![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
States of matter |
Different forms of matter, in which observable properties are different (ex: gas, liquid, solid) |
|

Gas |
(Vapor) has no fixed volume or shape however can conform to the shape of the container. Molecules move fast and are far apart. |
|

Liquid |
Has distinct volume independent of its container, but no specific shape. Molecules move fast but are packed closely together. |
|

Solid |
Has both a definite shape and volume. Molecules still move fast, however do not have much space to move freely. |
|

Pure substance |
(Or just substance) matter that has distinct properties and a composition that doesn't vary from sample to sample. (Ex: water and table salt *sodium chloride*) |
|
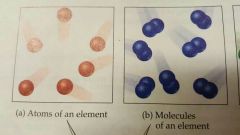
Elements |
Substances that cant be decomposed into smaller substances. Each element is composed of only one kind of atom (118 known elements) *all substances are either elements or compounds* |
|

Compounds |
Are substances composed of two or more elements. They contain two or more kinds of atoms (ex: water *hydrogen and oxygen*) |
|

Mixture |
Combinations of two or more substances in which each substance retains its chemical identity. |
|

Homogeneous mixtures |
Mixtures that are uniform in composition. (also called a Solution *example: salt or sugar dissolved in water) |
|

Heterogenous Mixture |
A mixture that does not have the same composition, properties, and appearance throughout. (Example: rocks, wood *they vary in appearance and texture*) |
|
|
Physical properties |
Characteristics that can be observed without changing the identity and composition of the substance (example: color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, hardness) |
|
|
Chemical properties |
Describe the way a substance may change or react to form other substances. (Example: flammability) |
|
|
Intensive properties |
Characteristics that do not depend on the amount of substance. (Example: temperature, melting point) |
|
|
Extensive properties |
Characteristics that depend on the amount of the sample. (Example: mass and volume) |
|
|
Filtration |

A form of separating mixtures |

