![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
|
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
|
|
|
A 5 yo boy has developed progressive limping. At first painless, it now hurts to run & walk. The pain is in the anterior thigh. The pain is relieved by rest. Parents recall no trauma
|
Legg-Calve-Perthes
|
|
|
At what age range should Legg-Calve-Perthes be considered?
|
4-12 years
|
|
|
What gender most commonly gets Legg-Calve-Perthes?
|
Boys (4:1)
|
|
|
What are the associations with Legg-Calve-Perthes?
|
Poverty
Low birth weight Hernias Undescended testes |
|
|
What is the presentation of Legg-Calve Perthes?
|
Limping that is at first painless, but can proceed to pain that is worsended by activity & relieved by rest
Pain is reported in the groin, hip, thigh, or knee |
|
|
What is the diagnostic test for Legg-Calve-Perthes?
|
radiographs show wide articular space, then necrosis.
Follow-up films during reconstitution reveal a flattened femoral head; later it becomes spherical |
|
|
What is the treatment for Legg-Calve-Perthes disease?
|
Self-healing process
Goal of therapy is to MAINTAIN JOINT MOBILITY -this is done via CONTAINMENT = maintaining the hip in the acetabulum |
|
|
What is a complication of Legg-Calve-Perthes?
|
Osteoarthritis
|
|
|
Describe Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
What are some associated conditions? (4) |
Occurs in the newborn period but should be considered up to 3 years of age
20% of patients have a + family hx Ligamentous laxity, maternal estrogens, breech position, & torticollis |
|
|
What signs are useful in diagnosing DDH?
|
Barlow, Ortolani, & Galeazzi signs
|
|
|
Displacement of the femoral head from the femoral neck b/c of a stress fracture thru the femoral capital epiphyseal plate
|
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
|
|
|
What are the associations with SCFE? (3)
|
Obesity, deficient gonadal development, & hypothyroidism
|
|
|
An obese kid presents with groin pain referred to the anteromedial knee & thigh, limp, & accentuated external rotation
|
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
|
|
|
What do radiographs show in SCFE?
|
medial displacement of the epiphysis
Bare upper portion of the femoral neck Wide growth plate |
|
|
ABnormal curvature of the spine caused by misalignment in the frontal plane = ?
|
Scoliosis
|
|
|
a 12 yo girl is seen for routine physical exam. She voices no complaints. Exam is remarkable for asymmetry of the posterior chest wall on bending forward. One shoulder appears higher than the other when she stands up
|
Scoliosis
|
|
|
What is the best way to screen for scoliosis?
|
Adams test = forward bending
Radiographs are the gold standard for evaluating suspected scoliosis |
|
|
When is surgery considered in Scoliosis?
|
> 45 degrees
|
|
|
What is recommended to slow down progression of the curves in Scoliosis?
|
Bracing
|
|
|
What are 3 complications of Scoliosis?
|
1. Degenerative joint disease
2. Cardiorespiratory disease 3. Poor self-esteem |
|
|
Congenital Scoliosis is caused by vertebral anomalies such as __________. It is associated with these 3 things
|
Hemivertebrae
GU anomalies (renal agenesis horseshoe kidneys, obstructive uropathy) Congenital heart disease Spinal Dysraphism **early surgical treatment is indicated b/c of the underlying pathophysiology |
|
|
What syndromes are associated with scoliosis?
|
1. Neurofibromatosis
2. Marfan 3. VACTERL 4. Goldenhar = malar/maxillary hypoplasia, microtia (small ear), hemivertebrae |
|
|
Talipes Equinovarus
|
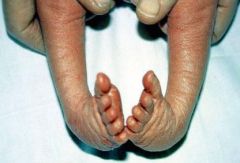
A newborn is noted to have a foot that is stiff & slightly smaller than the other one. The affected foot is medially rotated & very stiff, with medial rotation of the heel
|
|
|
What are associated disorders of Talipes Equinovarus?
|
1. developmental hip dysplasia
2. Amniotic bands = congenital disorder caused by entrapment of fetal parts (usually a limb or digits) in fibrous amniotic bands while in utero 3. Spina bifida 4. Arthrogryposis = rare congenital disorder that causes multiple joint contractures and is characterized by muscle weakness and fibrosis |
|
|
What gender is Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) more common in?
|
Boys
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Talipes Equinovarus?
|
Serial casting & surgery
|
|
|
The forefoot is adducted, but the hindfoot is normal; the forefoot can be brought to the neutral position. Observation, passive range of motion, & casting may treat this condition
|
Metatarsus Adductus (Metatarsus Varus)
|
|
|
Tibial torsion is usually secondary to _____. Treatment is not necessary b/c this condition resolves on its own
|
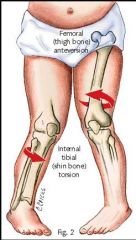
in utero positioning
|
|
|
This is more common in children older than 2 years & is more common in girls. It is affected by sitting position. Rx is usually an attempt to correct sitting position
|
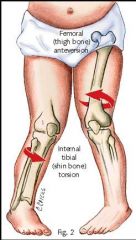
Femoral Anteversion
|
|
|
What does Retinoblastoma have an association with?
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
This bone tumor can be induced by exposure to radiation
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
Where is Osteosarcoma most commonly found?
|
Long bones at the METAPHYSIS
-distal femur -proximal humerus -proximal tibia |
|
|
This bone tumor usually presents with pain at the tumor site; limitation of motion & a palpable, visible tumor are other findings. Deep bone pain awakening an adolescent at night should make one suspicious.
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
Bone tumor with "sunburst" appearance
|
Osteosarcoma
|
|
|
What are common sites of metastatis for Osteosarcoma?
|
Lung & bone
|
|
|
What is treatment for Osteosarcoma?
|
Surgery & Chemo
|
|
|
What present a worse prognosis for Osteosarcomas?
|
Pelvic tumor
|
|
|
"Onion skin" periosteal elevation
|
Ewing Sarcoma
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Ewing Sarcoma?
|
Surgery, radiation, chemo
|
|
|
Ewing Sarcoma
|

-
|
|
|
This occurs when there is no longitudinal arch of the foot. It is a variation of normal feet. It is usually seen in children older than 6 years of age, is usually asymptomatic & requires no treatment
|
Pes Planus = flat feet
|
|
|
What is Pes Planus sometimes associated with?
|
1. Heel cord contractures
2. Cerebral palsy |
|
|
This arises from the capsule or tendon sheaths & appears as a painless NONPULSATILVE SWELLING on the posterior aspect of the knee. It becomes more prominent on knee extension. Rx is usually not necessary b/c it resolves spontaneously. Excision is recommended for large, painful lesions. DDx includes Lipoma, aneurysm, neuroma, & rarely tumors
|
Popliteal cyst (Baker cyst)
|
|
|
Traction apophysitis of the TIBIAL TUBERCLE caused by overuse
|
Osgood Schlatter disease
|
|
|
This presents with localized tenderness & swelling over the tibial tubercle
|
Osgood Schlatter disease
|
|
|
This occurs after sudden traction on the arm, usually in kids younger than 4 years old. The child cries immediately & won't move the arm. The arm is held paritally flexed at the elbow & pronated
|
Radial head subluxation (Nursemaid's elbow)
|
|
|
How do you correct Radial head subluxation?
|
reduction by gentle supination w/ pressure over the radial head
|

