![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What surrounds each kidney? two layers...
|
Kidneys are surrounded by the RENAL CAPSULE and that is surrounded by the RENAL FAT PAD.
|
|
|
Where in the body do you find the Kidneys
|
Either side of the Vertebral Column behind the Peritoneum (lining of the abdominal cavity)
|
|
|
What is the Hilum and where would you find it?
|
On the Medial side of the kidney , its where the renal artery and nerves enter , and the renal vein and ureter exit the kidney
|
|
|
What main arteries and veins link to the kidneys?
|
The Left and Right RENAL ARTERIES AND VEINS
|
|
|
The urinary system consists of 4 Main components?
|
Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder and Urethra.
|
|
|
The Hilum opens into a cavity in the Kidney called the...? this cavity follows on to the.... then into several funnel shaped...
|
Renal Sinus. Within the Renal Sinus the urinary channel is enlarged to form the Renal Pelvis. Funnel shaped structures called Calyces extend from the pelvis to the kidney tissue.
|
|
|
When existing the kidneys, the urine flows back out the hilum and into the what??
|
The Ureters. Left and Right
|
|
|
In regards to the kidney, there is two main tissue areas inside the kidney?
|
Inner - Medulla Is the Renal Pyramids (coneshaped)
outer - Cortex ( the base of the pyramids extend into the cortex) |
|
|
Name or draw the parts to the Nephron.
|
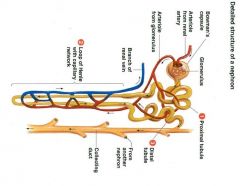
|
|
|
Inner layer of the Bowman's Capsule surrounds the Glomerulus what specialised cells would you find in there? What do they do
|
Podocytes. Pores in their walls and gaps between them. The Podocytes and the Walls of the Glomerular Capillaries form Filteration Membrane
|
|
|
Branching off the Abdominal Aorta is the RENAL _________, from this they go to inter______ arteries, then to the _______ Arteries then to the ________ arteries. then to the _______ Arterioles. then go through the ____________.
|
1: Arteries
2: Interlobar 3: Arcuate Arteries 4:InterloBULAR Arteries 5: Afferent Arterioles 6: Glomerulus/Nephron |
|
|
The blood enters into the Glomarulus Capillaries via the Afferent Arterioles. it exists from the _________ Arterioles into the _____________ Capillaries, which surround the proximal, distal convoluted tubules and loop of Henle
|
1: Efferent Arterioles
2: Peritubular Capillaries |
|
|
Once the blood has been filtered through the Glomarulus and Peritubular capillaries it enters into the _____________ Veins which go to the _______ Veins, then into the _________ Veins then finally the _______ veins.
|
1 : Interlobular Veins
2: Arcuate Veins 3: Intelobular Veins 4: Renal Veins |
|
|
What do the Ureters do?
|
carries Urine from the Renal Pelvis to the Urinary Bladder.
|
|
|
URINARY BLADDER
What is made of? Where is it found? how much urine can it hold? |
Made of Transitional Epithelium tissue. Also has a muscular layer to force urine out.
It is found in the pevic cavity Holds up to 1 litre of urine |
|
|
Explain the two Sphincters relating to the bladder where are they found?
|
Internal Urinary Sphincter - smooth muscle (involuntary)
External Urinary Sphincter - Skeletal muscle (voluntary) surrounds the urethra as it extends to either the end of penis or vestibule anterior of vagina |
|
|
What is in urine?
3 organic waste products in urine? 5 excess ions found in urine? |
Urine is mostly water
contains Urea,Uric acid and creatine. Contains Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Bicarbonate and Hydrogen. |
|
|
What is...
FILTERATION percentage of plasma that flows through glomerulus that becomes filtrate (into the nephron for urine) |
Filteration is the movement of Plasma across the filtration membrane of the renal corpuscle.(blood cells and large molecules do not cross)
19% of plasma through the G, becomes filtrate. |
|
|
The formation of filtrate depends on the pressure difference called _______ , which forces fluid from the glomerular capillaries through the filteration membrane. more pressure means more _____. Cardiovascular shock man make pressure ____
|
Filteration Pressure
Filtrate (urine) Drop, meaning very minimal or no urine. |
|
|
What is Reabsoption? where? and what?
|
Absorption of substances from the tubule back to the blood.
Proximal convoluted Tubule - water(by osmosis), proteins,amino acids,glucose,soduim etc active transport ...Decending loop - Water Ascending loop - Sodium and chloride ions. |
|
|
Tubular Secretion
|
Secretion of substances into the tubule from the blood. active or passive. eg drugs and toxins
|
|
|
HORMONE MECHANISMS
Secreted by the posterior pituitary gland - regulates the amount of water reabsorption by the distal convoluted tubules &collecting duct to much = .... and to little = |
ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE
High levels- reabsorption increased -more concertrated urine.(effects from decreased blood pressure) Lower Levels - less urine concerntration(effects from alcohol, stops ADH being released) |
|
|
Secreted by the Adrenal Gland regulates the rate of active transport in distal portion of nephron and collecting duct.. what is the hormone?
if its present?? if its not?? |
ALDOSTERONE
Present - Soduim ions and chloride ions are actively absorbed from nephron not present - not actively absorbed. |
|
|
When blood pressure increase the Right Atruim cells secrete this.
what is it and what does it do? |
Atrial Natriuretic factors - reduces ability of the kidneys to concerntrate the urine, increasing urine volume.
|
|
|
symphathetic innervation is what?
|
causes constriction of the arteries to the kidneys causing decrease in urine production. e.g during shock or exercise.
|
|
|
What is Micturition Reflex?
|
urine movement stretches the bladder wall, causing the bladder to contract and the sphincters to relax, external sphincter is controlled by the brain for "convenience".
|
|
|
Body Fluid Compartments? two types, explain?
|
intracellular fluid compartment - water,electrolytes inside the cell. 63% of body water.
Extracellular F.C. 37% of total body water, outside the cells inc. interstitial fluid,blood plasma, lymph vessel fluid. |
|
|
ROLES OF THE KIDNEY
1:___ 2:____ 3:Reg blood volume and pressure, reg plasma ion concentration, stabilizing blood pH, concervising nutrients |
1: Excretion - Removal of organic waste products from body fluid - co2, urea, ammonia
2:Elimination - Discharge of waste products (nitrogenous) into the environment 3: Homeostatic regulation of blood plasma |
|
|
What is Acidosis and the types and effects?
|
Acidosis - is blood pH below 7.35 cns malfunction, comatose. Respiratory-cannot eliminate enough CO2. Metabolic -excess acidic substance due to high metabolic rate or kidney failure in eliminating hydrogen ions in the urine.
|
|
|
What is Alkalosis and types and effects?
|
Blood pH above 7.45 causing Hyperexcitability of nervous system.can cause tetanic contractions &convulsions. Respiratory from hyperventilation. Metabolic From rapid elimination of hydrogen ions eg vomiting, or excess aldosterone from adrenal gland.
|
|
|
EFFECTTS OF AGING ON URINARY SYSTEM?
|
urine in babys is less concerntrated and incontence is normal, lack of control over sphincter. same in elderly. Elderly also change in porosity of the filter membrane (gradual decline in kidney function). bladder tone decreases with age
|
|
|
KIDNEY FUNCTIONS
|
-Maintain h2o balance in body and maintain osmolality of body fluids
- Maintain plasma volume -Excretion wastes - produce Renin -convert vitamin D into its active form |

