![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
--- States of Actin Filaments ---
1) 2) 3) |
1) Nucleation
2) Elongation 3) Steady State |
|
|
--- States of Actin Filaments ---
Lag Phase? |
Nucleation
|
|
|
--- States of Actin Filaments ---
Growth Phase? |
Elongation
|
|
|
--- States of Actin Filaments ---
Equilibrium Phase? |
Steady State
|
|
|
*** *** is the term used to describe the degradation/construction nature of microtubules.
|
Dynamic instability
|
|
|
*** are made out of 13 protofilaments.
|
Microtubules
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Protofilaments are composed of these subunits... |
1) α-tubulin and β-tubulin
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
Composed of # ***... |
13 protofilaments
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Though all subunits have *** 2) only the *** subunit gets ***. |
1) GTP
2) β-tubulin --- hydrolyzed |
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) The *** end has the α-tubulin subunit. |
1) minus
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) The *** end has the β-tubulin subunit. |
1) plus
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Newly formed mictotubules are on the *** end 2) where the *** subunit is. |
1) plus
2) β-tubulin |
|
|
1) *** *** takes place in microtubules.
2) *** *** takes place in actin. |
1) Dynamic stability
2) Tread milling |
|
|
1) Dynamic stability takes place in ***.
2) Tread milling takes place in ***. |
1) microtubules
2) actin |
|
|
*** is a drug from the Pacific Yew.
|
Taxol
|
|
|
Taxol is a drug from the *** ***.
|
Pacific Yew
|
|
|
1) Acrylamide gel fuck up *** ***
2) causing the disease *** ***. |
1) intermediate filaments
2) peripheral neuropathy |
|
|
*** is the rate-limiting step for microtubule formation.
|
Nucleation
|
|
|
γ-TuRC?
|
γ-Tubulin Ring Complex
|
|
|
*** acts as a scaffold for α/β-tubulin dimers to begin polymerization.
|
γ-TuRC
γ-Tubulin Ring Complex |
|
|
Nucleation is the rate-limiting step for *** formation.
|
microtubule
|
|
|
*** is the first subunit attached to γ-TuRC followed by ***.
|
α-tubulin
β-tubulin |
|
|
--- MicroTubule Organizing Center ---
1) Is also known as the ***. 2) γ-TuRC serve as *** sites. 3) Pair of *** are located in the cytosol. |
1) centrosome
2) nucleating 3) Centrioles |
|
|
MTOC?
|
MicroTubule Organizing Center
|
|
|
Microtubules grow from γ-TuRC of the *** AKA ***.
|
centrosome
MicroTubule Organizing Center |
|
|
*** grow from γ-TuRC of the centrosome AKA MicroTubule Organizing Center.
|
Microtubules
|
|
|
--- Microtubules ---
1) Accidental loss of *** *** causes rapid shrinkage and its gain causes rapid growth. |
1) GTP cap
|
|
|
GDP-tubulin dimer forms a *** protofilament.
|
curved
|
|
|
GTP-tubulin dimer forms a *** protofilament.
|
straight
|
|
|
1) ***-tubulin dimer forms a curved protofilament.
2) ***-tubulin dimer forms a straight protofilament. |
1) GDP
2) GTP |
|
|
1) *** only walks towards negative end of microtubule...
2) It complexes with *** protein to 'walk.' |
1) Dynein
2) kinesin |
|
|
Draw the flagellum.
|
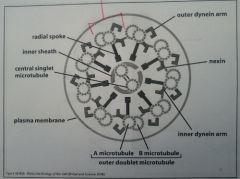
|
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
1) # outer *** microtubules. 2) # central *** microtubules. |
1) 9 --- doublet
2) 2 --- singlet |
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Outer doublet microtubules are made up of... 1) Complete *** microtubule. 2) Incomplete *** microtubule. |
1) A
2) B |
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
1) How many parts? 2) How many inner parts? 3) How many outer parts? 4) Missing? |
1) 9
2) 2 3) 6 4) Plasma membrane |
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Name Inner Parts... |
(2) Inner Sheath
(2) Central singlet microtubule |
|
|
--- Flagellum ---
Name Outer Parts... inside to outside |
1) Radial Spoke
2/3) Inner/Outer dynein arm 4) Nexin 5/6) Outer doublet microtubule(complete A / incomplete B microtubule) |
|
|
G-Actin?
|
globulin actin
|
|
|
G-actin uses *** protofilaments.
|
13
|
|
|
F-actin uses *** protofilaments.
|
11
|
|
|
ARP?
ARC? |
Actin-Related Proteins
Actin-Related Complexes |
|
|
ARC can attach to actin filaments at *** angles.
|
70 degree
|
|
|
Actin polymerization is *** faster at *** end than *** end.
|
10x
positive negative |
|
|
*** is a family of actin-binding proteins which disassembles actin filaments.
|
Cofilin
|
|
|
*** gets rid of old actin.
|
Cofilin
|
|
|
A *** is something formed out of four sub-units.
|
tetramer
|
|
|
1) These two filaments are similar....
2) This filament is different.... |
1) actin --- microtubules
2) intermediate filaments |
|
|
1) α-helical region in ***
2) coiled-coil *** 3) ***(adjective) *** of two coiled-coil dimers 4) # *** packed together end to end 5) # tetramers twisted into a rope-like *** |
1) monomers
2) dimer 3) staggered tetramer 4) many tetramers 5) eight --- filament |
|
|
*** *** fuck up intermediate filaments and cause peripheral neuropathy.
|
Acrylamide gel
|
|
|
1) ALS?
2) AKA *** 3) Disease of the *** *** 4) Usually causes death in # ***. |
1) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
2) Lou Gehrig's disease 3) motor neurons 4) 3 years |
|
|
1) *** is a protein used to determine the source of metastasized cancer cells.
|
1) Keratin
|
|
|
1) *** is cancer of the epithelial.
2) *** is cancer of the connective tissue. |
1) Carcinoma
2) Sarcoma |
|
|
1) Keratins are polymers of *** ***.
2) They are characterized VIA their unique ***. |
1) intermediate filaments
2) kDa |
|
|
These drugs affect microtubules
1) Colchicine works by *** 2) Vineblastine/Vincristine works by *** 3) Taxol works by *** |
1) preventing polymerization
2) preventing polymerization 3) stabilizing |

