![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
-
|
-
|
|
|
Presents with watery diarrhea, which can last for up to 7-10 days. It can be accompanied by 3-4 days of vomiting. Fever may be present
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
Causes a mild diarrhea in immunocompetent infants, but causes severe diarrhea in AIDS pts
|
Cryptosporidium
|
|
|
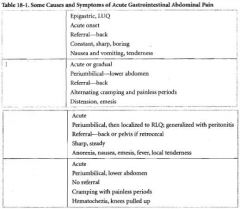
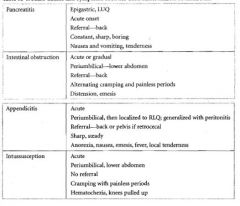
When is treatment of Salmonella diarrhea indicated?
|
-only for < 3 mo of age
-toxic patient -disseminated dz -or if its S. typhi |
|
|
What is the treatment for Shigella diarrhea?
|
Tri/Sulfa = Bactrim
|
|
|
What is Entamoeba treated with?
|
Metronidazole
|
|
|
Obstipation = ?
|
absence of bowel movements
|
|
|
Constipation = ?
|
infrequent passage of hard, dry stools
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
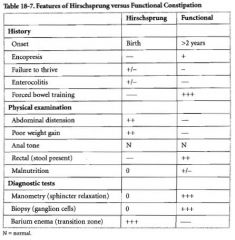
What is the most common cause of constipation outside of infance?
|
Functional constipation = voluntary withholding
|
|
|
What should constipation in the neonate be considered until proven otherwise?
|
Hirschprung
|
|
|
What is the treatment for functional constipation?
|
Initial cleaning out, & may involve dietary manipulation, stool softeners, & counseling
|
|

-
|
-
|
|
|
A newborn presents with bilious vomiting with every feed. Abdominal film reveals a double bubble
|
Duodenal Atresia
|
|
|
What is the association with Duodenal Atresia?
|
Trisomy 21
|
|
|
When does Duodenal Atresia usually present?
|
usually in the first day of life
-there may be a history of Polyhydramnios |
|
|
A 4 month-old is admitted w/ episodes of apnea occurring 20-30 minutes after feeds. The mother states the baby has been spitting up since birth. She is at the 5th% for weight
|
GER = occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter pressure is reduced
|
|
|
What associated conditions is GER more common in?
|
pts with Developmental Delay & Cerebral Palsy
|
|
|
Patients presents with GER & opisthotonus ( condition, caused by a tetanic spasm of the back muscles, in which the trunk is arched forward while the head and lower limbs are bent backward)
|
Sandifer syndrome
|
|
|
How would you diagnose GER?
|
pH probe is the standard
Other imaging studies include technetium scanning & barium swallow |
|
|
What is the treatment for GER?
|
Antireflux measures such as elevating the head of the bed & thickening of feeds.
Medical management = antacids, prokinetics, H2-receptor blockers, PPI's Failure of medical management results in surgical correction w/ a Nissen Fundoplication |
|
|
A 4 week old boy has nonbilious projectile vomiting. Exam is remarkable for a small mass palpated in the abdomen
|
Pyloric Stenosis
|
|
|
What is the gender ratio for Pyloric Stenosis?
|
Boys 4:1
|
|
|
What is the presentation of Pyloric Stenosis?
|
1. nonbilious projectile vomiting
2. usually AFTER 3 WEEKS of age 3. baby remains hungry after vomiting 4. olive may be palpated 5. peristaltic wave may be seen |
|
|
What does the BMP show in Pyloric Stenosis?
|
Hypokalemic, Hypochloremic Metabolic Alkalosis
|
|
|
A 15 month-old child is seen for cramping, colicky abdominal pain of 12 h duration. He has had 2 episodes of vomiting & a fever. Exam is remarkable for a lethargic child; abdomen is tender to palpation. Leukocysotis is present. During examination, the patient passes a bloody stool with mucus
|
Intussusception
|
|
|
When do most intussusceptions occur?
|
6-24 months of age
|
|
|
What vaccine was associated with Intussusception?
|
Rotavirus vaccine
|
|
|
Acute onset of cramping, colicky abdominal pain. Pts may have vomiting. Pt may develop fever & become lethargic. Sausage-shaped mass may be palpated
|
Intussusception
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic test for Intussusception?
|
Barium enema or Air Enema
|
|
|
A 2 year old boy presents with a 1 wk history of painless rectal bleeding. Exam is unremarkable. Abdomen is soft & nontender. Rectal examination is unremarkable
|
Meckel Diverticulum
|
|
|
Most frequent congenital anomaly of the GI tract
|
Meckel Diverticulum
|
|
|
What are the rules of 2 with Meckel Diverticulum?
|
1. presents in about 2% of infants
2. peak incidence is by 2 years of age 3. contains 2 types of tissue 4. 2 cm in size 5. located 2 feet from ileocecal valve |
|
|
Painless rectal bleeding
|
Meckel Diverticulum
|
|
|
What can be a complication of Meckel Diverticulum?
|
Intussusception
Inflammation mimicking appendicitis Can perforate & cause peritonitis |
|
|
What is the diagnostic test for Meckel Diverticulum?
|
Technetium scan for gastric mucosa in the bowel
|
|
|
An 8 year old is seen in the emergency department w/ persistent vomiting & mental status changes. On exam he is combative & has a seizure, becomes apneic, & requires intubation. Lab tests are remarkable for hypoglycemia & elevated ammonia. The pt had recently recovered from a viral URI
|
Reye Syndrome
|
|
|
Define Reye Syndrome
|
Encephalopathy with fatty degredaton of the liver
|
|
|
What is the etiology of Reye Syndrome?
|
Recent viral URI or Varicella with concomitant use of Aspirin
|
|
|
What is the presentation of Reye Syndrome?
|
-hx of recent viral URI
-after 5-7 days they then present w/ abrupt onset of protracted vomiting -delerium, combative behavior, & stupor quickly ensue. can progress to seizures, coma, & death -focal neurologic signs are absent |
|
|
What are the lab tests like in Reye Syndrome?
|
Ammonia, Transaminases, CK, & LDH are markedly elevated
Hypoglycemia |

