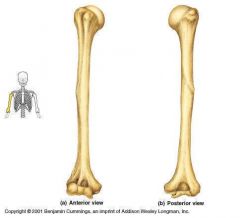
|
|
|
Name the ligaments and bursae of the glenohumeral joint
|
-joint capsule -glenohumeral ligament -coracohumeral ligament -subdeltoid bursa -subaromial bursa |
|
|
Describe the joint capsule of the glenohumeral joint
|
-goes from the glenoid fossa to the neck of the humerus
|
|
|
Describe the glenohumeral ligament of the glenohumeral joint
|
-ligament attaches to the capsule, capsular ligament
|
|
|
Describe the coracohumeral ligament of the glenohumeral joint
|
-ligament that runs from the coracoid process of the scapula to the humerus -provides a roof for the articulation |
|
|
Describe the subdeltoid bursa of the glenohumeral joint
|
-below the deltoid -found between the deltoid muscle and the joint capsule |
|
|
Describe the subaromial bursa of the glenohumeral joint
|
-below the acromion process -found between the acromion process and the coricoacromial ligament and joint capsule |
|
|
What are the muscles that comprise the rotator cuff
|
-subscapularis -supraspinatus -infraspinatus -teres minor |
|
|
What are the average range of movement of the glenohumeral joint WRT flexion
|
0-180 degrees of flexion
|
|
|
What is the average range of movement of the glenohumeral joint WRT extension
|
0-45 degrees of extension
|
|
|
What is the average range of movement of the glenohumeral joint WRT abduction
|
0-180 degrees of abduction
|
|
|
What is the average range of movement of the glenohumeral joint WRT medial/lateral rotation
|
90 degrees for each movement
|
|
|
What are the muscles that move the shoulder/arm
|
-deltoid -coracobrachialis -supraspinatus -pectoralis major -latissimus dorsi -teres major -infraspinatus -teres minor -subscapularis |
|
|
What is the origin of the anterior deltoid
|
-lateral third of the clavicle
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the anterior deltoid
|
-deltoid tuberosity
|
|
|
What is the action of the anterior deltoid
|
-shoulder abduction, flexion, medial rotation, and horizontal adduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the anterior deltoid
|
-axillary nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the middle deltoid
|
-acromion process
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the middle deltoid
|
-deltoid tuberosity
|
|
|
What is the action of the middle deltoid
|
-shoulder abduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the middle deltoid
|
-axillary nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the posterior deltoid
|
-spine of scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the posterior deltoid
|
-deltoid tuberosity
|
|
|
What is the action of the posterior deltoid
|
-shoulder abduction, extension, hyperextension, lateral rotation, horizontal abduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the posterior deltoid
|
-axillary nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the supraspinatus
|
-supraspinous fossa of the scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the supraspinatus
|
-greater tubercle of the humerus
|
|
|
What is the function of the supraspinatus
|
-shoulder abduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the supraspinatus
|
-suprascapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the pectoralis major
|
-medial third of clavicle, sternum, costal cartilage of the first 6 ribs
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the pectoralis major
|
-lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of the pectoralis major
|
-shoulder flexion (first 60 degrees), shoulder extension (first 60 degrees), shoulder adduction, medial rotation, horizontal adduction
|
|
|
What is innervation of the pectoralis major
|
-lateral and medial pectoral nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the latissimus dorsi
|
-spinous processes of T7 through L5 -posterior surface of sacrum, iliac crest, and lower three ribs |
|
|
What is the insertion of the latissimus dorsi
|
-medial floor of bicipital groove of humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of the latissimus dorsi
|
-shoulder extension, adduction, medial rotation, hyperextension
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the latissimus dorsi
|
-thoracodorsal nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of teres major
|
-axillary border of scapula near the inferior angle
|
|
|
What is the insertion of teres major
|
-crest below lesser tubercle inferior to the latissimus dorsi muscle attachment
|
|
|
What is the action of teres major
|
-shoulder extension, adduction, and medial rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of teres major
|
-lower subscapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of infraspinatus
|
-infraspinous fossa of scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of infrapspinatus
|
-greater tubercle of humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of infraspinatus
|
-shoulder lateral rotation, horizontal abduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of infraspinatus
|
-suprascapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of teres minor
|
-axillary border of scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of teres minor
|
-greater tubercle of humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of teres minor
|
-shoulder lateral rotation, horizontal abduction
|
|
|
What is the innervation of teres minor
|
-axillary nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of subscapularis
|
-subscapular fossa of the scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of subscapularis
|
-lesser tubercle of the humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of subscapularis
|
-shoulder medial rotation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of subscapularis
|
-upper and lower subscapular nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of coracobrachialis
|
-coracoid process of the scapula
|
|
|
What is the insertion of coracobrachialis
|
-medial surface of the humerus near the midpoint
|
|
|
What is the action of coracobrachialis
|
-stabilizes the shoulder joint
|
|
|
What is the innervation of coracobrachialis
|
-musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
What are the bones that make up the elbow complex
|
-humerus -ulna -radius |
|
|
Be able to identify the following bony landmarks on the humerus: -head -neck -shaft -greater tubercle -lesser tubercle -deltoid tuberosity -bicipital groove -trochlea -capitulum -medial epicondyle -lateral epicondyle -lateral supracondylar ridge -olecranon fossa |
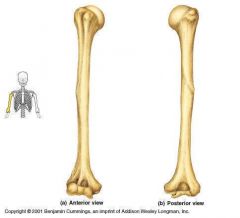
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following bony landmarks on the ulna: -olecranon process -trochlear notch -coranoid process -radial notch -ulnar tuberosity -styloid process |
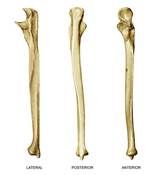
|
|
|
Be able to identify the following bony landmarks on the radiuis: -head -radial tuberosity -styloid process |
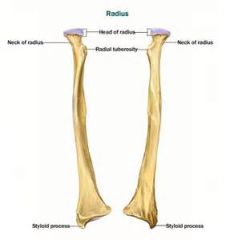
|
|
|
Describe the elbow joint
|
-trochlea of humerus articulates with trochlear notch of ulna. -head of radius articulates with the capitulum of humerus -uniaxial joint (flexion and extension) |
|
|
How many degrees of flexion does the elbow joint have?
|
-145 degrees
|
|
|
Describe the radioulnar joint
|
- articulation between the radius and the ulna -articulates at both ends (proximally and distally) -proximal end= head of radius pivots within the radial notch of ulna -distal end= ulnar notch of radius rotates around the head of the ulna -uniaxial, pivot joint (pronation and supination) |
|
|
How many degrees of pronation does the radioulnar joint have?
|
-80 degrees
|
|
|
How many degrees of supination does the radioulnar joint have?
|
-90 degrees
|
|
|
Define carrying angle of the elbow
|
-angle between the longitudinal axis of humerus and the forearm -angle tends to be greater in women than in men |
|
|
What is the normal carrying angle of the elbow for men?
|
-5 degrees |
|
|
What is the normal carrying angle of the elbow for women?
|
-10 to 15 degrees
|
|
|
Define cubitus varus (varum)
|
-gunstock deformity -when the carrying angle is decreased |
|
|
Define cubitus valgus (valgum)
|
-when the carrying angle is increased
|
|
|
List the ligaments of the elbow complex
|
-medial collateral ligament -lateral collateral ligament -annular ligament -interosseous membrane |
|
|
Identify the medial collateral ligament
|
-medial aspect of joint -triangular shaped ligament -from medial epicondyle of humerus to the medial side of the elbow |
|
|
Identify the lateral collateral ligament
|
-lateral aspect of joint -triangular shaped ligament -from lateral epicondyle of humerus to lateral side of ulna |
|
|
Identify the annular ligament
|
-attaches anteriorly and posteriorly to the radial notch of the ulna -holds the radius in place against the ulna |
|
|
Identify the interosseous membrane
|
-flat, tough fiberous membrane that holds the radius and ulna together
|
|
|
Identify the joint capsule of the elbow complex
|
-attaches around the distal end of the humerus and encompasses the trochlea and capitulum
|
|
|
Describe the brachialis
|
-underneath the biceps muscle -crosses one joint -attaches to ulna -forearm is pronated when using this muscle |
|
|
What is the origin of the brachialis
|
-distal half of humerus, anterior surface
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the brachialis
|
-coronoid process and ulnar tuberosity of the ulna
|
|
|
What is the action of the brachialis
|
-elbow flexion
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the brachialis
|
-musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
Describe the biceps brachii
|
-two heads -superficial muscle of arm -crosses two joints (shoulder and elbow) -attaches to radius -forearm is supinated when using this muscle |
|
|
What is the origin of the biceps brachii
|
-long head: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula (lateral and sits within the bicipital groove) -short head: coracoid process of scapula (medial) |
|
|
What is the insertion of the biceps brachii
|
-radial tuberosity of radius
|
|
|
What is the action of the biceps brachii
|
-elbow flexion -forearm supination |
|
|
What is the innervation of the biceps brachii
|
-musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
Describe the brachioradialis
|
-in forearm -attaches to distal part of humerus and to radius -forearm is neutral when using this muscle |
|
|
What is the origin of the brachioradialis
|
-lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the brachioradialis
|
-styloid process of the radius
|
|
|
What is the action of the brachioradialis
|
-elbow flexion
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the brachioradialis
|
-radial nerve
|
|
|
What are the muscles that causes flexion for the elbow joint
|
-brachialis -biceps brachii -brachioradialis |
|
|
Describe the triceps brachii
|
-crosses two joints -one head attaches to the scapula and the other two do not |
|
|
What is the origin of the triceps brachii
|
-long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scacpula -lateral head: inferior to greater tubercle on posterior humerus -medial head: posterior surface of humerus |
|
|
What is the insertion of the triceps brachii
|
-olecranon process
|
|
|
What is the action of the triceps brachii
|
-elbow extension
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the triceps brachii
|
-radial nerve
|
|
|
What are the muscles that causes extension in the elbow joint
|
-triceps brachii
|
|
|
Describe the pronator teres
|
-proximal -longer in length |
|
|
What is the origin of the pronator teres
|
-medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of ulna
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the pronator teres
|
-lateral aspect of radius at its midpoint
|
|
|
What is the action of the pronator teres
|
-forearm pronation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the pronator teres
|
-median nerve
|
|
|
Describe the pronator quadratus
|
-square shaped -distal forearm |
|
|
What is the origin of the pronator quadratus
|
-distal one fourth of ulna
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the pronator quadratus
|
-distal one fourth of radius
|
|
|
What is the action of the pronator quadratus
|
-forearm pronation
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the pronator quadratus
|
-median nerve
|
|
|
What are the muscles that causes pronation in the forearm
|
-pronator teres -pronator quadratus |
|
|
Describe the supinator
|
-lateral aspect of elbow joint on radial side -supinates along with biceps brachii |
|
|
What is the origin of the supinator
|
-lateral epicondyle of humerus and adjacent to ulna
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the supinator
|
-anterior surface of the proximal radius
|
|
|
What is the action of the supinator
|
-forearm supination
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the supinator
|
-radial nerve
|
|
|
What muscles causes supination in the forearm
|
-supinator -biceps brachii |

