![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do infants with possible heart failure present?
How might an older child present? |
1. feeding difficulties
2. easy fatigability 3. sweating while feeding 4. rapid respirations 1. SOB 2. Dyspnea on exertion |
|
|
What might rales on ausultation indicate?
|
Pulmonary edema & Left-sided heart failure
**Rales = crackles caused by explosive opening of alveoli |
|
|
What heart problem might Hepatomegaly suggest?
|
Right-sided heart failure
|
|
|
What is a prominent Precordium seen with?
|
Cardiomegaly
Precordium = region over the heart |
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
Apical heave = ?
|
LV enlargement
|
|
|
Substernal thrust = ?
|
RV enlargement
|
|
|
Hyperdynamic precordium = ?
|
Volume overload
|
|
|
Silent Precordium = ?
|
Pericardial effusion or cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
Thrill = ?
|
Palpable equivalent of murmur at area of maximum auscultation
|
|
|
Ejection click = ?
|
early-to-mid systolic; associated w/ pulmonary atery or aortic stenosis or dilatation
|
|
|
S3 = ?
|
may be normal in older children & adolescents w/ slow heart rate
|
|
|
Gallop = ?
|
S4 always abnormal; poor compliance of ventricle; atrial kick during ventricular filling
|
|
|
Systolic ejection murmur = ?
|
usually implies increased flow or stenosis across one of the ventricular outflow tracts
|
|
|
Pansystolic murmur = ?
|
related to blood exiting contracting ventricle via an abnormal opening or AV insufficiency
|
|
|
Continuous murmur = ?
|
systolic murmur that spills into diastole & indicates continuous flow
|
|
|
To-and-fro murmur = ?
|
systolic component ends before S2, & diastolic murmur begins after semilunar valve closure
-Aortic stenosis & aortic insufficiency |
|
|
Late Systolic Murmur = ?
|
may be heard after a midsystolic click; hallmark is Mitral Valve prolapse
|
|
|
Venous hum = ?
|
Turbulence of blow flow in jugular venous system; hear in Anterior upper chest & neck in systole & diastole
|
|
|
Wide pulse pressure ( >40 mm Hg) = ?
|
Thyrotoxicosis
PDA AI AV fistula |
|
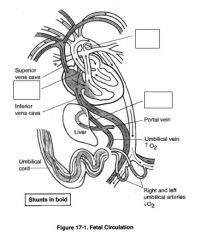
-
|
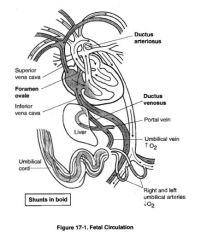
-
|
|
|
A 5 yo boy is seen for routine physical exam. Parents voice no concerns. Weight & height are at 75th%. Vital signs are normal. Exam is remarkable for a soft musical 2/6 murmur best heard at the left lower sternal border
|
Innocent murmur = functional, normal, insignificant, or flow murmurs
Result from flow thru a normal heart, vessels, & valves |
|
|
When are most innocent murmurs heard (at what age range)?
|
3 & 7 years of age
|
|
|
An innocent murmur is never _____. An innocent murmuris a soft, _____ or _____ best heard at the _______ border. Innocent murmurs are never greater than grade ______
|
Diastolic
Soft or Vibratory Left lower to midsternal border 2/6 |
|
|
High pitched, blowing, early systolic murmurs best heard in the second let parasternal space with the pt lying down
|
Pulmonary flow murmurs
|
|
|
Heard in the neck or anterior chest. It is heard in systole & diastole but can disappear w/ compression of the jugular vein
|
Venous hum
|
|
|
A 3-month-old child presents w/ poor feeding, poor weight gain, & tachypnea. Exam reveals a harsh, pansystolic 3/6 murmur at the left lower sternal border, & hepatomegaly
|
VSD
|
|
|
MC congenital cardiac malformation
|
VSD
|
|
|
Biventricular hypertrophy & notched peaked P waves
|
Large VSD
|
|
|
What are complications associated with VSD?
|
Endocarditis
Pulmonary HTN leading to Eisenmenger |
|
|
What are the most common defects in ASD?
|
Ostium secundum
|
|
|
Presentation: Many pts are asymptomatic. Exercise intolerance may develop in older childre. Systolic ejection murmur is heard in the left mid & upper sternal border; usually there is no thrill. Wide fixed split of S2
|
ASD
|
|
|
What does a chest radiograph show in ASD?
|
Enlarge RA & Ventricle
|
|
|
What are 3 complications of ASD?
|
Atrial dysrhythmias
Valvular insufficiency (mitral/tricuspid) Heart failure |
|
|
What is the defintion of PDA?
|
failure of closure of the Ductus Arteriosus leading to blood flow from Aorta -> Pulmonary Artery
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for PDA?
|
1. Girls (2:1)
2. Maternal Rubella infection 3. Premature infants |
|
|
When is a PDA beneficial?
|
providing Pulmonary blood flow when there is an associated Right Ventricular outflow tract obstruction, or in supplying systemic flow in Coarctation of the Aorta
|
|
|
Wide pulse pressure & bounding Arterial pulses with apical heave & a thrill heard at the 2nd left intercostal space
Machinery or to-and-from murmur heard in both systole & diastole |
PDA
|
|
|
What does CXR show in PDA?
|
Prominent Pulmonary Artery & increased Pulmonary Vascular markings
|
|
|
What is the treatment for PDA?
|
Indomethacin
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for Coartation of the Aorta?
|
Turner Syndrome
Boys 2:1 |
|
|
A 6 month old infant is prone to epidoses of restlessness, cysnosis, & gasping respirations. Symptoms resolves when he is placed in the knee chest position. Exam reveals an underweight infant, wich a harsh holosystolic murmur & a single second heart sound
|
Tetralogy of Fallot
|
|
|
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
|
IHOP
-Interventricular Septum defect = VSD -RV HYPERTROPHY -Overriding aorta -Pulmonary Stenosis |
|
|
When does Acyaontic (pink) Tetralogy occur?
|
when there is sufficient pulmonary blood flow caused by mild obstruction (mild PS) & shunting across the VSD is balanced
|
|
|
What does CXR show in TOF?
|
boot-shaped heart w/ uptilted apex
lung fields are clear reflecting decreased pulmonary blood flow |
|
|
What does ECG show in TOF?
|
RVH & right axis deviation
|
|
|
What is the treatment for TOF?
|
Management includes maintaining the Ductus open in severe Right-sided obstructive lesions
Surgical correction is the definitive treatment Blue spells are treated w/ knee chest position, sedation, O2, & avoiding acidosis |
|
|
What is the major complication associated with TOF?
|
Cerebral thrombosis secondary to extreme polycythemia & dehydration
-more common in pts < 2 yoa Brain abscess, while less common is more common in pts > 2 yoa |
|
|
This blue baby is more common in infants of Diabetic mothers & in boys
|
Transposition of Great Vessels
|
|
|
MC congenital heart disease to present w/ cyanosis in the first 24 h of life
|
Transposition
|
|
|
CXR demonstrates increased pulmonary blood flow as the pulmonary vascular resistance decreases
The appearance of an EGG ON A STRING is caused by the change in relationship of the great vessels as they exit the heart |
Transposition
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Transposition?
|
PGE1 to maintain the ductus open until surgical correction is performed
|
|
|
Right ventricular blood backs up to the RA & is shunted across the foramen ovale. Cyanosis occurs after 2-3 days when the ductus closes. Single second heart sound is heard
|
Pulmonary Atresia
|
|
|
ECG shows tall spiked P waves of right atrial enlargement & also shows LVH
|
Pulmonary Atresia
|
|
|
Pt presents w/ cyanosis at birth & a pansystolic murmur is heard along the left sternal border, S2 sound is single. CXR shows decreased pulmonary bloood flow
|
Triscuspid Atresia
-causes RV outflow obstruction -no outlet from the RA to the RV & blood shunts across the foramen ovale |
|
|
Describe Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
|
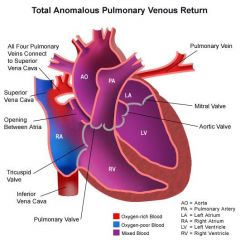
All the pulmonary veins drain back into the systemic venous circulation thru a circuitous route. These veins have a high risk of obstruction, leading to pulmonary congestion & pulmonary HTN.
Mixed blood reaches the LA thru an ASD or Foramen Ovale |
|
|
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
|
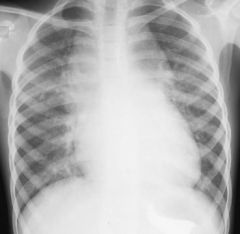
Chest radiograph shows the characteristic "snowman" pattern
|
|
|
This is when a single vessel arises from the Ventricles, supplying systemic, pulmonary, & coronary blood flow
What is always present? |
Truncus Arteriosus
VSD |
|
|
Underdevelopment of the left heart that results in a small left heart, & the right ventricle is forced to do all the work. This results in inadequate systemic circulation & pulmonary venous hypertension. Infants quickly develop cyanosis, dyspnea, & hepatomegaly. Cardiomegaly develops rapidly on chest radiograph. ECG shows RVH
|
Hypoplastic Left heart
|
|
|
A 7 yo girl presents to the office w/ a 3 wk hx of progressive dyspnea, malaise, & fatigue. She recently recovered from a viral syndrome. Physical examination is remarkable for a holosystolic murmur & hepatomegaly
|
Myocarditis
|
|
|
What are the MCC of Myocarditis?
|
Viruses = Adenovirus & Coxsackie B
|
|
|
What is the most common presentation of Myocarditis?
|
Heart failure
-less common are arrhythmias & sudden death |
|
|
What does CXR show in Myocarditis?
What does ECG show? |
Large heart & pulmonary edema
Sinus tachycardia, reduced QRS complex, & abnormal S & ST waves |
|
|
Characterized by thickened, white, fibroelastic endocardium. Clinical manifestations include congestive heart failure, dyspnea, & poor feeding in infants
|
Endocardial Fibroelastosis
Heart transplantation is indicated after failure of medical management of CHF |
|
|
A 6 yo girl complains of severe joint pains of her elbows & wrists. She has had a fever for teh past 4 days. Past hx reveals a sore throat 1 month ago. Exam is remarkable for swollen, painful joints & a heart murmur.
|
Acute Rheumatic fever
|
|
|
What are the major criteria for Acute Rheumatic Fever?
|
1. Carditis
2. Polyarthritis 3. Erythema marginatum 4. Chorea 5. Subcutaneous nodules JONES = joints, O for heart shape, Nodules, Erythema, Sydenham chorea |
|
|
What is the treatment for Acute Rheumatic Fever?
|
-rx of the Strep infection & monthly penicillin prophylaxis
-Salicylates help control the arthritis & carditis -Steroids are used when there is carditis with heart failure |
|
|
What is teh most common complication of Acute Rheumatic Fever?
|
Valvular disease
-in order of frequency: Mitral, Aortic, Tricuspid, Pulmonary |
|
|
A 6 yo boy has had high intermittent fevers for 3 weeks, accompanied by chills. He has a past history of biscuspid aortic valves & recently had dental work
|
Endocarditis
|
|
|
Most common pathogen of endocarditis after dental work
|
Strep viridans
|
|
|
MC pathogen of endocarditis if no underlying heart disease is present
|
S. aureus
|
|
|
What is teh cause of Primary HTN?
|
Unknown underlying cause
Predisposing factors include: -hereditary -salt intake -stress -obseity |
|
|
All children w/ Secondary HTN should have what done?
|
Renal evaluation including culture, US, renin levels, BUN, & Creatinine
|

