![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
204 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Computer Forensics?
|
The procedural preservation, identification, extraction, documentation, and interpretation of computer media for evidence and/or root cause analysis.
|
|
|
What does Computer Forensics involve?
|
Involves scientifically examining and analyzing data from computer storage media so that the data can be used as evidence in court.
|
|
|
What methods of Investigation do Computer Forensics and Network Forensics use, Differentiate them!
|
Network forensics uses log files to determine: When users logged on or last used their logon IDs, Which URLs a user accessed, How he or she logged on to the network, and from what location
Computer investigations functions : Vulnerability assessment and risk management, Network intrusion detection and incident response, Computer investigations. |
|
|
Where the partition table is located and how is it represented using EnCase?
|
MBR contains a 64-byte partition table located at byte offsets 446 to 509. Each of up to four partitions is described by 16 bytes in the 64-byte table. The MBR reads its own partition table for the boot indicator byte that marks one of the partitions as the active partition.
|
|
|
What type of information is in the partition table?
|
Boot Byte,Starting Head ,Starting Cylinder
& Sector ,Partition Type ,Ending Head ,Ending Cylinder & Sector,Relative Sector ,Total Sectors |
|
|
What does a security incident comprises of?
|
An unexpected, unplanned event that could have a negative impact on IT resources, requires immediate action to prevent further negative impacts, and violates security policies of circumvents security mechanisms.
|
|
|
How can you tell if a partition is active?
|
byte offset 446 will have a hex value 80 denoting it is active
|
|
|
How can you tell if a partition is not active?
|
byte offset 446 will have a hex value of 0
|
|
|
What are the two types of incidents?
|
1.Examine computers used in committing a crime. (Computer provide a location for data relative to their criminal activities.)
2. Examine computers targeted in a crime. (Victims) |
|
|
How does an individual become EnCE certified?
|
-Possess licensed EnCase software with an order number.
-18 months total investigative experience with at least 6 months experience in computer forensic examinations. -Experience must be verified via signed application and endorsement -All application and supporting documents -Complete Phase I and Phase II of Exam or 80 hours of authorized classroom training with 18 months total investigative experience including 6 months of computer forensics examinations OR 3 hours of authorized classroom with 2years total investigative experience. |
|
|
What are the 5 rules of evidence?
|
1.Admissible
2.Authentic 3.Complete 4.Reliable 5.Believable |
|
|
Allocation unit
|
Same as a cluster
|
|
|
Cluster
|
1.Storage allocation units of 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, or more bytes
2. Assigned logical addresses as they are assigned by the OS vs. Sectors that are physical addresses. 3. Consist of one or more sectors, and a cluster is the smallest unit in which a file or directory can be stored |
|
|
Block
|
512 bytes each. Data Storage Unit, AKA allocation unit or cluster.
|
|
|
Metadata
|
Data within Data describing Data
|
|
|
Volume
|
A collection of addressable sectors that are used by an OS or application to store data.
|
|
|
Partition
|
A collection of consecutive sectors within a VOLUME, and those sectors are addressable by a single file system specific to and contained within that partition!
|
|
|
BCD
|
Boot Configuration Data. Is a file located in the Boot directory, which in turn is located in the root of the system volume. This file contains a database of boot-time configuration data, and, interestingly, the file format is the same as that of a registry hive file.
|
|
|
MBR
|
Master Boot Record. Is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives The MBR holds the information on how the logical partitions, containing file systems, are organized on that medium.
|
|
|
VBR
|
Volume Boot Record. First sector of the logical volume
|
|
|
FAT12
|
Supports 2^12 clusters theoretically or 4,084 in reality. Designed as a file system for floppy diskettes. 12-bit cluster addresses
|
|
|
FAT16
|
Supports 2^16 clusters theoretically or 65,524 in reality. 16 bit FAT entry. 16-bit cluster addresses
|
|
|
FAT32
|
Supports 2^32 clusters theoretically or 67,092,481 in reality. Overcame the limitation of 512 entries.
|
|
|
NTFS
|
New Technology File System. The most secure file system of all we have studied. 32-bit cluster addresses (28 bits used) => 228 clusters. Drive size up to 8TB with 32KB clusters. Can become slow and inefficient. Video applications and large databases often exceed FAT32 limitations
|
|
|
Who needs computer forensics and the general uses of computer forensics?
|
Law enforcement to: Defend the innocent, Prosecute the guilty, Prosecute crimes involving computers and other digital devices.
Military to: Prosecution of internal computer related crimes. Security Agencies: Anti-terrorism efforts, Protection of U.S. by provisions such as the patriot act. The general uses of computer forensics: Employee misconduct , What happened to this computer, Accidental deletion or possible malicious deletion of data by users, and what can be recovered |
|
|
What is evidence and where it may be
|
Evidence is: Porn, Emails, Accounting discrepancies, Finger prints, RAID 5..etc
Where may be: Undeleted files, Deleted files, Windows registry, Print spool files, Hibernation files, Temporary files …(.tmp), Slack space, Swap files, Browser cache, Removable media |
|
|
Obfuscation
|
To obscure, or attempt to hide something
|
|
|
The different hardware components?
|
Basically all hardware that makes up a complete computer, IE, ROM, RAM, Hard drive, CPU (Microprocessor), Mother board, Case, Heat Sink and Fan, Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) Controller , Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
|
|
|
What is a file system?
|
A system or method of storing and retrieving data on a computer system that allows a hierarchy of directories, sub-directories, and files.
|
|
|
Power-up sequence. View Diagram
|
1. Power Button
2. BIOS: The Bios immediately runs the POST and then prepares the system for the first program to run. 3. POST : Power On Self Test: Checks the system board, mem, keyboard, floppy, HD, ETC for presence and reliability. 4. BIOS From Add-in Cards: A dd in cards such as SCSI drives controller cards can have a BIOS on the card that loads at this time. These BIOS's normally detect devices and load information into the BIOS data area in RAM. 5. Load RAM with BIOS: A special RAM BIOS data area of 256 bytes contains results of the system check identifying the location of attached devices. 6 Check for boot sequence from either A drive or C drive 7. MBR (IF C) 8. Boot partition (If C) 9. Boot Record (If C) 10. IO.sys 11. Msdos.sys 12. Config.sys 13. Command.Com 14. Autoexec.bat |
|
|
4th Amendment
|
Part of the Bill of Rights which guards against unreasonable searches and seizures, along with requiring any warrant to be judicially sanctioned and supported by probable cause.
|
|
|
What is Slack Space?
|
Data between the end of the logical file to the end of the cluster containing the data. The unused space in a disk cluster.
|
|
|
What happens to deleted files?
|
Pointer to file is deleted and space is freed up as available by the OS
|
|
|
End of File
|
EOF or hex value of 0xFFFF. This is the last cluster in the chain
|
|
|
What does FAT consist of?
|
Consists of 2 major components:
1. Directory Entries 2. File Allocation Tables |
|
|
What are the major components of FAT
|
1.Reserved area for Volume Boot Sector
2.File Allocation Table area 3.Data Storage Area |
|
|
Advantages of using FAT?
|
?
|
|
|
Advantages of using NTFS?
|
Is more robust, providing stronger security, greater recoverability, and better performance with regard to read, write, and search capabilities. Among other features, it includes support for long filenames, a highly granular system of file permissions and access control, and compression of individual files and directories.
|
|
|
ISO 9660
|
Are file sytems for CD’s:
Revision of High Sierra, first standard of CDs uses 8 dot 3 file naming (only 8 character names, no file extensions allowed) Sub-directories only 8 deep files had to be contiguous |
|
|
Joilete
|
Are file sytems for CD’s:
Microsoft extension to ISO 9660 Files can be 64 characters long 8 layer deep subdirectories |
|
|
UDF
|
Are file sytems for CD’s:
Universal Disk Format Fairly new Uses technique called packet writing Allows for 255 character file names |
|
|
What is Reserved area on a disk?
|
Consists of the volume boot sector, often abbreviated as simply boot sector. The size of this reserved area is defined within the boot-sector data
|
|
|
What is reserved area on a disk used for?
|
The System Reserved partition is used to hold the system boot manager.
Consists of the volume boot sector, often abbreviated as simply boot sector. The size of this reserved area is defined within the boot-sector data, but most often FAT12 and FAT16 systems use only one sector for this data. FAT32 systems, the size of this area is likewise defined in the boot sector, but because it contains significantly more data, it will be several sectors in length (sectors 0, 1, and 2, with backups at sectors 6, 7, and 8), and the reserved area will usually be 32 sectors in length. |
|
|
Boot sectors 4 distinct segments?
|
1.Jump Instructions to the boot code
2.BIOS parameter block 3.Boot Code and Error Messages 4.Signatures such as the all important 55AA |
|
|
What is FAT1?
|
File Allocation Table
Located at the beginning of a FAT volume, immediately following the volume boot record. File allocation table track the allocation status of all clusters and also track fragmentation. |
|
|
What is FAT2?
|
Exact copy of Fat1
|
|
|
What are directory entries?
|
Critical for the FAT system
For every file and directory within a partition, a directory entry exists. 32 bytes long |
|
|
What does Bookmarking do?
|
References to specific files or data
critical skill |
|
|
File Directory Structure
|
Organization of files into a hierarchy of folders
|
|
|
Basics of NTFS
|
?
|
|
|
Maximum number of clusters supported by FAT
|
FAT12 4,084
FAT16 65,524 FAT32 67,092,481 |
|
|
What is the #1 safety concern to all 1st responders?
|
Personal Safety
|
|
|
What is needed prior to an investigation?
|
Planning is the most important task to have a successful investigation.
Know as much information before arriving at the location to minimize “unknowns”. Know the location for the investigation. Could there be weapons? Is it a business? Are the personnel involved dangerous, computer savvy? Do you think they have the capability of erasing data or circumventing the investigation? |
|
|
What are you looking for in an investigation?
|
What type of evidence is believed to be present? Are you searching for bootleg software
on a company computer? Are you looking for child pornography? Are you looking for a set of “cooked books” in an embezzlement case? |
|
|
What items need to be brought along for an investigation?
|
Bring toolkits, Latex gloves, Digital camera, Extension cords, UPS, Switch or hub, Crossover cables, Spare internal floppy drive, CD’s, EnCase bootable floppies, Extra hard drives, Field imaging software and storage, Lots of cables i.e. serial, SCSI, SATA etc, Tags or labels for evidence, logbook,
|
|
|
Securing the scene?
|
Security team – establish a perimeter, make entry, secure area
|
|
|
What are the different search authorities?
|
law enforcement setting, the authorization could be a search warrant, consent to search,
or a call from a victim whose computer system is in some way involved in their victimization, as in a network-intrusion case. In a non–law-enforcement setting, the authorization to search for evidence may be a directive from corporate counsel, it may be authorized by policy pursuant to an incident-response activation, or it may be a court order to a special master for the court in a civil matter. |
|
|
What teams are used in an investigation?
|
2 teams are designated
Security team – establish a perimeter, make entry, secure area. Search team – conduct the actual search Include the recorder Photographer Search and seizure specialist Digital evidence specialist |
|
|
How do you create a bootdisk or boot CD in EnCase?
|
Tools>Create Boot Disk and choose to either create a floppy, or choose ISO image to create a CD
|
|
|
What files do we need to change to create a forensic boot disk?
|
COMMAND.COM and IO.SYS
|
|
|
What 3 options do we have for boot disks?
|
Update existing boot floppy.
Overwrite disk with a boot floppy image. Change from a system disk to a boot floppy. |
|
|
What is HPA?
|
Host Protected Area
Purpose is to create a place at the end of the drive for vendors to store information (recovery, security, registration, and so on) that will not be seen by the BIOS and hence protected from user access or erasure |
|
|
What is DCO?
|
Dynamic Configuration Overlay
Intended as a means of limiting the apparent capacity of a drive. DCO space will appear at the end of the drive and is not seen by the BIOS |
|
|
DOS Boot Process?
|
Target computer is turned off.
Disconnect the power cord and inspect the interior Disconnect data cable from all hard drives Insert forensics boot disk. If a CD is used put a paper clip in hole to open up the CD player. Reconnect power cord and start the computer and enter the setup mode. Locate boot order and make note of the order then make a change to boot from either the floppy or the CD. Save the changes Verify that your boot environment works with the drives disconnected. If you are using a hard drive on the target machine to store the image then connect it and test the boot environment. If all is well turn off the machine by powering down and disconnecting the power cord. Reconnect the target hard drive. Reconnect the power cord and keep a hand on it just incase you have to abort. Boot to the boot disk. |
|
|
Network Cable Acquisition?
|
DEF: Using a network cable to acquire hard drives.
Reasons to use Network Acquisition: When you want to view the invisible HPA and DCO data. Acquiring data from a laptop. Gaining fast access to data, and Previewing data before acquiring. Network cable – Usually a crossover cable to allow 2 similar devices to directly connect. The transmit goes to the receive on one end and the other end the wires are switched to allow communication. |
|
|
What is error granularity?
|
This feature set was first offered with EnCase 5 and is available
in EnCase for Windows, DOS, and Linux. In versions of EnCase earlier than version 5, if an error was found in one sector, the remaining sectors in that block were zeroed out to increase the speed of the acquisition, meaning data was lost. Numerically, this means a block of data contains 64 sectors, or 32,768 bytes. If only one sector (512 bytes) were bad, 32,256 bytes of good data would have been zeroed out when brought into the evidence file |
|
|
What are the different types of FastBloc?
|
Allow you to view data directly in the Windows Explorer
Fastbloc classic-SCSI interface with host Fastbloc LE- Lab Edition IDE interface, better suited for permanent install Fastbloc FE - Field Edition allows for USB2 or 1394a (Firewire) host interfaces |
|
|
What is LinEn?
|
Linux EnCase
|
|
|
What is EE?
|
EnCase Enterprise (Civilian Version)
|
|
|
What is FIM?
|
Field Intelligence Model (Law Enforcement and Government)
|
|
|
What is the differences between EE and FIM?
|
EE can be purchased and used by anyone.
FIM is only for Law Enforcement and Government |
|
|
What do drive acquisitions require?
|
Using cross over cables to connect
|
|
|
What is Network Forensics?
|
The capture,recording, and analysis of network events in order to discover the source of security attacks or other problem incidents.
|
|
|
An Oath- A declaration in writing made upon oath before a person authorized to administer oaths. Especially used as evidence in court.
|
Affidavit
|
|
|
The act or process of bringing or contesting a legal action in court. Also known as a judicial proceeding or contest.
|
Litigation
|
|
|
VBR
|
Volume Boot Record (Volume Boot Sector) AKA "Boot Sector". It is the first sector of a logical volume.
|
|
|
Involves obtaining and analyzing digital information for use as evidence in civil, criminal, or administrative cases.
|
Computer Forensics
|
|
|
Yields information about how a perpetrator or hacker gained access to a network.
|
Network Forensics
|
|
|
Involves recovering information from a computer that was deleted by mistake or lost during a power surge.
|
Data Recovery
|
|
|
Popular Computer Forensics Tool
|
EnCase
|
|
|
In this type of case, a suspect is tried for a criminal offense, such as burglary, murder or molestation.
|
Criminal
|
|
|
Provides a record of clues to crimes that have been committed previously and is an aid for all current and future investigations.
|
Police blotter
|
|
|
Groups of sectors that hold content data.
|
Allocation units
|
|
|
The Master Boot Record on a hard drive.
|
MBR partition
|
|
|
Usually appears when a computer starts or connects to the company intranet, network, or virtual private network (VPN) and informs the end user that the organization reserves the right to inspect computer systems and network traffic at will.
|
Warning banner
|
|
|
What is the difference between computer forensics and network forensics?
|
Computer forensics focus on end user systems and devices. Network forensics focus on information systems and communications in a networked environment.
|
|
|
How is computer forensics different than data recovery?
|
Data recovery is reconstruction and/ or retrieval of information lost by a user, software or mechanical failure. Forensics is a legally accepted practice of preserving and analysis of digital information.
|
|
|
What are 5 hardware components of a computer?
|
Chassis
Motherboard RAM Power Supply Hard Drive |
|
|
1.Admissible
2.Authentic 3.Complete 4.Reliable 5.Believable |
The 5 rules of evidence
|
|
|
Formats that divide a disk drive into partitions. Examples include GUID partition table, NTFS MAster Boot Record, Apple Partition Table.
|
Partition Table
|
|
|
AKA "Allocation Unit". Unit of disk space allocation for files and directories. Smallest logical amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file.
|
Cluster
|
|
|
Can be used in place of the term "drive. A single accessible storage area with a single file system.
|
Volume
|
|
|
Any space left over between the last byte of the file and the first byte of the next cluster.
|
Slack Space
|
|
|
MFT
|
Master File Table
In NTFS, all file data are stored as metadata in the Master File Table. |
|
|
First sector of the logical volume.
|
VBR
|
|
|
A volume that can store up to 4, 084 clusters.
|
FAT12
|
|
|
Overcame the limitation of 512 entries
|
FAT32
|
|
|
A revised High Sierra standard by the International Organization for Standardization.
|
ISO 9660
|
|
|
Signifying the end of a file.
|
EOF or FFFF
|
|
|
The most secure file system of all we have studied.
|
NTFS
|
|
|
The exact size of a file in bytes.
|
Files logical size
|
|
|
Boot Sector
|
55AA
|
|
|
16 bit FAT entry
|
FAT16
|
|
|
A system that has been around for a very long time that is used in floppy drives, flash media and CD's.
|
FAT
|
|
|
What is the reserved area on a hard drive?
|
This is the HPA (Host Protected Area or Hidden Protected Area) Not normally visible to the OS where booting, diagnosis, and recovery resides.
|
|
|
What is DOS 8 dot 3?
|
Short File Name/SFN. Used by old versions of DOS and Windows prior to Windows 95.
|
|
|
What happens when a file is deleted without going to the recycle bin?
|
Pointer to the file is deleted and space is marked as available by the OS. The data remains until overwriting.
|
|
|
What steps are taken when a file is read?
|
The OS calls for the files directory path and reads the information that constitutes the file.
|
|
|
What is the directory entry status byte?
|
First byte of the 32-byte directory entry. First character of a valid file or directory. Name may contain 0xE5, 0x05. 0x00 means not used.
|
|
|
Documentation showing the seizure, custody and control, and analysis of evidence.
|
Chain of Custody
|
|
|
The process of placing evidence into containers for transport and labeling said containers with contents and tracking.
|
Bagging and Tagging
|
|
|
Allows one to take snapshots of a system. Available only to Law Enforcement and Government.
|
Field Intelligence Model (FIM)
|
|
|
Evidence stored in RAM or otherwise lost when device loses power.
|
Volatile Digital Device
|
|
|
AKA "Search Warrant". Court order issued by a judge authorizing search for evidence.
|
Search Authorization
|
|
|
What is the most important consideration when responding to a forensic call?
|
Planning
|
|
|
What items would you take to a forensics call?
|
"Everything" Make a checklist including things such as toolkits,gloves, cameras.
|
|
|
What items are considered evidence?
|
Physical evidence = skin, hair, fingerprints, etc.
Digital evidence = Computer files, Computer logs and screen shots. |
|
|
How do you prepare for a call to examine digital evidence?
|
Know as much information as possible before arriving to minimize unknowns.
|
|
|
Who are typically involved in a search and seizure process?
|
Security Team
Search Team |
|
|
Who typically makes up a search team?
|
Recorder
Photographer Search and seizure specialist Digital evidence search and seizure specialist |
|
|
What is the definition of a CPU?
A. The physical computer case that contains all its internal components B.The computer's internal hard drive C.A part of the computer whose function is to perform data processing D. A part of the computer that stores and manages memory. |
C. A CPU is the central processing unit, which means it's a microprocessor that performs data processing, in other words, interprets ans executes instructions.
|
|
|
What is the BIOS?
A. BIOS stands for Basic Input Output system and is a combination of low-level software and drivers that function as the interface, intermediary, or layer between a computer's hardware and it's operating system. B. BIOS stands for Bootstrap Initialization Operating System and is a combination of low-level software and drivers that function as the interface, intermediary, or layer between a computer's hardware and it's operating system. C. BIOS stands for Boot-level Input Output System and is a combination of low-level software and drivers that function as the interface, intermediary, or layer between a computer's hardware and it's operating system. D. BIOS stands for Boot Initialization Operating System ans is a combination of low-level software and drivers that function as the interface, intermediary, or layer between a computer's hardware and it's operating system. |
A. BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System ans consists of all the low-level software that is the interface between the system hardware and its operating system. It loads, typically, from three sources: The ROM/BIOS on the motherboard; the various BIOS ROMs on video cards, SCSI cards, and so forth; and finally. the device drivers.
|
|
|
What is the definition of POST?
A. A set of computer sequences the operating system executes upon a proper shutdown. B. A diagnostic test of the computer's hardware and software for presence and operability during the boot sequence prior to running the operating system. C. A diagnostic test of the computer's software for presence and operability during the boot sequence prior to running the operating system. D. A diagnostic test of the computer's hardware for presence and operability during the boot sequence prior to running the operating system. |
D. Power On Self-Test is a diagnostic test of the computer's hardware, such as the motherboard, memory, CD-ROM drive, and so forth. POST does not test the computer's software.
|
|
|
Is the information stored on a computer's ROM chip lost during a proper shutdown?
|
No, Information contained on a ROM chip, read-only memory, is not lost after the computer has been shutdown.
|
|
|
Is the information contained on a computer's RAM chip accessible after a proper shutdown?
|
No. Unlike a ROM chip, information contained on a computer's RAM chip is not readily accessible after proper shutdown.
|
|
|
Can information in the BIOS ever change?
|
Yes. Although not very common, information stored in the BIOS can change, such as when the BIOS needs to be upgraded to support new hardware.
|
|
|
What is the purpose or function of a computer's ROM chip?
A. Long-term or permanent storage of information and instructions. B. Temporary storage area to run applications. C. Permanent storage area for programs and files. D. A portable storage device. |
A. ROM (read-only memory) contains information about the computer, such as hardware configuration. Unlike RAM, the information is not lost once power is disconnected.
|
|
|
Information contained in RAM memory (system's main memory), which is located on the motherboard, is _____.
A. volatile B. nonvolatile |
A. Information contained in RAM memory is considered volatile, which means the data is lost after the computer has been disconnected.
|
|
|
What is the maximum number of drive letters assigned to hard drive(s) partitions on a system?
A. 4 B. 16 C. 24 D. Infinity |
C. The answer is 24 drive letter (C-Z), with drive letters A and B reserved for floppy driaves.
|
|
|
The smallest area on a drive that data can be written to is a _____, while the smallest area on a drive that a file can be written to is a _____.
A. bit and byte B. sector and cluster C. volume and drive D. memory and disk |
B. Data is written to sectors, and files are written to clusters.
|
|
|
The size of a physical hard drive can be determined by which of the following?
A. The cylinder x header x sector B.The cylinder x head x sector x 512 bytes C. The total LBA sectors x 512 bytes D. Adding the total size of partitions E. Both B and C |
E. Multiplying C/H/S gives total amount of sectors in older systems if the number of sectors per track is constant. When it is not, total LBA sectors give total sectors. Multiplying the total number of sectors from the appropriate method by 512 bytes per sector gives the total number of bytes for the physical drive. Adding up the total size of partitions does not include areas outside the partitions, such as unused disk area.
|
|
|
Which is not considered exclusively an ouput device?
A. Monitor B. Printer C. CD-RW drive D. Speaker |
C. A CD-RW (rewritable) drive is both an input and output device, as opposed to a CD drive, which only reads and inputs data to the computer system.
|
|
|
The electrical pathway used to transport data from one computer component to another is called what?
A. Bus B. RAM C. CMOS D. BIOS |
A. A Bus performs two functions: it transports data from one place to another and directs the information where to go.
|
|
|
What is the main component of a computer to which essential internal devices such as CPU, memory chips, and other chipsets are attached?
A. BIOS B. Motherboard C. Expansion card D. Processor |
B. The motherboard is the main circuit board used to attach internal hardware devices to it's connectors.
|
|
|
IDE, SCSI, and SATA are different types of interfaces describing what device?
A. RAM chips B. Flash memory C. CPUs D. Hard drives |
D. IDE (Intergrated Drive Electronics), SCSI (Small Computer System Interface), and SATA (Serial ATA, or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) describe different hard drive interfaces.
|
|
|
What do the terms master, slave, and cable select refer to?
A. External SCSI devices B. Cable types for external hardware C. Jumper settings for internal hardware such as IDE hard drives and CD drives. D. Jumper settings for internal expansion cards. |
C. Master, slave, and Cable Select are settings for internal devices such as IDE hard drives and CD drives to identify and differentiate the devices on the same channel.
|
|
|
What can you assume about a hard drive the is pinned as CS?
A. It's an IDE drive B. It's a SATA drive C. It's a SCSI drive D. All of the above. |
A. SATA and SCSI hard drives do not require jumper setting configurations.
|
|
|
What is found at Cylinder 0, Head 0, Sector 1 on a hard drive?
A. Master boot record B. Master file table C. Volume boot record D. Volume boot sector |
A. The master boot record is always located at the first physical sector on a hard drive. This record stores key information about the drive itself, such as the master partition table and master boot code.
|
|
|
What is the first sector on a volume called?
A. File allocation table B. Volume boot record or sector C. Master boot record D. Volume boot device |
B. The first sector on a volume is called the volume boot record or volume boot sector. This sector contains the disk parameter block and volume boot code.
|
|
|
Which of the following is incorrect?
A. The MBR is typically written when the drive is partitioned with FDISK or DISKPART. B. A file system is a system or method of storing and retrieving data on a computer system that allows for a hierarchy of directories, subdirectories, and files. C. The VBR is typically written when the drive is high-level formatted with a utility such as format. D. The partition table is contained within the MBR and consists of a total of 16 bytes, which describes up to four partitions using 4 bytes each to do so. |
D. All are true statements, except for a portions of D. The partition table is contained within the MBR and consists of a total of 64 bytes, not 16 bytes, which describes up to four partitions using 16 bytes each to do so, not 4 bytes each.
|
|
|
On a FAT file system, FAT is defined as which of the following?
A. A table consisting of master boot record and logical partitions B. A table created during the format that the operating system reads to locate data on a drive. C. A table consisting of file names and file attributes D. A table consisting of a file names, deleted file names, and their attributes. |
B. The FAT (file allocation table) is created by the file system during format and contains pointers to clusters located on a drive.
|
|
|
How does a corrupted sector located in the data area of a hard drive affect the corresponding cluster number on a FAT in a FAT table?
A. It does not affect the corresponding cluster number on a FAT table; therefore, the rest of the sectors associated with the assigned cluster can still be written to. B. It does not affect the corresponding cluster number on a FAT table; only the corrupted portion of the sector is prevented from being written to. C. It does affect the FAT table. The corresponding cluster number is marked as bad; however, only the corrupted sector within the cluster is prevented from being written to. D. It does not affect the FAT table. The corresponding cluster number is marked as bad, and the entire cluster is prevented from being written to. |
D. When the FAT table marks a cluster as being bad, the entire cluster is prevented from being written to.
|
|
|
Which of the following describes a partition table?
A. It is located at cylinder 0, head 0, sector 1. B. Is located in the master boot record. C. It keeps track of the partitions on a hard drive. D. All of the above. |
D. A partition table is located in the master boot record and is always located in the very first sector of a physical drive. The partition table keeps track of the partitions located on the physical drive
|
|
|
Which selection keeps track of a fragmented file in a FAT file system?
A. File allocation table B. Directory structure C. Volume boot record D. Master file table |
A. The FAT table assigns numbers to each cluster entry pointing to the next cluster in the cluster run until the last cluster is reached, which is marked as EOF.
|
|
|
If the FAT table lists cluster number 2749 with a value of 0, what does this mean about this specific cluster?
A. It is blank and contains no data. B. It is marked as bad and cannot be written to. C. It is allocated to a file. D. It is unallocated and is available to store data. |
D. When the FAT table marks a cluster as 0, it is unallocated clusters, which means it is freely available to store data.
|
|
|
Which of the following is true about a volume boot record?
A. It is always located at the first sector of its logical partition. B. It immediately follows the master boot record C. It contains BIOS parameter block and volume boot code. D. A and C. |
D. The Volume Boot Record is always located at the first sector of its logical partition and contains the BIOS parameter block and volume boot code.
|
|
|
The NTFS file system does which of the following?
A. Supports long file names. B. Compresses individual files and directories. C. Supports large file sizes in excess of 4GB D. All of the above. |
D. The NTFS file system supports long file names, compresses files and directories, and supports file sizes in excess of 4 GB.
|
|
|
How many clusters can a FAT32 file system manage?
A. 2 x 32 = 64 clusters B. 2^32 = 4,294,967,296 clusters C. 2 x 28 = 56 clusters D. 2^28 = 268, 435, 456 clusters |
D. A FAT32 file system theoretically allows up to 228 = 268,435,456 clusters. The extra 4 bits are reserved by the file system, however, and there is an MBR-imposed limit of 67,092,481 clusters, which means FAT32 is capable of supporting a partition size of 2 terabytes.
|
|
|
The FAT tracks the _____ while the directory entry tracks the _____.
A. file name and file size. B.file's starting cluster and file's last cluster (EOF) C. file's last cluster (EOF) and file's starting cluster D.file size and file fragmentation. |
C. The FAT tracks the location of the last cluster for a file (EOF), while the directory entry maintains the file's starting cluster number.
|
|
|
How many copies of the FAT does each FAT32 volume maintain in its default configuration?
A. One B. Two C. Three D. Four |
B. EAch volume maintains two copies (one for backup):FAT1 and FAT2.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true regarding the NTFS file system?
A. Data for very small files can be stored in the MFT itself and is referred to as resident data. B. Cluster allocation is tracked in the $Bitmap file. C. Data that is stored in clusters is called nonresident data. D. Cluster allocation is tracked in the File Allocation Table (FAT). |
D.
|
|
|
A file's physical size is?
A. Always greater than the file's logical size B. The number of bytes in the logical file plus all slack space from the end of the logical file to the end of the last cluster. C. Both A and B D. None of the above |
B. A file's physical size is the number of bytes to the end of the last cluster, and a file's logical size is the amount of bytes that the actual file contains. A file's physical size can be the same as its logical size.
|
|
|
A directory entry in a FAT file system has a logical size of which of the following?
A. 0 bytes B. 8 bytes C 16 bytes D. One sector |
A. A directory entry in a FAT file system has no logical size.
|
|
|
Each directory entry in a FAT file system is _____ bytes in length.
A. 0 B. 8 C. 16 D. 32 |
D. In a FAT file system each directory entry is 32 bytes in length.
|
|
|
By default, what color does EnCase use to display directory entries within a directory structure?
A. Black B. Red C. Gray D. Yellow |
B. Because directory entries are just names with no logical size and because they do not contain any actual data, EnCase displays the information in red.
|
|
|
What is the area between the end of a file's logical size and the file's physical size called?
A. Unused disk area B. Unallocated clusters C. Unallocated sectors D. Slack Space |
D. The area between a file's logical size and its physical size is commonly referred to as slack space.
|
|
|
What three things occur when a file is created in a FAT32 file system?
A. Directory entry for the file is created, the FAT assigns the necessary clusters to the file, and the file's data is filled in to the assigned clusters. B. The file name is entered in to the FAT, the directory structure assigns the number of clusters, and the file's data is filled in to the assigned clusters. C. The directory entry for the file is created, the number of clusters is assigned by the directory structure, and the file's data is filled in to the FAT D. The directory structure maintains the amount of clusters needed, the file name is recorded in the FAT, and the file's data is filled in to the assigned clusters. |
A. The directory structure records the file's information, the FAT tracks the number of clusters allocated to the file, and the file's data is filled in to the assigned clusters.
|
|
|
How does EnCase recover a deleted file?
A. It reads the deleted file name in the FAT and searches for the file by its starting cluster number and logical size. B. It reads the deleted file name in the directory entry and searches for the corresponding file name in unallocated clusters. C. It obtains the deleted file's starting cluster number and size from the directory entry to obtain the data's starting location and number of clusters required. D. It obtains the deleted file's starting cluster number and size from the FAT to locate the starting location and amount of clusters needed. |
C. EnCase recovers deleted files by first obtaining the file's starting cluster number and its size from the directory entry. EnCase determines the number of clusters needed based on the file's size and then attempts to recover the data from the starting extent through the amount of clusters needed.
|
|
|
What does EnCase do when a deleted file's starting number is assigned to another file?
A. EnCase reads the entire existing data as belonging to the deleted file B. EnCase only reads the amount of data from the existing file that is associated with the deleted file. C. EnCase marks the deleted file as being overwritten D. EnCase does not display deleted file name when the data has been overwritten. |
C. When EnCase determines that the starting cluster listed in the FAT has been reassigned to an existing file, it reports the previously deleted file as being overwritten.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not true regarding the exFAT file system?
A. Cluster allocation is tracked in the File Allocation Table (FAT). B. When a file is deleted, the corresponding entries in the File Allocation Table (FAT) are reset or zeroed out. C. Cluster allocation is tracked in an allocation bitmap. D. An entry in the FAT of 00 00 00 00 means that the FAT is not tracking allocation for this file. |
A.
|
|
|
What is the first consideration when responding to a scene?
A. Your safety B. The safety of others C. The preservation of evidence D. Documentation |
A. Without consideration for your own personal safety, none of the other considerations can be accomplished.
|
|
|
What are some variables regarding a facility that you should consider prior to responding to a scene?
A. what types of structure is it? B. How large is the structure? C. What are the hours of operation? D. Is there a helpful person present to aid in your task? E. All of the above |
E. When responding to a facility, your most helpful ally is prior knowledge of the location, its hours of activity, and the people who occupy it.
|
|
|
What are some of the variables regarding items to be siezed that you should consider prior to responding to a scene?
A. Location(s) of computers B. Type of operating system C. Workstations or mainframes D. System-critical or auxiliary machine E. All of the above |
E. When responding to a facility, having prior knowledge of the types and functions of the computers and their locations will help reduce any unforeseen complications, thus easing the task.
|
|
|
Generally speaking, if you encounter a desktop computer running Windows 7, how should you take down the machine?
A. Shut down using Windows 7 B. Shut down by pulling the power cord from the outlet C. Shut down by pulling the plug from the computer box D. All of the above |
C. Pulling the plug on a workstation, unlike doing so on server, will not lose any critical information.
|
|
|
Generally speaking, if you encounter a computer running Windows 2008 Server, how should you take down the machine?
A. Shut down using its operating system B. Shut down by pulling the power cord from the outlet. C. Shut down by pulling the plug from the computer box. D. All of the above |
A. Unlike with Windows desktop computer, certain information may not be recovered if a server is not properly shut down. It is best to properly shut down a Windows server and document your actions.
|
|
|
Generally speaking, if you encounter a Unix/Linux machine, how should you take down the machine?
A. Shut down using its operating system B. Shut down by pulling the power cord from the outlet. C. shut down by pulling the plug from the computer box. D. All of the above. |
A. Unix/Linux machines can store critical information that may be lost if the machine is improperly shut down.
|
|
|
When unplugging a desktop computer, from where is it best to pull the plug?
A. The back of the computer B. The wall outlet C. Both A or C |
A. When unplugging a desktop computer, it is best to unplug a power cord from the back of the computer at the power supply. Unplugging a cord from the outlet connected to an uninterrupted power supply (UPS) will not shut down the computer.
|
|
|
What is the best method to shut down a notebook computer?
A. Unplug from the back of the computer B. Unplug from the wall C. Remove the battery D. Both A and C |
D. Removing both the power cord (AC) and the battery (DC) will ensure that no electricity is being fed to the computer.
|
|
|
Generally speaking, if you encounter a Macintosh computer, how should you take down the machine?
A. Shut down using the operating system B. Shut down by pulling the power cord from the outlet. C.Shut down by pulling the plug from the computer box D. All of the above. |
C. A MAC should generally be shut down by pulling the power plug from the back of the computer.
|
|
|
Which selection displays the incorrect method for shutting down a computer?
A. DOS: Pull the plug B. Windows 2000: Pull the plug C. Windows XP: Pull the plug D. Linux: Pull the plug |
D. The best way to shut down a Linux/Unix system is to perform a proper shutdown using the operating system.
|
|
|
When shutting down a computer, what information is typically lost?
A. Data in RAM memory B. Running processes C. Current network connections D. Current logged-in users E. All of the above |
E. When the system is shut down normally or the plug is pulled, all the other live system-state data mentioned is lost.
|
|
|
Which of the following is not acceptable for "bagging" a computer workstation?
A. Large paper bag B. Brown wrapping paper C. Plastic garbage bag D. Large antistatic plastic bag E. All of the above are acceptable for bagging a workstation |
C. A plastic garbage bag has properties that are conducive to static electricity discharge, which could damage sensitive computer components, including media
|
|
|
In which cicumstance is pulling the plug to shut down a computer system considered the best practice?
A. When OS is Linux/UNIX B. When the OS is Windows 2007 and known to be running a large business database application C. When the OS is Windows (NT/2K/2003/2008) Server D. When Mac OS X Server is running as a web server E. None of the above |
E. In all circumstances described, the best course of action would be a normal shutdown, and thus pulling the plug is considered best practice for any of these.
|
|
|
How is the chain of custody maintained?
A. By bagging evidence and sealing it to protect it from contamination or tampering B. by documenting what,when, where, why, how, and by whom the evidence was removed from the evidence room C.By documenting in a log the circumstances under which evidence was removed from the evidence control room. D. By documenting the circumstances under which evidence was subjected to analysis E. All of the above |
E. The evidence steps described here are an important component in maintaining the chain of custody and hence the integrity of the evidence
|
|
|
It is always safe to pull the plug on a Windows 7 Enterpricse operating system.
A. True B. False |
B. In a business setting, anything is possible. A large business database could be hosted on a Windows 2000 operating system, as could a number of other critical applications, which include access control systems, critical process software, life-support systems, life-safety alarm monitoring , and so forth.
|
|
|
On a production Linux/Unix server, you must generally be which user to shut down the system?
A. sysadmin B. administrator C. root D. system |
C. Generally, unless configured otherwise, you must be root to shut down a Linux/Unix system in a production environment. This prevents a typical user from stopping the system and halting mission-critical computing processes.
|
|
|
When would it be acceptable to navigate through a live system.
A. To observe the operating system to determine the proper shutdown process B. To document currently opened files (if Enterprise/FIM edition is not available) C. To detect mounted encryption D. To access virtual storage facility (if search warrant permits; some are very specific about physical location) E. All of the above |
E. Certain information may not be retrievable after the system has been shut down. Given that, it is acceptable to access a system to retrieve information of evidentiary value as long as the actions are justified, documented, and explained
|
|
|
A console prompt that displayed backslashes (\) as part of its display would most likely be which of the following?
A. Red Hat Linux operating system B. Unix operating system C. Linux or Unix operating system logged in as root D. MS-DOS |
D. Microsoft PC operating systems use backslashes for the directory path structure, whereas Linux/Unix uses forward slashes (/) for the same purpose.
|
|
|
When called to a large office complex with numerous networked machines, is it always a good idea to request the assistance of the network administrator?
A. True B. False |
B. Although most of the time the network administrator knows much more about the computers than the responding examiner and may be of great help, requesting that person's assistance may be detrimental to the investigation if the network administrator is the target of the investigation. As part of your preplanning. you must determine whether the administrator is part of the problem or part of the solution before you make such an approach.
|
|
|
Subsequent to a search warrant where evidence is seized, what items should be left behind?
A. Copy of the affidavit B. Copy of the search warrant C. List of items seized D. A and B E. B and C |
E. Upon leaving the scene of a search, you should leave behind a copy of the signed search warrant and a list of items seized.
|
|
|
When acquiring a hard drive using Linux boot disk with LinEn, what would be the cause of EnCase not detecting partition information?
A. The drive has been FDisked and the partition(s) removed. B. The partition(s) are not recognized by Linux C. Both A and B D. None of the above |
C. When partitions have been removed or the partitions are not recognized by DOS, EnCase still recognizes the physical drive and acquires it as such.
|
|
|
LinEn contains a write blocker that protects the target media from being altered.
A. True B. False |
B.
|
|
|
As a good forensic practice, why would it be a good idea to wipe a forensic drive before reusing it?
A. Chain-of-custody B. Cross-contamination C. Different file and operating systems D. Chain of evidence E. No need to wipe |
B. Although EnCase only examines the contents within the evidence files, it is still good forensic practice to wipe/sterilize each hard drive prior to reusing it to eliminate the argument of possible cross-contamination.
|
|
|
If the number of sectors reported by EnCase does not match the number reported by the manufacturer for the drive, what should you do?
A. Suspect HPA B. Suspect DCO C. Boot with EnCase for DOS and switch to Direct ATA access D. Boot with LinEn in Linux E. All of the above |
E. You should suspect an HPA or a DCO, Booting with LinEn or booting with EnCase for DOS with Direct ATA access should enable you to see all sectors.
|
|
|
When acquiring digital evidence, why shouldn't the evidence be left unattended in an unsecured location?
A. Cross-contamination B. Storage C. Chain-of-custody D. Not an issue |
C. Digital evidence must be treated like any other evidence, whereas a chain of custody must be established to account for everyone who has access to the property.
|
|
|
Which describes an HPA? (Choose all that apply)
A. Stands for Host Protected Area B. Is not normally seen by the BIOS C. Is not normally seen through Direct ATA access D. Was introduced in the ATA-6 specification |
A and B. HPA stands for Host Protected Area and is not normally seen by the BIOS. It was introduced in the ATA-4 specification. not ATA-6, and is seen when directly accessed via the Direct ATA mode.
|
|
|
Which describes a DCO?
A. Was introduced in the ATA-6 specification B. Stands for Device Configuration Overlay. C. Is not normally seen by the BIOS D. It may contain hidden data, which can be seen by switching to the Direct ATA mode in EnCase for DOS. E. All of the above |
E. All are correct statements with regard to DCO.
|
|
|
At which user level must the examiner function when using LinEn?
A. Administrator B. Admin C. Root D. Any user E. None of the above |
C
|
|
|
Reacquiring an image and adding compression will change the MD5 value of the acquisition hash.
A. True B. False |
B. When reacquiring an image, the MD5 of the original data stream remains the same despite the compression applied.
|
|
|
When reacquiring an image, you can change the name of the evidence.
A. True B. False |
B. When reacquiring, you can change the compresssion, you can add or remove a password, you can change the file segment size, you can change the block and error granularity sizes, or you can change the start and stop sectors. Other properties can't be changed.
|
|
|
Which of the following should you do when creating a storage volume to hold an EnCase evidence file that will be created with EnCase for LinEn? (Choose all that apply)
A. Format the volume with the FAT file system. B. Give the volume a unique label to identify it. C. Wipe the volume before formatting to conform to best practices, and avoid claims of cross-contamination. D. Create a directory to contain the evidence file. E. Format the volume with the NTFS file system. F. All of the above. |
F
|
|
|
In Linux, what describes hdb2? ( choose all that apply.)
A. Refers to the primary master B. Refers to the primary slave C. Refers to hard drive number 2 D. Refers to the second partition E. Refers to the secondary master |
B and D. Here, hdb2 refers to the second partition on the primary slave.
|
|
|
In Linux, what describes sdb? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Refers to an IDE device B. Refers to a SCSI device C. Refers to a USB device D. Refers to a FireWire device |
B, C, and D. Linux will name an IDE device , normally with hda, hdb, hdc, or hdd, to denote their position on the ATA controller (primary master, primary slave, secondary master, secondary slave, respectively). sdb is the second SCSI device, and since LINUX calls USB or FireWire devices SCSI devices, any of the three (B,C, or D) could be represented by sdb
|
|
|
When acquiring USB flash memory, you should write-protect it by doing what?
A. Engaging the write-protect switch, if equipped. B. Modifying the registry in Windows XP SP2 (or higher) to make USB read-only C. Using ENBD/ENBCD USB DOS drivers and having EnCase for DOS "lock" the Flash media D. Using LinEn in Linux with automount of file system disabled. E. Using FastBloc SE to write-block USB, FireWire, SCSI drives F. All of the above |
F. All are methods of write-protecting USB devices, some arguably better than others, but methods nevertheless.
|
|
|
Which are true with regard to EnCase Portable? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Storage media must be prepared using the Portable Management tool before it can be used by EnCase Portable. B. If booting using the EnCase Portable Boot CD to boot, the EnCase Portable dongle must also be connected so that the license can be accessed. C. The EnCase Portable can triage and collect evidence in a forensically sound manner from live machines or to do so in a boot mode. D. The EnCase Portable can be configured with custom tasks created by the examiner using the Portable Management tool. |
A.B.C.D.
|
|
|
LinEn can be run under both Windows and DOS operating systems.
A. True B. False |
B.
|
|
|
When using LinEn, the level of support for USB, FireWire, and SCSI devices is determined by what?
A. The drivers built into LinEn B. The drivers provided with the ENBCD C. The distribution of Linux being used D. A and B E. None of the above |
C. The level of support for USB, FireWire, SCSI, and other devices is totally dependent on the Linux distribution being used to run LinEn. For the most support, try to use the latest Linux distribution available.
|
|
|
How should CDs be acquired using EnCase?
A. DOS B. Windows |
B. CDs can be safely acquired in the Windows enviroment
|
|
|
Select all that are true about EE and FIM.
A. They can acquire or preview a system live without shutting it down. B. They can capture live system-state volatile data using the Snapshot feature. C. With EE, the SAFE is on a seperate PC, administered by the keymaster. D.With FIM, the SAFE is on the examiner's PC and the keymaster and the examiner are the same person. E. FIM can be licensed to private individuals. |
A, B, C, D. A FIM can be licensed only to law enforcement or military customers. All other statements are correct.
|
|
|
Which of the following are true? (Choose all that apply.)
A. LinEn contains no write-blocking capability. Rather, write blocking is achieved by disabling the automount feature within the host Linux operating system. B. LinEn contains its own onboard write-blocking drivers and therefore can be safely run on any version of Linux. C. LinEn can format drives to both NTFS and FAT formats. D. Before using a target drive onto which to write evidence files, LinEn must be used to unlock the target drive and render it writable. E. LinEn can format drives to EXT2 or EXT3 format. |
A.
|
|
|
SAFE
|
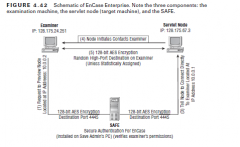
Secure Authentication For EnCase
|
|
|
Steps for Tableau (FastBloc) Acquisition
|
1. Connect your FastBloc to your host computer via either a USB or a 1394a/b connection (both are available on FastBloc2 FE), but not both. The host computer can be running when you make this connection, or you can make your connections while the computer is off and then boot the system.
2. Your target drive should be set for master or single if it is a Parallel ATA (PATA). Adjust the jumper accordingly. 3. Connect the DC power from the FastBloc to the target hard drive. 4. Connect the IDE cable from FastBloc to the target hard drive. 5. Connect the power supply to FastBloc, and power on FastBloc. 6. If the host computer is not on, boot it up at this time. 7. You can confirm that FastBloc (or Tableau) was detected and mounted by opening the Device Manager (right-click My Computer, and choose Properties; on the Hardware tab, choose Device Manager). Under Disk Drives, you should see FastBloc listed, 8. Run EnCase in Windows on the host examination computer to which FastBloc is attached. 9. On the screen that follows, since FastBloc mounts the drive locally, choose Add Local Device. 10. On the screen that follows, accept the defaults for now, unless you are using a legacy FastBloc, meaning one predating the Tableau units. 11. Confirm that EnCase, through the BIOS interface in Windows, is able to see all the sectors on the drive as reported by the manufacturer. 12. Upon clicking Finish, you’ll see your evidence object appear as a row on the Evidence tab, which is immediately to the right of the Home tab. 13. To preview your evidence object or drive, you should place a blue check on it and click Load Selected Device on the Evidence Tab toolbar, or you can simply double-click the object. 14. At this stage you can preview the drive, searching and bookmarking as is necessary. 15. If you opt to acquire the FastBloc/Tableau device, you can do so at this time. |
|
|
Shut down of systems. What steps need to be taken and in what order?
|
DOS – photograph and pull plug
Windows 3.1 - photograph and pull plug Windows 95 - photograph and pull plug Windows NT workstation - photograph and pull plug Windows NT Server - photograph and shut down normally Windows 98\Me - photograph and pull plug Windows 2000 - photograph and pull plug Windows 2000 Server – photograph and normal System shutdown procedures Windows XP - photograph and pull plug Windows 2003 Server - photograph and normal System shutdown procedures Windows Vista - photograph and pull plug Linux\Unix - photograph and normal System shutdown procedures MAC - photograph and normal System shutdown procedures |
|
|
3 A's of Computer Forensics
|
Acquire
Authenticate Analyze |

