![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
154 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
1. The Stone Breakers
2. Courbet 3. poor workers, comments on class. 4. Realism 5. flat |
|

|
1. The Third Class Carriage,
2. Daumier 3. Realism 4. caricaturist 5. lithography 6. "lonely crowd" |
|

|
1. Luncheon on the Grass
2. Manet Realism 3. known prostitute, not myth or exotic 4. Realism 5. no perspective |
|

|
1. Olympia
2. Manet Realism 3. no perspective 4. We are included 5. Cat, flower and necklace = sex 7. power, position, class (wealthy enough to have a servant), known prostitute. 8. Realism 10. Manet was a flaneur |
|

|
Woman Hopping
Muybridge 3. replaced sketch book 4. created multiple points of view 5. saved cost of models |
|

|
1. Horse Galloping
2. Muybridge 3. Proved that all four of a horse feet are off the ground at once when it gallops 4. Used 12 cameras 5. Degas used |
|

|
1. Blessed art thou Among Women
2. Kasebier 3. Pictoralist: dreamlike, painterly pictures 4. imitate the dominate paradigm of painting to gain legitimacy. 5. religious iconography 6. entrance into the world/independence 7. religion in every day realism 8. realism with idealism 9. radical form: women in white not realistic she blends in - pics are were before documents of reality 10. radical content: Hail Mary |
|

|
1. City of Ambition
2. Steiglitz 3. A Pictoralist: dreamlike, painterly pictures 4. allowed snow, steam and fog to upstage the the buildings 5. supported by kodak, experimented, legitimized photography in american 6. blurry emphasized simplistic shapes and abstraction. |
|

|
1. The Orchestra
2. Degas Realism 3. cropping- Japonisme. 4. artist was a flaneur 5. artist cut to increase crop 6. sporadic brushwork = tutus movement |
|

|
1. On the Bank of the Seine
2. Monet Impressionism 3. plein-air (outdoors) 4. didn't add oil to his paint to keep it chalky 5. complementary colors |
|

|
1. The Gare St Lazare: arrival of a Train
2. Monet Impressionism 3. Made 10 paintings of this scene at different times for different light used hue modeling. 4. Brushwork creates a blurry, pulsating world 5. artist trying to capture the rapid changes of industrialization. |
|

|
1. The Child's Bath
2. Cassatt Impressionism 3. the overhead viewpoint = Japanese 4. sanctified the roll of mothers by depicting them as Madonna and Child. 5. reflected the artist's interest in the importance of women in society 6. regular bathing was only recently becoming the custom |
|

|
1. Mr. and Mrs. I.N. Phelps Stokes
2. Sargent Realism 3. art history 4. New woman 5. American nouveau riche = non-conventional |
|

|
1. Eiffel Tower (image 1 of 2)
2. Eiffel 3. didn't hide materials used to make 4.1889 Paris International Exposition 5. Bldg techniques same as for bridge pylon 6. twice the height of any structure then in Paris |
|

|
1. Eiffel Tower (image 1 of 2)
2. Eiffel 3. didn't hide materials used to make 4.1889 Paris International Exposition 5. Bldg techniques same as for bridge pylon 6. twice the height of any structure then in Paris |
|
|
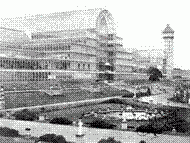
1. Crystal Palace (image 1 of 2)
2. Paxton 3.ferrovitreous: cast iron and glass. 4. shopping mall and beginning of consumer capitalism 5. international trade fair. |
|

|
1. Crystal Palace (image 1 of 2)
2. Paxton 3.ferrovitreous: cast iron and glass. 4. shopping mall and beginning of consumer capitalism 5. international trade fair. |
|

|
1. Brooklyn Bridge (image 1 of 2)
2. Roebling 3. America's Arch of Triumph 4. Gothic Revival facade hides totally modern design 5. cables evoke cubism design |
|

|
1. Brooklyn Bridge (image 1 of 2)
2. Roebling 3. America's Arch of Triumph 4. Gothic Revival facade hides totally modern design 5. cables evoke cubism design |
|

|
1. A Sunday on La Grande Jatte
2. Seurat - Post-Impressionism 3 6 x 10 scale = history paintings 4. pointillism = dots of pure color, eye mixes 5. Realism = middle class leisure |
|

|
1. A Still Life with Apples
2. Cezanne - Post Impressionism 3. Post Impressionist: rejected the requirements of Realism & used myth and dreams in their work. 4. No collective vision/style 5. flat/crop = Japanese |
|

|
1. Mont Ste-Victoire as Seen from Bibemus Quarry
2. Cezanne - Post Impressionism 3. Post Impressionist: rejected the requirements of Realism & used myth and dreams in their work. 4. No collective vision/style 5. flat/crop = Japanese 6. more than 60 versions show progression to abstraction. |
|

|
1. The Apparition (Dance of Salome)
2. Moreau - Symbolism 3. femme-fatale 4. in Symbolist novel Against Nature. 5. Symbolist = dreams |
|

|
1. The Eye Like a Strange Balloon Mounts Toward Infinity
2. Redon - Symbolism 3. Predated, but embraced by Symbolists who expressed fears and desires abstractly and dream-like 4. Mentioned in a symbolist novel Against Nature 5. visual poem dedicated to Poe. |
|

|
1. The Dream
2. Rousseau - Symbolism 3. less industrialized cultures = pure and spiritual. 4. Self-taught 5. Flat stage-like scene 6. symbols of sexuality: flute, snake, flowers |
|

|
1. The Vision After the Sermon
2. Gauguin - Symbolism 3. rejected the requirements of Realism & used myth and dreams in their work. 4. No collective vision/style 5. modern society bad, yearned for a utopia 6. Influenced by stained glass and cloisonne |
|

|
1. Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?
2. Gauguin - Symbolism 3. rejected the requirements of Realism & used myth and dreams in their work. 4. No collective vision/style 5. modern society bad, yearned for a utopia 6. Influenced by stained glass and cloisonne |
|

|
1. Starry Night
2. Van Gogh - Post Impressionism: Symbolism 3. rejected the requirements of Realism & used myth and dreams in their work. 4. No collective vision/style 5. modern society bad, yearned for a utopia |
|

|
1. La Goulue
2. Toulouse-Loutrec - Post Impressionism 3. Art for the demimond or fringe society depicting clubs and brothels 4. flat/crop = Japanese 5. Differs from Degas because fewer marks, larger planes of color make the image more cartoonish. |
|

|
1. Christ's Entry into Brussels
2. Ensor - Post Impressionism: Symbolism 3. strange, dreamlike imagery of fantasy, escapism and psychology 4. complimentary colors, red and green add to the garishness of the work. 5. influenced by cartoon, graffiti and children's art. 6. considered to be a sarcastic response to Seurat's pollyanna depiction of modernity. |
|

|
1. Salome With the Head of John the Baptist
2. Beardsley - Post Impressionism: Symbolist with Art Nouveau technique 3. femme fetal 4. Based on Oscar Wilde's play. 5. Art Nouveau style |
|

|
1. A Wooded Landscape in Three Panels
2. Tiffany - Art Nouveau 3. Arts and Crafts 4. used silver technique to make glass glow 5. emphasis on the organic and high quality hand crafting |
|

|
1. The Kiss
2. Klimt - Post Impressionism: Symbolism 3. The strong blocks = masculine. flowers = feminine 4. gold = religious art influence 5. dominating male - subjugated woman. 6. Symbolism |
|

|
1. The Scream
2. Munch - Post Impressionism: Symbolism 4. Brushwork and color emphasize the writhing internal emotions displayed. 5. The calm people in the background |
|

|
1. Casa Mila
2. Gaudi - Art Nouveau 4. seashore, waves, seaweed and sand castles 5. nature = spiritual |
|

|
1. Interior Stairwell, Tassel House
2. Horta 3. Art Nouveau 4. wrought iron allowed design 5. Glass ceiling allows natural light emphasizing the organic |
|

|
1. Wainright Building
2. Sullivan 3. First skyscrapers 4. sharp linear elements = emphasize height 5. steel = facade not load bearing = freedom of design |
|

|
1. Robie House
2. Frank Lloyd Wright 3. Cantilevered = unobstructed views. 3. Prairie Houses 4. Japanese influence = total design 5. Froebel blocks = ability to design complex spaces |
|

|
1. Woman with the Hat
2. Matisse 3. Fauvism reflected in the bold, free use of color. Fauves = wild beasts. 4. differed from expressionism because color not used to express psychology, but as an exercise in design. 5. Radical form in the use of color and bushwork, but traditional content of a portrait. |
|

|
1. The Joy of Life
2. Matisse - Fauvism 3. 1 year after Woman with a Hat, but major style change. Dispensed with logical space and scale and increased abstraction. 4. Evokes the classical content of roman styles. 5. Inspired Picasso to paint Women of Avignon |
|

|
1. Women of Avignon
2. Picasso - Analytical Cubism 3. viewer = patron 4. fruit = lust. 5. Inspired by Matisse's The Joy of Life 6. femme fatale 7. freed line, plane, mass and color from its representational role and laid the foundation for Analytic Cubism |
|

|
1. The Portuguese
2. Braque - Analytical Cubism 3. Cubism = blocks of difference perspective 4. Emphasized the idea that art is a signing system like language. 4. Traditional content used to emphasize radical form. 5. Worked closely with Picasso during this period. 6. Monochromatic images allowed artist to focus on new style. |
|

|
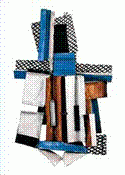
1. Guitar, Sheet Music and Wine Glass
2. Picasso - Collage 3. Collage painting = canvas "window" gone 4. Collage is pasting objects onto the canvas. 5. Synthetic Cubism - images built up rather than broken down into abstract form as in Analytic Cubism. 6. Music abstract like their art. |
|
|
1. Violin
2. Picasso - Synthetic Cubism 3. Extending Synthetic Cubism to sculpture in a form Constructions or #D assemblages of materials 4. Constructivism is an assemblage of 3 dimensional materials. 5. Focus still on traditional content with radical form 6. music theme because abstract like his art |
|

|
1. Bird in Space
2. Brancusi - Modern Sculpture 3. Used minimalism to shed his work of the clutter of visual reality to pursue invisible essential truths. 4. Used only a few themes in many different materials as a way to explore psychological and visual elements of the material. 5. Grew up in a very rural not modern environment. |
|

|
1. Self Portrait with an Amber Necklace
2. Modersohn-Becker - German Expressionism 3. radical content: female artist representing herself nude. reclaims the female form for women. 4. Precursor to German Expressionist: primitive and spiritual seen as the "earth mother" 5. She increased the primitive feel of the painting by using pasty paint and an intentionally awkward pose. |
|

|
1. Street, Dresden
2. Kirchner - German Expressionism 3. Die Bruke = the Bridge to the future 4. Influenced by the idea of Nietzsche 'superhuman' 5. The clashing colors create a disturbing image that reflects the artists negative opinion of prostitutes 6. garish, non-idealistic 7. the isolation of a big city |
|

|
1. The Last Supper
2. Nolde - German Expressionism 3. complementary colors red and green used to emphasize the emotion of the subjects and the artist 4. the primitive "sketchiness" actually make the subjects look more real. 5. Influenced by African art. 6. Die Bruke member (the bridge) - influenced their use of color. |
|
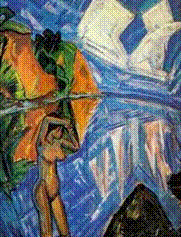
|
1. A Crystal Day
2. Heckel - German Expressionism 3. German Expressionist - The Bridge 4. Used Cubist elements to express the spirituality and power of nature 5. The flatness expresses how everything is part of one thing. |
|
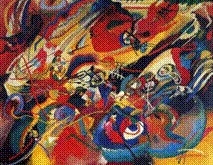
|
1. Sketch 1 for Composition VII
2. Kandinsky - German Expressionism 3. Blue Rider group 4. Heavily influenced by folk culture. 5. believed artists used an abstract vocabulary of color to communicate with the soul 6. Influenced by recent scientific discoveries that matter is not stable, but always in flux. 7. 1 of 10 works that became progressively more abstract. 8. Wrote Concerning the Spiritual in Art 9. Embraced the Apollonian spirit of science |
|

|
1. Animal Destinies
2. Franz Marc - German Expressionism 3. Wanted to portray spirituality in his work 4. Inspired by what he called "animal's virginal sense of life" 5. believed Western, industrialized society was spiritually bankrupt. 6. The Dionysian, unconstrained 7. Planes not use for perspective, but to accentuate the primal |
|

|
1. The Niesen
2. Klee - German Expressionism 3. done in watercolor. 4. a trip to Tunisia influenced his use of color 5. There are influences of Cubism in the shapes, Expressionism in the color and Fauvism in the folk art primitiveness 6. An armiture for design and color principles |
|

|
1. Self Portrait
2. Schiele - Austrian Expressionism 3. watercolor, charcoal on paper 4. a great departure from traditional nudes, the body is the opposite of the traditional ideal. 5. unabashed sexuality that differs from the American ideal of fake perfection 6. Raw, primal Dionysian |
|

|
1. The Tempest
2. Kokoschka - Austrian Expressionism 3. became known as the Freud of painting because his subjects seemed so troubled. 4. Influenced by Van Gough 5. The work is Expressionist and conveys anxiety in both brushstroke and color. 6. Dionysian 7. Brush strokes are expressive, not a study in form |
|
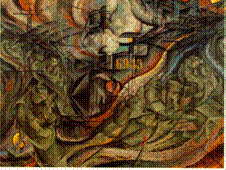
|
1. States of Mind I: Farewells
2. Boccioni - Italian Futurist 3. Visualized movement and energy. Called for the embrace of modernity 4. Member of the Italian Artistic Family 5. Used Cubism to relay the motion and energy of the modern world 6. Their manifesto was more important than any other contribution - after all movements had a manifesto |
|

|
1. Installation Photograph of His Paintings in 0
-10 2. Malevich - Suprematism 3. Artist called himself a Cubo-Futurist for the blending of the two styles. 4. Black Square hung Icon (a window into the spiritual realm) 5. Influenced by the Russian idea of Zaum which is a language based on syntax in which meaning is implied in sound and pattern. 6. Black square is all emotion, white border is void of emotion 7. |
|

|
1. Counter Relief
2. Tatlin - Constructivism 3. tension in structure 4. abstract is now off of the canvas 5. Way ahead of his time for this style |
|

|
1. Suprematist Composition: Airplane Flying
2. Malevich - Supremetism 3. Cubo-Futurist. Embraced machine and industry. 4. Created an Opera Victory under the Sun with zaum: invented words and syntax in which meaning came from sound/pattern 5. Suprematist refers to the supremacy of feeling. |
|
|
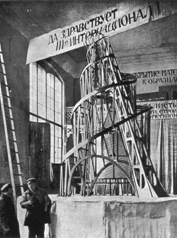
1. Model to Monument to the Third International
2. Tatlin - Constructivism 3. Art into life - design of the functional 4. Was a model for a real bldg that was never built using modern materials of steel and glass. 5. embraced the democratic aspect of mass production. |
|

|
1. Model to Monument to the Third International
2. Tatlin - Constructivism 3. Art into life - design of the functional 4. Was a model for a real bldg using modern materials of steel and glass. 5. embraced the democratic aspect of mass production. |
|

|
1. Untitled Advertising Poster
2. Rodchenko - Constructivism 3. after WWII advertisers use art to compete for the eye 4. embraced Tatlin's idea of functional design 5. There is no space, flat, geometric and mechanical 6. After WWII advertisers use art to compete for your attention |
|

|
1. Design for Sportswear
2. Stepanova - Constructivism 3. embraced Tatlin's idea of functional design 4. bright colors and sharp geometric evoke energy and machines. 5. Classless design for a new type of society. |
|

|
1. I and The Village
2. Chagall - Cubism & Fantasy 3. Used Cubism to bring disperate objects together. 4. Use of color influenced by Fauvism 5. The circular elements evoke the cycle of life or the seasons. 6. Primitive bridge to modern form 7. introduces the magical 8. uses naive characters influenced by folk art |
|

|
1. Melancholy and Mystery of a Street
2. de Chirico - cubism, sybolism 3. influenced by Nieztsche's suggestion that there is another reality beneath this one. 4. used skewed conventional content to evoke an eeriness. 5. influenced representational Surrealsim 6. overarching things working in the background we can't grasp |
|

|
1. The Entombment of the Birds and the Butterflies
2. Arp - Zurich Dadasim 3. Dada artist who believed that life was random and absurd. 4. Piece came from a random doodle, named when complete. 5.Dadism starts as a literary movement 6. FIRST ANTI-ART MOVEMENT 7. The style removed the artist from the work |
|

|
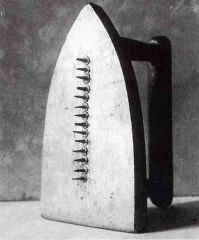
1. Nude Descending a Staircase
2. Duchamp - New York Dadaism 3. used Cubism - influenced by motion studies (photography) 4. His work the Fountain argued that art is 5. Art as ideas not just visual 7. Created 'Ready Made" art - The Fountain. The artist gets to say its art. 8. Fountain also a comment on the power of viewing - types of looking - environment 9. What makes art? Not skill - its the thinking of the artist |
|
|
1. Gift
2. Man Ray - Surrealism 3. help establish photography in Dada and Surrealist circles as on par with painting. 4. Created rayograms- camerless pictures. 5. His work bridge Dada to Surrealism |
|

|
Cadeau (Gift) (2 of 2) 1921
2. Man Ray - Surrealism 3. help establish photography in Dada and Surrealist circles as on par with painting. 4. Created photograms - camerless pictures. 5. His work bridge Dada to Surrealism |
|

|
Untitled 1922
2. Man Ray - Surrealism 3. help establish photography in Dada and Surrealist circles as on par with painting. 4. Created photograms - camerless pictures. 5. His work bridge Dada to Surrealism |
|

|
1. The Spirit of Our Time
2. Hausmann - German Dadasim 3. a member of club Dada and leader of Berlin Dada 4. used found objects in a style he called assemblage 5. a mindless dummy surround by the detritus of contemporary German life. 6. differed from other dadaist because used the art to convey a political message instead of an anti-art msg |
|

|
1. The Spirit of Our Time
2. Hausmann - German Dadaism 3. a member of club Dada and leader of Berlin Dada 4. used found objects in a style he called assemblage 5. a mindless dummy surround by the detritus of contemporary German life. 6. differed from other dadaist because used the art to convey a political message instead of an anti-art msg |
|

|
1. Cut with the Kitchen Knife
2. Hoch - German Dadaism 3. Collage, but to distance technique from fine art called it photomontage. 4. crowded disparate elements symbolize the hectic chaotic life in Germany 5. Title refers to her cutting the machine made images and making of them something human. |
|

|
1. As in the Middle Ages, So in the Third Reich
2. Hartfield - German Dadaism 3. swastika coopted by Nazis actually an ancient symbol of energy 4. photomantage 5. Political Critisism of the Nazis |
|
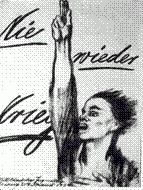
|
1. Never Again War!
2. Kollwitz - German Dadaism 3. Barred from the academy because a woman 4. shunned painting as elitist and used print & drawings that could be mass produced. 5. she used strident marks and strong value contrasts to increase the emotion in her work. 6. sympathized with the poor and working class |
|

|
1. Germany a Winter's Tale
2. Grosz - Post War German Dadaism & Expressionism 3. Post War German Expressionist also seen as a Dadaist 4. radical content: his desire to overthrown the main pillars of current German society: church, military and education. 5. Radical form: used cubist techniques to create a collage-like vision of a man surrounded by many forces. 5. |
|
|
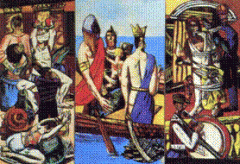
1. Departure
2. Beckmann - Post War German Expressionism 3. German Expressionist whose style was influenced by his experiences in WWI 4. Used Surrealist techniques to emphasize the jarring emotions of his work. 5. Nazis deemed his art degenerate 6. used compressed space, jagged shapes and thick black lines to emphasize the hellish mood of the work. |
|

|
1. Composition
2. Miro - Surrealism 3. 1 of a series based on collages made from catalog cuttings glued to cardboard. 4. used a minimal vocabulary of color and form 5. juxtaposition of hazy washes and abstract forms creates an otherworldly environment |
|

|
1. The Entire City
2. Ernst - Surrealism 3. Developed Frottage: making rubbings of ordinary objects and then finding an image in the design. 4. This work uses Grottage which is the same but with paint. 5. made several paintings on the same theme 6. made after the rise of Hitler and suggests the end of civilization. |
|

|
1. The Persistence of Memory
2. Dali - Surrealism 3. Surrealist: mysterious dream scape of metaphors. 4. Influenced by Freudian psychology 5. painted in a self-induced paranoid frenzy |
|

|
1. An Analuian Dog (Film Stills)
2. Dali - Surrealsim 3. Surrealist 4. used montage, juxtaposing unrelated events to force objects to be seen in new context. 5. Influenced by Freudian psychology |
|

|
1. Metamorphosis of Narcissus
2. Dali - Surrealism 3. Surrealist 4. Influenced by Freudian psychology 5. |
|
|
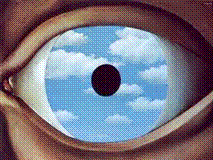
1. A False Mirror
2. Margritte - Surrealism 3. Surrealist 4. Conveys the superiority of the unconscious mind. Where iris is eclipsed sun 5. |
|

|
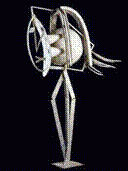
1. Object
2. Oppenheim - Surrealism 3. eroticism offered and denied: separate great, together repulsive 4. meant to provoke unconscious and repressed 5. minimalist technique evokes strong emotion |
|
|
1. Head of a Woman
2. Picasso - Surrealism 3. example of his surrealist work 4. established welded steel as major sculptural process 5. made with found objects like colanders and springs |
|

|
1. Guernica
2. Picasso - Cubism & Surrealism 3. painted in response to against the Nazi bombing of civilians in Spain 4. Portrays the suffering of a world always in conflict 5. The human faced bull is a symbol for brutality. The horse is a symbol for the People. 5. |
|

|
1. Behind the Gare Saint-Lazare
2. Cartier-Bresson - Surrealism 2. Surrealist pics could manipulate reality and create dreamlike sequences. 3. trained as a painter 4. wanted to find the extraordinary in the ordinary 5. sought the 'decisive moment' when intuition made art. 6. created a powerful dialog between object and man |
|
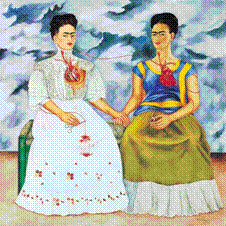
|
1. The Two Fridas
2. Kahlo - Mexican Art 3. cultivated a folk style 4. expressed her personal suffering in her work 5. Maintained a mexican context in her work 6. this work depicts her mixed ancestry European and indigenous. |
|

|
1. Composition No. II
2. Mondrian - De Stijl (The Style) 3. Founded a movement called The Style (De Stijl): mission spiritual not political 4. wanted to create geometric environments that represented universal harmony 5. Philosophy based on Theosophy 6. Called it Neo-Plasticism or new plasticism in which he tried to represent the underlying structure of the cosmos |
|
|
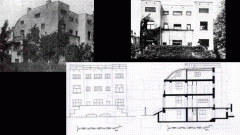
1.Steiner House
2. Loos - Early Modern Architecture 3. Antiornimentalism (ornim.. = wealth and oppression) 4. Geometric block like components 5. Function the most important criteria |
|
|
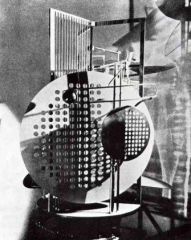
1. Light Space Modulator
2. Moholy-Nagy - Bauhaus 3. Constructivism 4. Planes of plastic, glass and steel that projected light 5. artist thought it could be used to study light and space and design new applications |
|
|
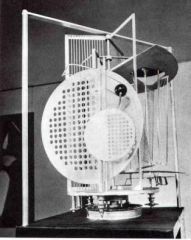
1. Light Space Modulator
2. Moholy-Nagy - Bauhaus 3. Constructivism 4. Planes of plastic, glass and steel that projected light 5. artist thought it could be used to study light and space and design new applications |
|

|
1. Bauhaus, Dessau
2. Gropius - Bauhaus 3. The Shop Block/Workshop wing 4. looks like a Constructivist structure from the air 5. building looks like its floating because the basement is set back |
|

|
1. Bauhaus, Dessau
2. Gropius - Bauhaus 3. The Shop Block/Workshop wing 4. looks like a Constructivist structure from the air 5. building looks like its floating because the basement is set back |
|

|
1. Villa Savoye
2. Le Corbusier - International 3. believed in the supremacy of the machine aesthetic 4. designed the utopian "ideal" home 5. used steel reinforced concrete because very adaptable 6. No ground floor, flat roof w/garden, horizontal windows, open plan, |
|

|
1. German Pavillion
2. Van Der Rohe - Bauhaus 3. Bauhaus 4. Less is more 5. Cantilevered roof |
|

|
1. German Pavillion
2. Van Der Rohe - Bauhaus 3. Bauhaus 4. Less is more 5. Cantilevered roof |
|

|
Interiors
Van Der Rohe - Bauhaus Less is More Total design for the ideal home (design all aspects) |
|

|
furniture
Van Der Rohe - Bauhaus Less is more total design for ideal home (design all aspects) |
|

|
1. Three Women
2. Leger - Purism 3. champion of modernity and technology 4. constructed on basic geometric shapes 5. colors are basic primary and binary colors 6. traditional brothel scene in technological harmony = new world order based on the machine and science |
|
|
AUGUSTUS WASHINGTON
|
first african american to graduate from dartmouth, free, went back to africa
|
|
|
REALISM - Primary artists
|
Manet: beginning of realism
Courbet Daumier Degas Sargent |
|
|
IMPRESSIONISM - primary artists
|
Monet
Degas Cassatt |
|
|
Innovative Architects
|
Paxton - Crystal Palace
Roebling - Brooklyn Bridge Eiffel - Eiffel Tower |
|
|
REALISM - main aspects
|
Contemporary life represented unembellished and unidealized
Drew on own society (contemporary and close by) Realists faithfully recorded social conditions Pursuit of the factual Realists faithfully recorded social conditions; Impressionists faithfully recorded optical conditions. |
|
|
IMPRESSIONISM - main aspects
|
Light & its reflection
Short brushstrokes Separating color Modern life Impressionists faithfully recorded optical conditions Realists faithfully recorded social conditions; Impressionists faithfully recorded optical conditions. |
|
|
POST-IMPRESSIONISM - primary artists
|
Cezanne
Van Gough Gauguin Seurat Toulouse-Lautrec |
|
|
POST-IMPRESSIONISM - main aspects
|
Rejected established premises of Realism and Impressionism
No collective way of seeing Japanese artistic techniques anti-bourgeoisie, anti-academic escape the modern world and provide an antidote |
|
|
SYMBOLISM - primary artists
|
Gauguin
Moreau Redon Ensor Sometimes Van Gough |
|
|
SYMBOLISM - main aspects
|
Objectify the subjective rather than subjectifying the objective.
Replaced conventional world with one of dreams Abstractly expressed sensations, moods, fears and desires. |
|
|
ART NOUVEAU - primary artists
|
Tiffany, Horta , Gaudi
|
|
|
ART NOUVEAU - main aspects
|
need to look up
|
|
|
FAUVES - primary artists
|
Matisse
|
|
|
FAUVES - main aspects
|
composed surface designs based on relationships of unmixed, intensely vibrant colors
|
|
|
CUBIST - ANALYTICAL - main aspects
|
Intellectually analyzed—took apart, then reconstructed—forms and volumes
Multiple vantage points and multiple interpretations of reality Elements: jagged, flat planes, viewer’s perception—endlessly shifted and denied fixed absolutes. Binaries obfuscated: front and back, opened and closed, solid and empty. Collages (and ultimately in constructions) during the Synthetic phase of Cubism. Asserted that art is found on a surface, not beyond a plane that we look through as if it were a window jagged, flat planes to a viewer’s perception—endlessly shifted and denied fixed absolutes. |
|
|
CUBIST - primary artists
|
Picasso
Braque |
|
|
CUBIST - SYNTHETIC
|
collages (and ultimately in constructions) during the broke the last barrier of the canvas as window
|
|
|
GERMAN EXPRESSIONISM - primary artists
|
The Bridge:
Max Beckmann Modersohn-Becker Nolde Heckel Blue Rider: Kandinsky - Beginning of total abstraction Marc Klee |
|
|
GERMAN EXPRESSIONISM - main aspects
|
CHANGE INTO BULLETS
Die Brucke used color and form expressively “tortured, anguished, brutally primitive, or passionately spiritual, reflecting cosmic forces.” Combining features of Fauvism, Cubism, and German folk art developed an abstract language The Bridge: The Bridge “to the future” Influenced by Nietzsche Ubermensch who lead the world to glorious future Influenced by Fauvists color studies, but used them to express emotion The Blue Rider Skepticism towards modern, industrial life Expressed a spirituality they believed resided beneath the surface of the visual world Influenced by folk art |
|
|
DADA - primary artists
|
Duchamp – used cubism, motion studies
Arp Hausmann Hoch Kollwitz |
|
|
DADA - main aspects
|
Nonsensical, nihilistic art
attacked bourgeoisie values, including a faith in technology. Aimed to wipe the philosophical slate clean and pave the way for a new world order. Chance and the absurd |
|
|
SURREALISM - primary artists
|
Man Ray
Picasso Ernst Miro Magritte Dali Cartier-Bresson Oppenheimer |
|
|
SURREALISM - main aspects
|
Rejected the machine age
Sought higher truths often using organic or biomorphic vocabulary. Influenced by the work of Freud on the unconscious and dreams. Sought to reveal invisible realities. Not spiritual ones, but elemental universal forces that drove all humans. |
|
|
CONSTRUCTIVISM - primary artists
|
Tatlin
Rodchenko Stepanova |
|
|
CONSTRUCTIVISM - main aspects
|
Constructivism and De Stijl hoped to reform society
Agent of social change Design scheme for a harmonious society Machine aesthetic Functional art for better living |
|

|
The Traveler
Lyubov Popova Fracturing of Cubism with the energy and movement of Futurism Shapes, lines, and form in contrast No push-pull; uniform oneness |
|
|
FERROVITREOUS STRUCTURES
|
Cast iron allowed buildings to span large unobstructed spaces.
|
|
|
THE SKYSCRAPER
|
Skeletons of steel that supported the load of the building changed the building façade from structural element to design elemen
|
|
|
THE BRIDGE - German Expressionism - main aspects
|
The Bridge “to the future”
Influenced by Nietzsche Ubermensch who lead the world to glorious future Influenced by Fauvists color studies, but used them to express emotion |
|
|
THE BLUE RIDER - German Expressionism - main aspects
|
Skepticism towards modern, industrial life
Expressed a spirituality they believed resided beneath the surface of the visual world Influenced by folk art |
|
|
THE BRIDGE - German Expressionism - primary artists
|
Beckmann
Modersohn-Becker Nolde Heckel |
|
|
THE BLUE RIDER - German Expressionism - primary artists
|
Kandinsky - Beginning of total abstraction
Marc Klee |
|
|
EXPRESSIONISM - Austrian - main aspects
|
Darker than German
Distorted, more grotesque Kandinsky developed an abstract language that expressed the universe’s mystical dimensions and flow of cosmic forces. |
|
|
EXPRESSIONISM - Austrian - primary artists
|
Kandinsky
Schiele |
|
|
DE STIJL - Primary artists
|
Mondrian
|
|
|
DE STIJL - main aspects
|
hoped to reform society
asymmetrical balance opposites held in equilibrium mirrored universal order meant as a single component in a comprehensive design scheme for a harmonious society |
|
|
BAUHAUS - primary artists
|
Moholy-Nagy
Gropius Van Der Rohe |
|
|
BAUHAUS - main aspects
|
A German art and design school
Founded by Gropius Dedicated to the creation of utilitarian design for “the new man” Art + technology Primary forms and colors Establish standard types for the things people use every day |
|
|
INTERNATIONAL STYLE - primary artists
|
Le Corbusier
|
|
|
INTERNATIONAL STYLE - main aspects
|
machine aesthetic
designed glass, steel, and concrete environments for better living unadorned, clean and geometric, floating, impersonal, and functional |
|
|
PURISM - primary artists
|
Leger
|
|
|
PURISM - main aspects
|
clean lines, pure forms and mathematical clarity
machine aesthetic everything parallel to the picture plane Primary and binary colors / building blocks of the color spectrum |
|
|
Plato
|
Art is bad
|
|
|
Artistotle
|
Results determine good or bad
|
|
|
Hume
|
Universal beauty determined by: Time or Experience
|
|
|
Kant
|
Beautiful = Agreeable + Good
Sublime = Awe |
|
|
Schopenhauer
|
Life is futile
Genius + Ideas = Art = Elevation to the Universal |
|
|
Hegel
|
Balance Form and Essence
Symbolic, Classical, Romantic |
|
|
Nietzsche
|
Appolline + Dionysiac = Healthy Society
Appolline = Idealization = Denial of Life Dionysiac = Embrace Life |
|
|
Freud
|
Art speaks to our unconcious
|
|
|
Heidegger
|
Art reveals truth
Art reveals culture and informs it |
|
|
Benjamin
|
Reproduction ends uniqueness
Art with an agenda |
|
|
Weitz
|
Art is not definable, but debate establishes criteria
|
|
|
Langer
|
Art communicates human feeling were language fails.
|
|

|
1. Fountain
2. Duchamp - New York Dadaism 3. His work the Fountain argued that art is 4. Art as ideas not just visual 5. Created 'Ready Made" art - The Fountain. The artist gets to say its art. 6. Fountain also a comment on the power of viewing - types of looking - environment 7. What makes art? Not skill - its the thinking of the artist |

