![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
133 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What the beverages are diuretics |
Tea coffee alcohol |
|
|
What is an artificial kidney and what is it used for |
Dialyzing machine that is used for dialysis. Used when the kidneys of a patient stops functioning |
|
|
Kidneys move where during deep inspiration |
Downward ~1 inch |
|
|
Components of urinary system |
2 kidneys 1 bladder 1 urethra 2 ureters |
|
|
Function of urinary system |
Excreting wastes Regulating blood composition |
|
|
Location of kidneys |
Lay in sagittal oblique plane in retroperitoneal cavity Located between 12 thoracic and 4 lumbar They lie asymetrical right is lower than left BC of liver |
|
|
Kidneys ureters and bladder are located |
In the Retroperitoneum |
|
|
What two muscles do the kidneys rest on |
Psoas and quadratus lumborum |
|
|
Each kidney is located ________ to the psoas and quadratus lumborum muscles |
Anterior |
|
|
Each kidney is located __________ to transverse abdominus muscle and liver/spleen |
Medial |
|
|
Length of kidneys range from |
9-12 cm |
|
|
Width of kidneys range from |
4-5 cm |
|
|
Height of kidneys range from |
2.5-3 cm |
|
|
Kidneys should have ____ cm in cortical thickness |
1cm |
|
|
Upper pole is the most _______ border of the kidney |
Superior |
|
|
Lower pole of kidney is the most ______ border of kidney and is more ________ than the upper pole |
Inferior Lateral |
|
|
Superior poles lie more |
Posterior medial |
|
|
Inferior poles lie more |
Anterior and lateral |
|
|
The kidney is composed of two distinct areas |
Renal sinus and the parenchyma Parenchyma holds the outer cortex and inner medullary pyramids |
|
|
The renal parenchyma is separated into cortex and medulla by the |
Arcuate vessels |
|
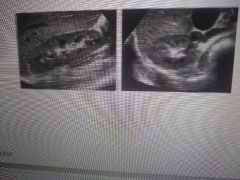
|
Longitudinal and transverse normal kidney |
|
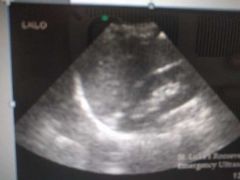
What muscle is seen here (bottom) |
Psoas |
|
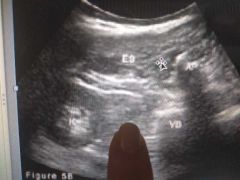
What muscle am I pointing at |
Psoas |
|
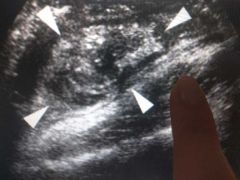
What muscle am I pointing at |
Psoas |
|
What muscle am I pointing at |
Quadratus lumborum |
|
What muscle am I pointing at |
Psoas |
|
What is arrow pointing at |
Quadratus lumborum muscle |
|
|
Where does Psoas muscle begin from |
Hilum of the kidneys |
|
|
Psoas lies (posterior/anterior)-(medial/lateral) to kidney |
Posterior medial |
|
|
Quadratus lumborum is located (posterior/anterior) to the lower (what fraction) to the kidney and courses (lateral/medial) to the psoas muscle |
Posterior 2/3 Lateral |
|
|
Which is the deepest later of Muscles located posteriolateral to each kidney |
Transverse abdominus muscle |
|
|
Three outer layers of a kidney |
True capsule Perirenal fat Gerota's fascia |
|
|
____________ or fibroid capsule is the most _______ layer of the outer kidney layers |
True capsule Most inner |
|
|
Which layer surrounds the true capsule |
Perirenal fat - layer of fat |
|
|
What does the gerota's fascia enclose |
Adrenal gland Kidney And perirenal fat |
|
|
Outer layer of the kidney |
Gerota's fascia |
|
|
What is the gerota's fascia surrounded by |
Pararenal fat - most superficial of kidney covering and forms part of the Retroperitoneal fat |
|
|
Pararenal fat |
most superficial of kidney covering and forms part of the Retroperitoneal fat |
|
|
Renal medulla Shape Contains |
Shaped like a pyramid Henle loop and collecting tubules |
|
|
Renal cortex: What is it What does it contain |
Outer layer Contains Bowman capsule Malphigian corpuscles and proximal/distal convoluted tubules |
|
|
Renal pelvis: Shape Location What happens here |
Funnel shaped Behind renal medulla Urine flows into here through minute openings to ureters
|
|
|
Renal hilum contains |
Renal artery Renal vein Lymphatics Ureter |
|
|
What is the collecting system of the kidneys |
Minor and major calyces |
|
|
Minor calyces How many per kidney It's function |
7-13 per kidney Receives urine from pyramid Forms border of renal sinus |
|
|
Major calyces How many per kidney Function |
2-3 Receives urine from minor calyces and convey urine to the renal pelvis |
|
|
Major calyces are also known as |
Funnel shaped tubes (infundibulum)- which connect minor calyx to renal pelvis |
|
|
How are the renal sinus echoes produces |

|
|
|
The upper end of the ureter divided into 2 or 3 ____________, each of which divided into 2 or 3 _____________ which ends in the pyramids |
Major calyces Minor calyces |
|
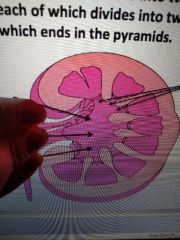
What's this |
Major calyces |
|
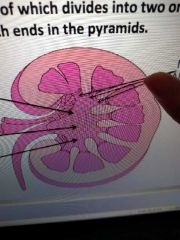
What's this |
Minor calyces |
|
|
Ureters |
Retroperitoneal structure that leave kidney carrying urine to bladder |
|
|
________________ are lateral branches of the abdominal aorta that are located just ( inferior/superior) to SMA |
Renal arteries Inferior |
|
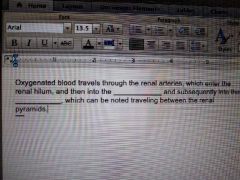
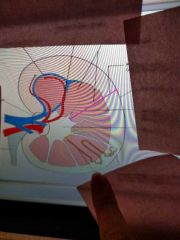
Renal vasculature: |
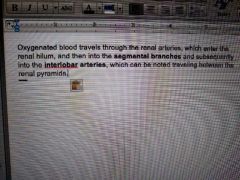
|
|
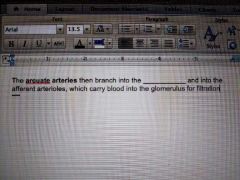
|
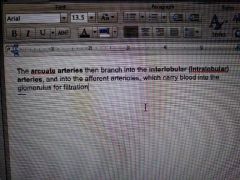
|
|
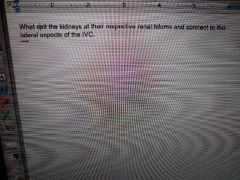
|
Renal Veins |
|
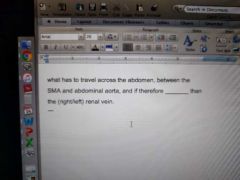
|
Left renal vein Longer Right |
|
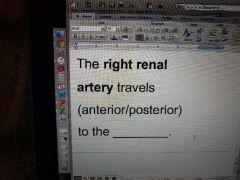
|
Posteriorly IVC |
|
|
Which renal artery is longer |
Right renal Artery |
|
|
Segmental artery after entering the renal hilum it divides into 4-5 segmental arteries. Does it have high or low resistance blood flow |
Low resistance |
|
|
Interlobar artery is a branch of segmental artery that courses alongside the renal pyramids. Does it have high or low resistance blood flow |
Low |
|
|
Arcuate artery: boundary between cortex and medulla. Branch off the interlobar artery located at base of the medulla What kind of blood resistance blood flow does it have |
Low |
|
|
Arterial supply to kidney is provided by what structures |
Renal Artery Testicular or ovarian artery Superior vesical artery |
|
|
Right renal artery may be visualised where |
Posterior to the IVC |
|
|
How are renal arteries best visualized |
Transverse axis |
|
|
What's the most helpful landmark for localizing renal arteries |
SMA |
|
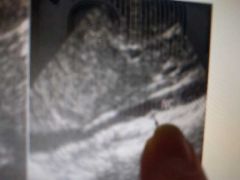
What's that dot |
Right renal artery |
|
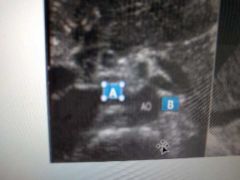
A? B? |
RRA LRA |
|
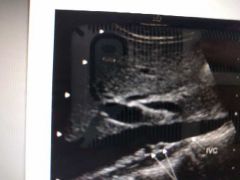
Two dots? |
Duplicate RRA |
|
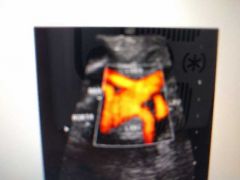
What's this |
Duplicate RRA |
|
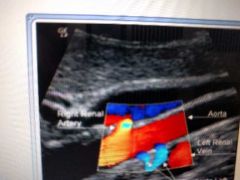
Blue? |
Duplicate left renal arteries |
|
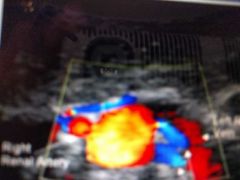
Blue on right side |
Duplicate left Renal arteries |
|

Two red lines |
Duplicate renal arteries |
|
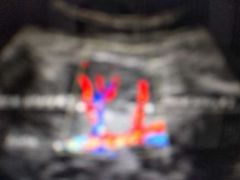
|
Duplicate renal arteries |
|

? |
Triplicate renal arteries |
|

|
Triplicate renal arteries |
|
|
RRV courses _________ to the RRA |
Anteriorly |
|
|
LEFT renal vein is (anterior/posterior) to the aorta and (anterior/posterior) to the SMA |
Anterior Posterior |
|
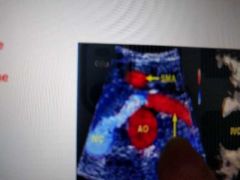
What's this |
LEFT renal Vein |
|

Bottom arrow |
LEFT renal vein |
|
|
What's the nutcracker phenomenon |
Aorta- LRV- SMA
The compression of the LEFT renal vein between aorta and SMA with impaired blood outflow often accompanied by distention of the distal portion of the vein. |
|
|
LRV connects to the____ |
IVC |
|
|
Ways to evaluate urinary system |
US IVP intravenous pyelogram NCCT -noncontrast computed tomography MRI |
|
|
Ultrasound used on kidney not just for masses but also.... |
Perirenal fluid collections like hematoma or abscess Determine Renal size and parenchymal detail Detecting enlarged ureters and hydronephrosis |
|
|
Indication for kidney US exam |

|
|
|
Patient preparation |
Nothing by mouth generally If bladder distended from rehydration the INTRARENAL COLLECTING SYSTEM also will become distended Some advocate fasting 6 hours- limit bowel gas |
|
|
Dilation of the collecting system had been noted in ________ |
Pregnant patients... Right kidney is generally involved with mild degree of hydronephrosis.. Goes back to normal after delivery |
|
|
Neonatal and pediatric kidneys may appear |
Lobulated Have prominent renal pyramids And or Subtle sonographic distinctive between renal cortex and sinus |
|
|
Normal adult kidneys Sonographic appearance? |
Elliptical in shape - longitudinal plane Rounded in transverse Less echogenic than the liver and spleen (or isoechoic)
|
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Renal capsule appearance |
Well defined echogenic line surrounding the kidney |
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Renal cortex appearance |
Fine mod/medium to low level echogenicity
Hypoechoic or isoechoic to liver/spleen |
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Medulla appearance |
Hypoechoic may appear anechoic |
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Columns of Berlin appearance |
Moderated medium to low echogenicity |
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Renal sinus |
Hyperechoic ... Most echogenic |
|
|
In normal adult kidneys: Arcuate vessels |
Small echogenic foci at corticomedullary junction |
|
|
Cortical thickness... If less than one cm...? |
Cortical thinning |
|
|
Cortical thickness minimum one cm... |
Normal |
|
|
Best way to evaluate kidneys |
Right: through liver Left: through spleen |
|
|
Patient position for kidney US |
Spine or decubitus |
|
|
Renal parenchyma should be compared to |
Spleen and liver parenchyma |
|
|
Technical aspects: High/low resolution, real time sector scanners should be used |
High |
|
|
Technical aspects: What is a high freq abdominal transducer most helpful in improving visualization of posterior acoustic shadowing add it is in the case of what |
Stones without shadow I know horrible question |
|
|
What should be used to routinely evaluate genitourinary tract stones |
Harmonic imaging |
|
|
Best position to place patient to evaluate renal size |
Decubitus coronal |
|
|
Bladder is a |
Muscular bag |
|
|
How many openings does the bladder have |
3 |
|
|
What is produced continuously and accumulates in the bladder until the increased pressure simulated the organs nervous receptors |
Urine |
|
|
Urethra is a ______ tube that passes from the anterior part of the urinary bladder to the outside of the body |
Membranous |
|
|
Is the urethra routinely visualized by ultrasound |
No |
|
|
How is bladder best visualized |
Moderately filled |
|
|
Post void bladder is scanned In __ planes.. Explain |
2 Anteriorposterior and transverse |
|
|
When it comes to the bladder a residue of less than __________ of urine is considered normal in an adult |
Less than 20 cc or ml |
|
|
Best modality of imaging the bladder |
Cystoscopy - usually used to examine bladder because it can diagnose early neoplasms |
|
|
What position used to demonstrate calculi movement |
Right or left decubitus |
|
|
Transabdominal ultrasound allows for visualization of most bladder lesions ______ than 5mm |
Greater |
|
|
US on bladder is performed with what kind of bladder |
Distended |
|
|
Bladder: Proper TCG allows for minimization of anterior wall_____ |
Reverberations |
|
|
How are ureteral Jets identified |
Doppler color |
|
|
When ureter is dialated it is best visualized in what angle |
Coronal- oblique with kidney as an acoustic window |
|
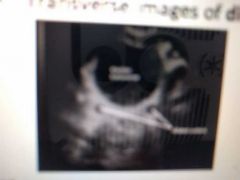
What is this |
Ureteric orifices (dilated) |
|
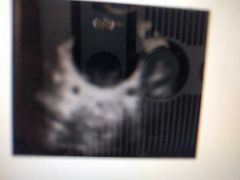
|
Ureteric orifices of Dilated ureters in transverse |
|

|
Ureter |
|
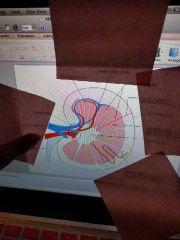
|
Renal artery |
|

|
Renal vein |
|
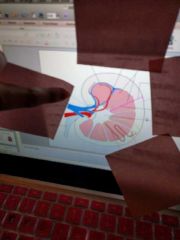
|
Renal hilus |
|
|
Interlobular vein |
|
Points to red |
Interlobular artery |
|
|
Renal pyramids |
|

|
Kidney cortex |
|

|
Renal capsule |
|

|
Medulla |
|
|
Pelvis renal |
|

|
Nephron |
|
|
Collecting duct |

