![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A joint in which the bones are connect by fibrocartilage |
Symphysis |
|
|
The turning of a bone around its own long axis |
Rotation |
|
|
Movable attachment of a muscle |
Insertion |
|
|
Freely movable joints |
Diarthrosis |
|
|
Freely movable joints exhibiting a joint cavity; also called a diarthrosis |
Synovial joint |
|
|
Bones united by cartilage; no joint is present |
Cartilage noise joints |
|
|
Movement of a body part so that it outlines a cone in space |
Circumduxtion |
|
|
Immovable joint |
Synarthrosis |
|
|
Inflammation of tendon sheaths, typically causes by overuse |
Tentonitis |
|
|
When chondrocytes divide and form new matrix, it leads to an expansion of the cartilage tissue from within. This process is called |
Interstitial growth |
|
|
The axial skeleton includes |
The ribs |
|
|
Which of the following is mismatched |
Short bones: examples include the vertebrae |
|
|
In adults yellow marrow is located |
In the medullary cavity of the long bones |
|
|
The structural unit of compact bone |
Osteon |
|
|
The notable hardness of the bone is attributed to |
The presence of inorganic hydroxyapatities |
|
|
What is the most common type of cartilage found between bones in freely movable joints |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Yellow bone marrow contains large percentage of |
Fat |
|
|
Spongy bones are made up of a framework called |
Trabeculae |
|
|
**(short answer question) _________ Are multinucleated cells that destroy bone |
Osteoclasts |
|
|
T/F Short irregular and flat bones have large marrow cavities in order to keep the weight of the bone light |
False |
|
|
T/F The structural unit of compact bone (osteon) resembles the growth rings of a tree trunk |
True |
|
|
**Short Answer Question. A round or oval hike through a bone that contains blood vessels and or nerves is called |
Forman |
|
|
Which bone cells form bone? |
Osteoblasts |
|
|
What indicates that a long bone has reached its adult length |
Closure of the epiphyseal plate |
|
|
Ossification of the ends of long bones |
Is produced by secondary ossification centers |
|
|
In some cases the epiphyseal plate of the long bones of children closes to early. What might be the causes? |
Elevated leveled of sex hormones |
|
|
Which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system? |
Communication |
|
|
** Short Answer. A bone embedded in a tendon is called ______ |
Sesamoid |
|
|
Functional classification of joints is based on |
The amount of movement allowed by the joint |
|
|
Which of the following does not represent a structural classification of joints |
Diarthrosis |
|
|
Which one is correctly paired? |
Synchondroses: a plate of hyaline cartilage unites the bone |
|
|
Most joints of the body are classified as ______ joints |
Synovial |
|
|
Lines the inside of the fibrous capsule of a joint |
The synovial membrane |
|
|
Synovial fluid does not: |
Strengthen synovial joints |
|
|
Which of the following is correctly paired? |
Multiaxial movement: movement in or around three planes |
|
|
Extension is an example of ______ movement |
Angular |
|
|
When a person makes a pinching motion with their thumb and forefinger they are exhibiting _____ movement |
Oppositional |
|
|
The shoulder and hips are examples of |
Ball and socket joints |
|
|
Which ligament would one tap to generate the knee-jerk reflex |
Patellar ligament |
|
|
Which of the following is correctly matched |
Osteoarthritis: degenerative joint disease |
|
|
T/F The origin of a muscle is attached to the movable bone |
False |
|
|
What joint permits essentially no movement |
Synarthrotic |
|
|
Which of the following refers to a joint that is immovable? |
Synarthrosis |
|
|
**Short Answer. The joint between the frontal and parietal bone is called a _____ joint. |
Suture |
|
|
Using a structural classification what type of joint is the epiphyseal plate? |
Cartilaginous joint |
|
|
____ Are cartilaginous joints |
Synchondroses |
|
|
**Short Answer. The type of joint between the carpal and the first metacarpal is a ______ joint |
Saddle |
|
|
**Short Answer. Moving yoir jar forward causing an underbite is called |
Protraction |
|
|
** Short answer. Turning the foot medial at the interarsal joint would be called |
Inversion |
|
|
Which type of joint allows opposition |
Saddle joint |
|
|
Synovial joints are classified into six main categories bases on |
The movements they allow |
|
|
Pointing the toes is and example of |
Plantar flexion |
|
|
Which joint has sacrificed stability to provide freedom of movement |
Shoulder |
|
|
Bending your head back until it hurts is an example of |
Hyperextension |
|
|
The terms inversion and eversion pertain only to the |
Feet |
|
|
Which movement increases the angle between bones |
Extension |
|
|
T/F Flexion on the ankle so that the superior aspect of the foot appraises the skin is called dorsiflexion |
True |
|
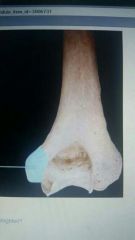
|
Lateral epicondyle |
|
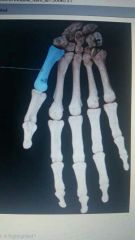
Which bone is highlighted |
1st metacarpal |
|
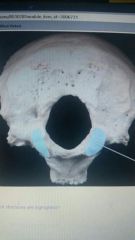
Which structure are highlighted? |
Occipital condyles |
|
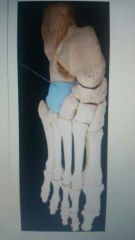
Which bone is highlighted? |
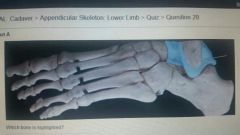
Cuboid |
|
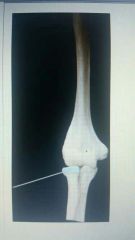
Which structure is highlighted? |
Head of radius |
|
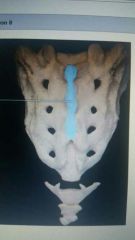
Which structure is highlighted? |
Transverse process |
|
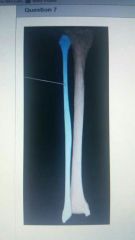
Which bone is highlighted? |
Fibula |
|
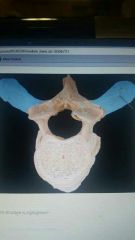
Which structure is highlighted? |
Median sacral crest |
|
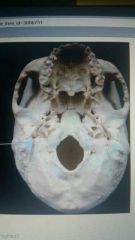
Which structure is highlighted |
Mastodon process |
|
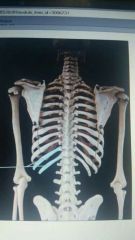
Which structures are highlighted |
Floating ribs |
|
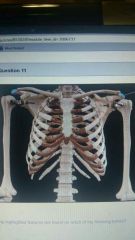
The highlighted features are found on which of the following bones? |
Scapula |
|
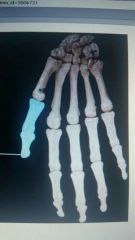
How would you classify the group of highlighted bones? |
Long bones |
|
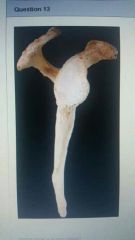
Which bone is in this image? |
Scapula |
|
|
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the parietal bones? |
They form the base of the skull |
|
|
Which is NOT a cranial bone? |
Vomer bone |
|
|
Which is NOT a cranial bone? |
Vomer bone |
|
|
How many lumbar vertebrae are there in a normal adult? |
Five |
|
|
Which of the following is correctly matched? |
Scoliosis: abnormal lateral curvature |
|
|
The spinal cord passes through the |
Vertebral foramina |
|
|
Which of the following does not form part of the thoracic cage? |
Clavicle |
|
|
Which of the following is a marki NV of the humerus |
Deltoid tuberosity |
|
|
False statement |
The pelvic outlet is narrower in a female than in a male. |
|
|
One of the roles of the fontanelles is to |
Allow for brain growth in the infant |
|
|
Which of the following bone groups is a part of the axial skeleton |
Facial bones |
|
|
Which bone is considered to be the keystone of the cranium |
Sphenoid |
|
|
What is the major function of the axial skeleton |
Provide central support for the body and protect internal organs |
|
|
The superior nasal conch is part of which bone? |
Ethmoid |
|
|
They hyoid bone is unique because it |
Is the only bone of the body that does not articulate with any other bone |
|
|
T/F The foramen magnum goes through the occipital bone |
True |
|
|
**Short answer The _______ is the primary bone in the septum of the nose |
Vomer |
|
|
T/F The dens articulates with the axis |
False |
|
|
Which of the following is the abnormal curve often seen in the pregnant woman as they attempt to preserve their center of gravity to ward the end of the pregnancy |
Lordosis |
|
|
What is the major function of the intervertebral discs? |
Absorb shock |
|
|
Which of the following is an abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebral column often seen in the thoracic region |
Scoliosis |
|
|
Which part of the vertebral column receives the most stressed by bearing most of the weight of the body |
the lumbar region |
|
|
T/F Ribs number 11 and 12 are true ribs because they have no anterior attachments. |
False |
|
|
T/F The layman's name for the scapula is the collarbone |
False |
|
|
Which of the following bone is part of the appendicular skeleton |
Humerus |
|
|
The articulation that most closely resembles a hinge in the body involves which bones |
Humerus-ulna |
|
|
When you hit your elbow and say you hit your funny bone you actually hit a nerve that runs across the bone surface. Over which bone can this nerve be found? |
Humerus |
|
|
T/F In the anatomical position the lateral forearm bone is the radius. |
True |
|
|
The "true wrist" or carpus consists of |
A group of eight short bones united by ligaments |
|
|
**Short answer. The smallest short bone in the hand is the |
Pisiform |
|
|
**Short answer. The largest foramen in the body is the ____ foramen. |
Obturator |
|
|
Which bone is in direct contact with the first metatarsal? |
Medial cuneiform |
|
|
**Short answer. The heel bone is called the |
Calcaneus |
|
|
The membranous areas between the cranial bones of the fetal skull are called |
Fontanelles |
|
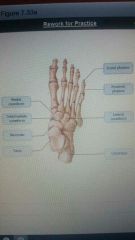
|
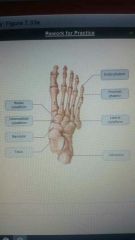
|
|
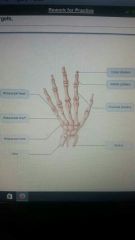
|
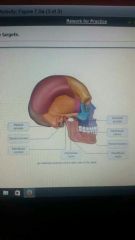
|
|
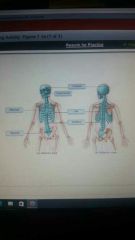
|
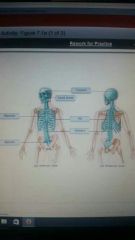
|
|
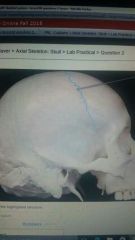
Identify the highlighted structure |
Coronal suture |
|
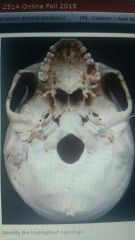
Identify |
Carotid canal |
|
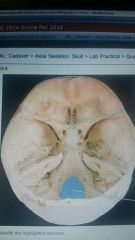
|
Foramen magnum |
|
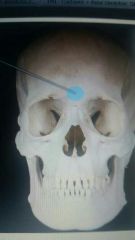
Identify the structure |
Glabella |
|
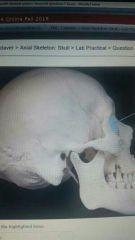
|
Lacrimal |
|
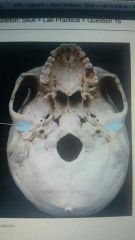
|
Mandibular fossa |
|
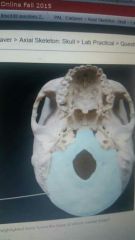
|
Posterior |
|
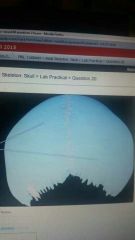
|
Parietal |
|
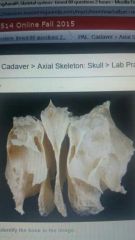
|
Ethmoid bone |
|
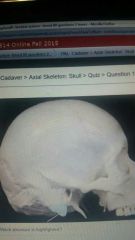
|
Mastoid process |
|
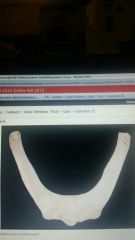
|
Hyoid |
|

|
Sacrum |
|
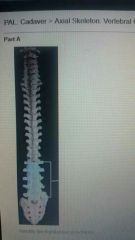
|
Lumbar |
|
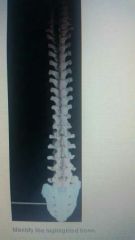
|
Sacrum |
|
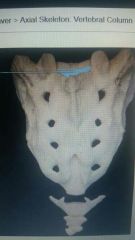
|
Sacral canal |
|
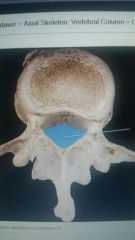
|
Vertebral foramen |
|
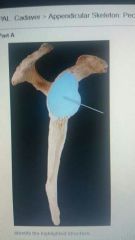
|
Glenside cavity |
|
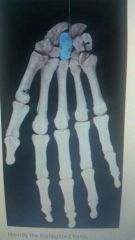
|
Capitate |
|
|
Greater tubercule |
|
|
Deltoid tuberosity |
|
|
Lesser tubercle |
|
|
Pisiform |
|
|
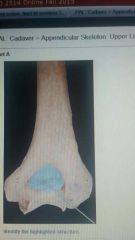
Olecranon fossa |
|

|
Styloid process |
|
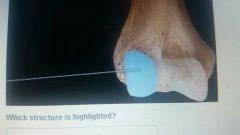
|
Capitulum |
|
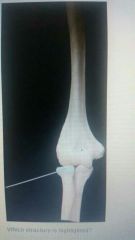
|
Head of radius |
|
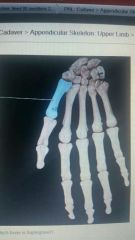
|
1st metacarpal |
|
|
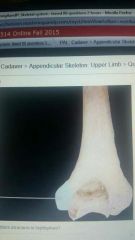
Medical epicondyle |
|
|
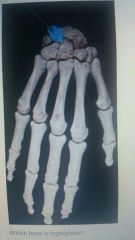
Lunate |
|
|
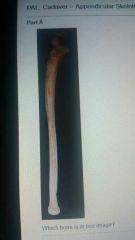
Ulna |
|
|
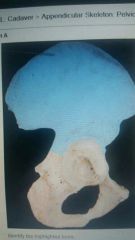
Ilium |
|
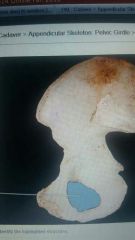
|
Obturator foramen |
|
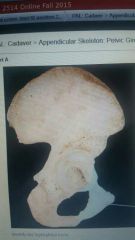
|
Pubis |
|
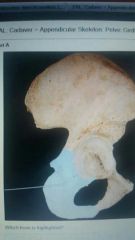
|
Ischium |
|
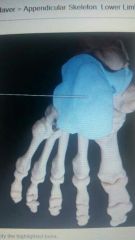
|
Calcaneus |
|
|
Distal phalanx |
|
|
Fibula |
|
|
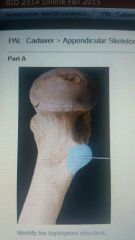
Lesser trochanter |
|

|
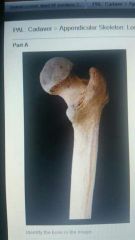
Linea aspera |
|
|
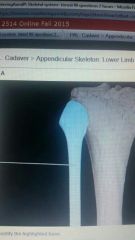
Femur |
|
|
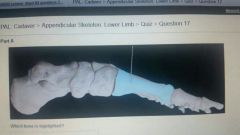
1st metatarsal |
|
|
Talus |
|
|
Each of the following bones is part of the pelvic girdle accept the |
Femur |
|
|
Mary fractured her pisiform bone in a fall. What part of her body was injured |
Wrist |
|
|
The 11th and 12th ribs are called floating ribs because they lack |
An anterior attachment to the sternum |
|
|
The foramen magnum would be found in the ______ bone |
Occipital |
|
|
The olecranon process is found on the |
Ulna |
|
|
What would you find in the lacrimal fossa |
The lacrimal sac |
|
|
When standing on the way most of your weight is transmitted to the ground by the |
Talus and calcaneus |
|
|
Which of the following bones would you most likely be involved in surgery to remove a tumor or the pituitary gland |
The Sella turcica |
|
|
Which of the following is not part of the axial skeletal |
Pectoral girdle |
|
|
Which of the following is the heel bone |
Calcaneus |
|
|
The crista galli is a projection from which bone |
Ethmoid |
|
|
At its distal end the femur articulates with the |
Tibia |
|
|
A common injury in the winter is a fall in which someone hits the back of his or her head on the ice which bone is most likely to be involved in this type of fall |
Occipital |
|
|
How many regions of the vertebral column are there |
Five |
|
|
Sutures connect all the bones of the skull except the |
Mandible |
|
|
The calvaria of the skull is another name for the |
Cranial vault |
|
|
The frontal sinuses are located |
Lateral to the glabella |
|
|
Which of the following cranial bones receives the condyle of the Mandible |
The temporal bone |
|
|
Which of the following sinuses are the high risk of infection spreading from the middle ear |
The mastoid sinuses |
|
|
Which of the following features is most likely to contain sutural bones |
The lambdoid suture |
|
|
Where would a dentist lidocaine to prevent pain in the lower teeth |
The mandibular foramen |
|
|
In a _____ the vertebral column is formed from 33 separate bones |
Fetus |
|
|
Which of the following spinal deformities is quite common during childhood in females |
Scoliosis |
|
|
C7 is referred to as the vertebra prominent because |
Its spinous process is larger than those of the cervical vertebrae |
|
|
The pectoral girdle does not quite satisfy the features of a true girdle because |
Posteriorly the medial ends the scapulae do not join each other |
|
|
The jugular notch on the sternum is |
In line with the second and third thoracic vertebra where the left common carotid artery is issued from the aorta |
|
|
When a person attempts to break his or her fall with an outstretched hand he or she often lines up with |
A Colles fracture |
|
|
What is the deepest bone in the skull |
Ethmoid |
|
|
Which of the following is a congenital abnormality of the appendicular skeleton |
Dysplasia of the hip |

