![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
kinesiology Foundation for practice of physical rehab is composed what 3 components |
anatomy biomechanics and physiology |
|
|
Biomechanics |
uses principles of physics to quantitatively study how forces interact withing a living body |
|
|
Physiology |
branch of bio that studies the normal function of living organisms |
|
|
Kinematics |
branch of mechanics that describes the motion of a body without regard to the forces or torques that may produce the motion |
|
|
rectilinear |
straight line |
|
|
curvilinear |
curved line |
|
|
Rotation |
rigid body moves in a circular path around pivot point |
|
|
how much motion at axis during rotation |
motion of rotation is zero at the axis |
|
|
Kinetics |
Branch of mechanics that describe the effects of forces on the body |
|
|
osteoporosis |
brittle bone |
|
|
Stiffness X/Y |
stress / strain |
|
|
Viscoelastic |
physical properties associated with stress-strain curve curve as a function of time |
|
|
Creep |
progressive strain of a material exposed to a constant load over time |
|
|
vector |
magnitude and direction |
|
|
Torque |
product of force X moment arm |
|
|
Moment Arm |
perpendicular distance between axis of rotation and force |
|
|
Static Rotary Equilibrium |
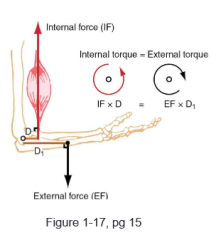
internal torque = External torque IF x D = EF x D1 |
|
|
Force produced with moment arm cause ____________ and produces _____________ |
torque, movement (Rotation) |
|
|
Force produced without a moment arm with will not cause a ____________ therefore no _________ and this type of force is important for ___________ |
Torque, rotation, stability |
|
|
"Isos" means |
Equal |
|
|
During _____________ contraction internal torque exceeds external torque producing a ________ in the direction of the __________ of the activated muscle |
Concentric, rotation, pull |
|
|
External torque exceeds internal torque with __________ muscle action.The joint ___________ in direction of the ___________ ____________ torque |
eccentric, rotates, larger external |
|
|
_________ or more muscle produce _______ in ___________ directions, yet resultant ___________ is in the _________ rotary direction |
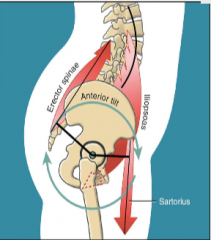
Two, forces, different, torque, same |
|
|
Internal and External forces typically act in similar linear directions, producing torques in ____________ rotary directions. Forces are on ____________ sides of the center of rotation in a ____ class lever |
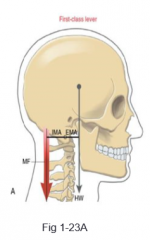
opposite, opposite, 1st |
|
|
Axis of rotation located at one end of a bone ______________ forces greater than the ____________ force. Forces are on the same side of the center of rotation and the ___________ force is closer to the center of rotation. This is a ________ class lever |
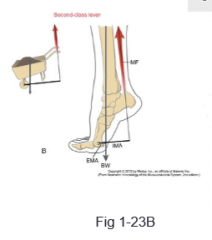
internal, external, external, 2nd |
|
|
Axis of rotation at ___________ end of a bone.____________ force has greater leverage(____________). Forces are on the _________ side of center of rotation (COR), and the muscle force is _________ to the COR |
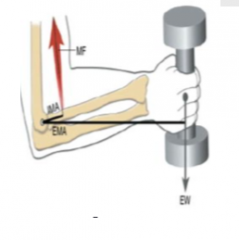
one, External, moment arm, same, closer |
|
|
Ratio of internal moment arm and external moment arm is ___________ 1st class lever_________ 2nd class lever ________ 3rd class lever_________ |
Mechanical advantage MA= IMA/EMA equal to, less than or greater than 1 greater than 1 less than 1 |
|
|
Work = |
W=F x D |
|
|
With 3rd class levers ________ internal forces are generated for small load activities |
large |

