![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the primary purpose of the musculoskeletal system?
|
physical internal support
|
|
|
What is an example of an exoskeleton?
|
arthropods
|
|
|
What is an endoskeleton?
|
Like what humans have. An inside skeletal system.
|
|
|
What is the axial portion of the skeleton?
|
The axial skeleton is the basic
framework of the body, consisting of the skull, the vertebral column, and the rib cage. |
|
|
What is the appendicular portion of the skeleton?
|
limb bones and the pelvic
and pectoral girdles. |
|
|
What are the two major components of the skeletal system?
|
bone and cartilage
|
|
|
What is cartilage made of?
|
chondrin
|
|
|
What is chondrin secreted by?
|
chondocytes
|
|
|
Most cartilage has blood vessels. (T or F)
|
False. Most cartilage is avascular.
|
|
|
Cartilage does not have nerves. (T or F)
|
True. It is devoid of nerves.
|
|
|
How does cartilage receive nourishment?
|
from capillaries in nearby connective tissue and via diffusion from bone.
|
|
|
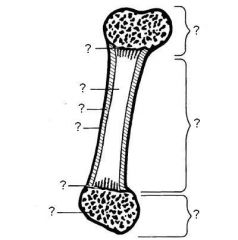
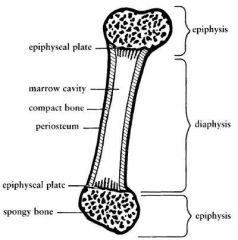
What are the two types of bone?
|
compact bone and spongy bone
|
|
|
In what type of bone is bone marrow located?
|
spongy bone
|
|
|
What is the function of red bone marrow?
|
It is involved in blood cell formation.
|
|
|
What is the function of yellow bone marrow?
|
It stores fat which the body consumes as a last resort in cases of extreme starvation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
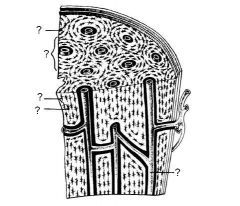
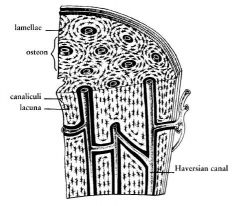
What are the two organic components of the bone matrix?
|
collagen fibers and glycoproteins
|
|
|
what are the six inorganic components of the bone matrix?
|
calcium, phosphate, hydroxide, sodium, potassium and magnesium ions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
what page did you leave off on?
|
131
|
|
|
What are osteoclasts involved in?
|
bone resorption
|
|
|
What are the two subcategories of bone formation?
|
endochondral ossification or intramembranous ossification
|
|
|
What is the basis behind endochondral ossification?
|
existing cartilage
is replaced by bone |
|
|
What is the basis behind intramembranous ossification?
|
connective tissue is transformed into, and replaced by bone.
|
|
|
What is the basis behind bone remodeling?
|
Bone remodeling is a life long process where old bone is removed from the skeleton (a sub-process called bone resorption) and new bone is added (a sub-process called ossification or bone formation). Calcium and phosphate are released (from old bone) into the blood then reabsorbed to make new bone.
|
|
|
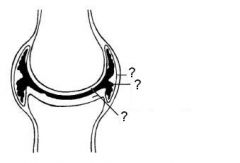
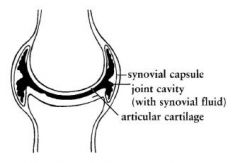
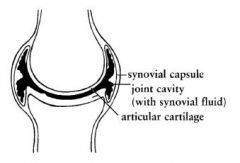
What is the purpose of synovial fluid?
|
to lubricate the joint
|
|
|
In a joint, what is the purpose of articular cartilage?
|
It is smooth and reduces tension during movement.
|
|
|
|
|
|
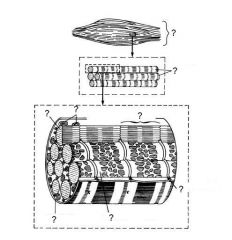
What are the three types of muscle in mammals?
|
skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle is innervated by the ____.
|
somatic nervous system
|
|
|
|
|
|
Due to the various bands in this type of muscle is also referred to as striated muscle. What type of muscle am I talking about?
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers have two subcategories. What are they?
|
White fibers & Red fibers
|
|
|
What are the unique features of white skeletal muscle fibers?
|
high myoglobin content / many mitochondria - This muscle is capable of sustained vigorious activity.
|
|
|
What are the unique features of red skeletal muscle fibers?
|
little myoglobin content / few mitochondria - This muscle is capable of a great rate of contraction.
|
|
|
White muscle fibers are also known as:
|
fast-twitch fibers
|
|
|
Red muscle fibers are also known as:
|
slow-twitch fibers
|
|
|
What kind of action is smooth muscle responsible for?
|
Smooth muscle is responsible for involuntary actions
|
|
|
What system is smooth muscle controlled by?
|
autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
T or F: Smooth muscle cells possess one centrally located nucleus.
|
True
|
|
|
Why is smooth muscle called smooth muscle?
|
They lack the striations of skeletal muscle.
|
|
|
What is myogenic activity?
|
Having the property of reflexively contracting without nervous stimulation.
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle is innervated by what?
|
autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
T or F: cardiac muscle, unlike smooth muscle, is not myogenic.
|
False. They both are myogenic.
|
|
|
What does a flexor muscle do?
|
contracts to decrease the angle of a joint
|
|
|
What does a extensor muscle do?
|
contracts to straighten the joint
|
|
|
What does a abductor muscle do?
|
moves a part of the body away from the body's midline
|
|
|
What does a adductor muscle do?
|
moves a part of the body toward the midline
|
|
|
What is the principle behind synergistic muscles?
|
Synergistic muscles are groups of muscles that work together to cause the same movement.
|
|
|
What is the major function of connective tissue?
|
To bind and support other tissue
|
|
|
Loose connective tissue has three types of fibers. What are these three fibers?
|
collagenous fibers; elastic fibers; reticular fibers
|
|
|
What are the two types cell types in connective tissue?
|
fibroblasts and macrophages
|
|
|
What is the key property of collagenous fibers which make up some of the connective tissue?
|
have great tensile strength
|
|
|
What is the key property of elastic fibers which make up some of the connective tissue?
|
endow connective tissue with resilience
|
|
|
What is the key property of reticular fibers which make up some of the connective tissue?
|
are branched, tightly woven fibers that join connective tissue to adjoining
tissue. |
|
|
What is the purpose of ligaments?
|
to hold two bones together
|
|
|
What is the purpose of creatine phosphate?
|
ATP is created without the supply of extra oxygen.
|
|
|
What oxygen related property does myoglobin have?
|
Myoglobin is a hemoglobin-like protein found in muscle tissue. Myoglobin
has a high 02 affinity; it binds to 02 from the bloodstream and holds onto it. |
|
|
How does myoglobin act during strenuous exercise?
|
During strenuous exercise, when muscle cells rapidly run out of available
0b myoglobin releases its 02' In this way, myoglobin acts as an additional oxygen reserve for active muscle. |

