![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition: changes in behavior over time, e.g. reflexes, gross/fine motor skills
|
Neurodevelopmental
|
|
|
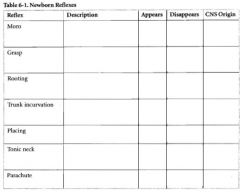
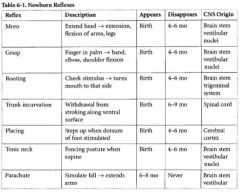
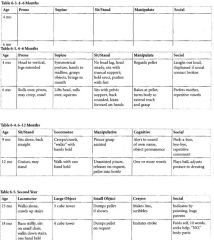
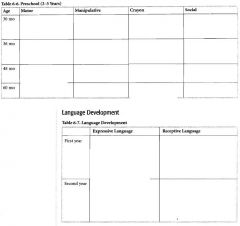
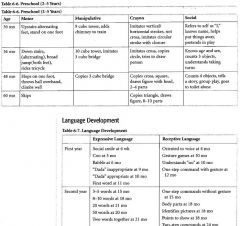
When do the majority of newborn reflexes disappear by?
|
4-6 months
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
-
|
|

-
|
-
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
How is ADHD diagnosed?
|
CLINICALLY
-diagnosis requires at least 6 criteria from inattentiveness, 6 from hyperactivity/impulsiveness, or both -symptoms must be seen by 7 years of age, last at least 6 months, be observed in MORE THAN 1 SETTING, be more than age appropriate, & IMPAIR FUNCTION |
|
|
What are some complications of ADHD?
|
1. Antisocial personalities
2. Alcohol & drug abuse **about 1/2 of pts with ADHD have normal adult lives **Aggressive, defiant children tend to do worse as adults |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat ADHD?
|
Methylphenidate
Dextroamphetamine Pemoline TCA Clonidine Bupropioin **Diets have absolutely NO VALUE in ADHD |
|
|
When is day & night bladder control usually attained?
|
by 5 years of age
|
|
|
What are the risk factors/etiology of Enuresis?
|
Incidence declines with age
Stron genetic predisposition for Primary Nocturnal Enuresis |
|
|
Define the 2 major types of Enuresis
|
Primary = pt has never achieved dryness for any significant period of time
Secondary = previously continent child becomes incontinent |
|
|
What is Secondary Enuresis usually secondary to?
|
Emotional difficulties
-birth of sibling -significant loss -family discord |
|
|
What are the subdivisions of Primary Enuresis?
|
Nocturnal only
Diurnal only = during day Nocturnal/Diurnal |
|
|
What is Nocturnal Enuresis associated with?
|
Maturational developmental delay of the bladder and may be a disorder of sleep & arousal
|
|
|
What is Diurnal Enuresis associated with?
|
waiting too long to void, UTI's, constipation, diabetes, stress incontinence
|
|
|
What drugs are commonly used for Enuresis?
|
Imipramine & Desmopressin (ADH)
|
|
|
Define Encopresis
|
Fecal incontinence after the age of 4 years
|
|
|
What are the Risk factors/Etiology of Encopresis?
|
*occurs more commonly in boys (5:1)
1. Toilet phobia 2. overly aggressively management of constipation 3. starting toilet training too early 4. painful defecation after diarrhea, fissures, or severe perianal rashes |
|
|
What are the presentation & treatment for Encopresis?
|
Presentation = secondary to stool retention, resulting in leakage of loose stools around the obstruction
Treatment: counseling for the child & parents; cleaning of impacted stool out of the colon |
|
|
Developmental disorder characterized by impaired social relatedness, deficits in verbal & nonverbal communication, & unusual responses to the environment
|
Autism
|
|
|
Autism develops before ______ of age. The cause is unknown. It is more common in ______
|
30 months
boys |
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of Autism?
|
1. failure to attach as an infant
2. delayed/absent social smile 3. delay in verbal & nonverbal communication skills 4. Stereotypical movements & a need for sameness 5. Outbursts of anger are common as well as self-injurious behavior **75% of patients are mentally retarded |
|
|
Describe Rett Syndrome
1. Inheritance 2. Boys or Girls? 3. Disease progress |
1. X-linked dominant
2. Girls 3. Development is normal until 1 year of age, when language & motor milestones regress & an ACQUIRED MICROCEPHALY is seen. HAND WRINGING & SIGHING are characteristic |

