![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The sum of all interior angles in a triangle is... |
...180 degrees. |
|
|
The perimeter of a triangle is... |
... the sum of all sides. |
|
|
Formula for the area of a triangle... |
Area = ½(Base) x (Height) |
|
|
Every side of a triangle must be longer... |
...than the difference of the lengths of the other two sides. |
|
|
Every side of a triangle must be shorter... |
...than the sum of the lengths of the other two sides. |
|
|
Definition of an Isosceles Triangle: |
Two sides are equal and two angles are equal. |
|
|
Definition of an Equilateral Triangle: |
Three sides are equal and all angles equal 60°. |
|
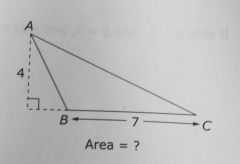
One base of a triangle is 7. The height drawn to the base is 4. Even though the height drawn to the base meets the base at a point that is on the extension of the base... |
...the height is still 4, and the formula Area = ½(Base) x (Height) applies. |
|
|
Parallel lines will never intersect. When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal... |
...corresponding angles are equal. |
|
|
Vertical angles are... |
...pairs of equal and opposite angles formed by the intersection of two straight lines. |
|
|
The sum of angles around a point is... |
...360°. |
|
|
A straight line is equivalent to an angle of... |
...180°. |
|
|
Perpendicular lines make an angle of... |
...90°. |
|
|
A right triangle has... |
...one 90° angle. |
|
|
The longest side of a right triangle is called... |
...the hypotenuse. |
|
|
In a right triangle, if the sides are a, b, and the hypotenuse is c, then... |
a² + b² = c² (Pythagorean theorem) |
|
|
A Pythagorean triplet consists of three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a2 + b2 = c2. Two examples are... |
3:4:5 5:12:13 |
|
|
For a right triangle for which the other two angles are 45° and 45°, the relationship between the sides will be... |
x : x : x√2 in which x√2 is the hypotenuse. This relationship can also be expressed as 1 : 1 : √2 |
|
|
For a right triangle for which the other two angles are 30° and 60°, the relationship between the sides will be... |
x : x√3 : 2x where 2x is the hypotenuse. This relationship can also be expressed as 1 : 2 : √3 (where 2 is the hypotenuse) |
|
|
Formula for the area of a circle: |
πr² |
|
|
Formula for the circumference of a circle: |
2πr = πd (where r is radius, and d is diameter) |
|
|
The length of an arc as a fraction of a circle's circumference is equal to... (arc length/circumference) |
...the degree measure of the corresponding central angle as a fraction of 360. arc length/circumference = n/360 |
|
|
The area of a sector as a fraction of a circle's area is equal to... (sector area/area) |
...the degree measure of the corresponding central angle as a fraction of 360. sector area/area = n/360 |
|
|
A line that has exactly one point in common with a circle is... |
..tangent to the circle, and it is perpendicular to the radius. |
|
|
If a triangle is inscribed in a circle so that one of its sides is a diameter of the circle... |
...then the triangle is a right triangle. |
|
|
A polygon is... |
...a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments. |
|
|
The sum of the interior angle measures of a polygon with n sides is equal to... |
(n - 2)180° |
|
|
A parallelogram is... |
...a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel. |
|
|
Parallelograms include... |
...rectangles and squares. |
|
|
In a parallelogram, the opposite sides are... |
...equal in length. |
|
|
In a parallelogram, the opposite angles are... |
...equal. |
|
|
Formula for the area of a parallelogram: |
Area = Base x Height |
|
|
In a parallelogram, the diagonals... |
...bisect each other. |
|
|
Formula for the area of a trapezoid: |
Area = ½(the sum of the bases)(height) |
|
|
2√2 divided by 2, or 2√2/2 is... |
2 |
|
|
Almost all solids on Test Day are uniform solids, which are... |
...solids in which the measure of each dimension is constant through the entire object. |
|
|
To determine the volume of a uniform solid, we... |
...multiply the area of the base by the area of the height. |
|
|
Formula for the volume of a cylinder: |
πr²h (where h is height) |
|
|
Formula for the volume of a rectangular solid: |
ℓ x w x h length x width x height |
|
|
Formula for the surface area of a rectangular solid: |
SA = 2(ℓw + ℓh + wh) |
|
|
Formula for the surface area of a cube with an edge of length e: |
SA = 6e² |
|
|
Formula for the surface area of a right circular cylinder: |
SA = 2πr² + 2πrh |
|
|
Aside from 3:4:5 and 5:12:13, list three more Pythagorean triples: |
7:24:25 8:15:17 |

