![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What two actions will the EIGRP DUAL FSM take if a link to a network goes down? (Choose two.)
a. put the route into passive mode b. query neighbors for a new route c. search routing table for a feasible successor d. run the SPF algorithm to find a new successor e. search topology table for a feasible successor |
b. query neighbors for a new route
e. search topology table for a feasible successor |
|
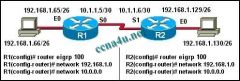
Host 192.168.1.66 in the network illustrated is unable to ping host 192.168.1.130. How must EIGRP be configured to enable connectivity between the two hosts? (Choose two.)
a. R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.128 b. R1(config-router)# auto-summary c. R1(config-router)# no auto-summary d. R2(config-router)# no auto-summary e. R2(config-router)# auto-summary f. R2(config-router)# network 192.168.1.64 |
c. R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
d. R2(config-router)# no auto-summary |
|
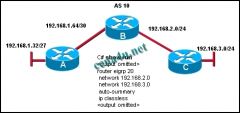
Refer to the exhibit. The company is using EIGRP with an autonomous system number of 10. Pings between hosts on networks that are connected to router A and those that are connected to router B are successful.
However, users on the 192.168.3.0 network are unable to reach users on the 192.168.1.32 network. What is the most likely cause of this problem? a. IP classless is enabled and is causing the packet to drop. b. The command network 192.168.1.32 was not issued on router C. c. The routers are not configured in the same EIGRP routing domain. d. Automatic summarization of the networks is causing the subnetted routes to be dropped. |
c. The routers are not configured in the same EIGRP routing domain.
|
|
|
What information is maintained in the EIGRP topology database for a destination route? (Choose three.)
a. the routing protocol b. the feasible distance of the route c. the highest cost of the route d. the SRTT value for the route e. the route cost as advertised by the neighboring router f. the physical address of the gateway interface |
a. the routing protocol
b. the feasible distance of the route e. the route cost as advertised by the neighboring router |
|
|
On a router running EIGRP, what database would maintain a list of feasible successors?
a. routing table b. neighbor table c. topology table d. adjacency table |
c. topology table
|
|
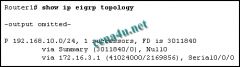
Refer to the exhibit. What is indicated by the P at the beginning of the topology entry?
a. the route is in a stable state b. the route is a preferred route c. DUAL is searching for a better route to this destination d. the exit interface is in passive mode and EIGRP advertisements are blocked |
a. the route is in a stable state
|
|
|
In the command router eigrp 20, what is the purpose of the number 20?
a. specifies the administrative distance for all EIGRP routes b. identifies the autonomous system number this EIGRP process will advertise c. determines what metric is added to all advertised routes d. indicates the number of addresses in the EIGRP routing domain |
b. identifies the autonomous system number this EIGRP process will advertise
|
|

Refer to the exhibit. In the topology table, what do the numbers 3011840 and 3128695 represent?
a. the route metric that is applied to those EIGRP routes for this router b. the trustworthiness of the routing information source c. the composite of the hop count and bandwidth to that destination network d. the total metric for that network as advertised by the EIGRP neighbor |
d. the total metric for that network as advertised by the EIGRP neighbor
|
|
|
Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRP? (Choose two.)
a. EIGRP is a distance vector routing protocol. b. EIGRP supports classless routing and VLSM. c. EIGRP is classified as a link-state routing protocol. d. EIGRP uses TCP for reliable delivery of EIGRP update packets. e. With EIGRP, loop-free paths are achieved through the use of hold-down timers. f. EIGRP sends a periodic update every 30 minutes. |
a. EIGRP is a distance vector routing protocol
b. EIGRP supports classless routing and VLSM. |
|
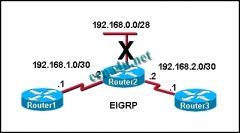
Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.0.0/28 goes down. What type of packet does Router2 immediately send to Router1 and Router3?
a. a query for network 192.168.0.0/28 b. an acknowledgment packet to 224.0.0.9 c. an update packet that is sent to 255.255.255.255 d. a packet that contains the new routing table for R2 e. unicast update packets to 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1 |
e. unicast update packets to 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1
|
|
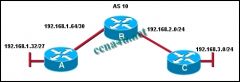
Refer to the exhibit. Which command will advertise the 192.168.1.64/30 network but not the 192.168.1.32 network on router A?
a. network 192.168.1.0 b. network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 c. network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.3 d. network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.7 e. network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.255 |
c. network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.3
|
|
|
What administrative distance would a router assign to a default route in EIGRP that is learned from a source external to the autonomous system?
a. 1 b. 5 c. 70 d. 90 e. 170 f. 190 |
e. 170
|
|
|
In which of the following tables does the EIGRP DUAL algorithm store the primary route to a destination? (Choose two.)
a. routing b. topology c. neighbor d. path e. shortest path |
a. routing
b. topology |
|
|
Which of the following types of routes will be denoted by EX in EIGRP routing table entries? (Choose two.)
a. routes learned from other routing protocols b. routes learned from any non-adjacent EIGRP routers c. any route with a hop count metric higher than 224 d. EIGRP routes that originate in different autonomous systems e. all passive routes in the routing table |
a. routes learned from other routing protocols
d. EIGRP routes that originate in different autonomous systems |
|
|
Which term defines a collection of networks under the administrative control of a single entity that presents a common routing policy to the Internet?
a. autonomous system b. contiguous networks c. process ID d. BGP |
a. autonomous system
|
|

Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is the only routing protocol enabled on this network. No static routes are configured on this router. What can be concluded about network 198.18.1.0/24 from the exhibited output?
a. A route to network 198.18.1.0/24 is not listed in the routing table. b. Packets that are destined for 198.18.1.0/24 will be forwarded to 198.18.10.6. c. EIGRP will perform equal cost load balancing across two paths when forwarding packets to 198.18.1.0/24. d. The router with interface 172.16.3.2 is a successor for network 198.18.1.0/24. |
b. Packets that are destined for 198.18.1.0/24 will be forwarded to 198.18.10.6.
|
|
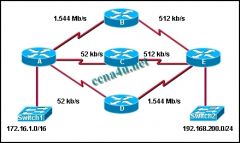
Refer to the exhibit. All interfaces have been configured with the bandwidths that are shown in the exhibit. Assuming that all routers are using a default configuration of EIGRP as their routing protocol, what path will packets take from the 172.16.1.0/16 network to the 192.168.200.0/24 network?
a. A,B,E b. A,C,E c. A,D,E d. Packets will load balance across the A,B,E and A,C,E paths. e. Packets will load balance across the A,B,E and A,D,E paths. f. Packets will load balance across the A,C,E and A,D,E paths. |
a. A,B,E
|
|
|
By default, which two metrics are used by EIGRP to determine the best path between networks?
a. MTU b. load c. delay d. bandwidth e. reliability |
c. delay
d. bandwidth |
|
|
Which of the following statements describes the bounded updates used by EIGRP?
a. Bounded updates are sent to all routers within an autonomous system. b. Partial updates are sent only to routers that need the information. c. The updates are sent to all routers in the routing table. d. Updates are bounded by the routers in the topology table. |
b. Partial updates are sent only to routers that need the information.
|
|
|
The show ip eigrp topology command output on a router displays a successor route and a feasible successor route to network 192.168.1.0/24. In order to reduce processor utilization, what does EIGRP do when the primary route to this network fails?
a. The router sends query packets to all EIGRP neighbors for a better route to network 192.168.1.0/24. b. The DUAL FSM immediately recomputes the algorithm to calculate the next backup route. c. Packets that are destined for network 192.168.1.0/24 are sent out the default gateway instead. d. The backup route to network 192.168.1.0/24 is installed in the routing table. |
d. The backup route to network 192.168.1.0/24 is installed in the routing table.
|
|
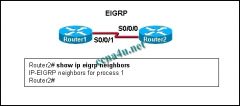
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output of show ip eigrp neighbors, what are two possible problems with adjacencies between Router1 and Router2? (Choose two.)
a. The routers are configured with different EIGRP process IDs. b. Automatic summarization was disabled. c. The hello timer for R1 was altered. d. The serial interfaces for both routers are in different networks. e. No feasible successors were found. |
a. The routers are configured with different EIGRP process IDs.
d. The serial interfaces for both routers are in different networks. |
|
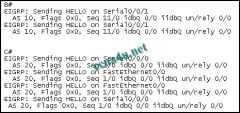
Refer to the exhibit. This is the debug output from 2 directly connected EIGRP routers. They are not forming an adjacency. What is the cause?
a. one router is a non-cisco router b. they have different autonomous-system numbers c. they are using difference sequence numbers d. they are sending incorrect hello types |
b. they have different autonomous-system numbers
|
|
|
What action does a link-state router take immediately upon receipt of an LSP from a neighboring router?
a. floods the LSP to neighbors b. calculates the SPF algorithm c. runs the Bellman-Ford algorithm d. computes the best path to the destination network |
a. floods the LSP to neighbors
|
|
|
Why is it difficult for routing loops to occur in networks that use link-state routing?
a. Each router builds a simple view of the network based on hop count. b. Routers flood the network with LSAs to discover routing loops. c. Each router builds a complete and synchronized view of the network. d. Routers use hold-down timers to prevent routing loops. |
c. Each router builds a complete and synchronized view of the network.
|
|
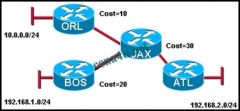
Refer to the exhibit. What kind of information would be seen in an LSP sent from router JAX to router ATL?
a. hop count b. uptime of the route c. cost of the link d. a list of all the routing protocols in use |
c. cost of the link
|
|
|
To achieve network convergence, what three steps does each link state router take? (Choose three.)
a. use automatic summarization to reduce the size of routing tables b. build a Link State Packet (LSP) containing the state of each directly connected link c. flood the LSP to all neighbors, who then store all LSPs received in a database d. discover neighbors and establish adjacencies using the hello packet sent at regular intervals e. construct a complete map of the topology and compute the best path to each destination network f. use the DUAL FSM to select efficient, loop-free paths, and insert routes into the routing table |
b. build a Link State Packet (LSP) containing the state of each directly connected link
c. flood the LSP to all neighbors, who then store all LSPs received in a database e. construct a complete map of the topology and compute the best path to each destination network |
|
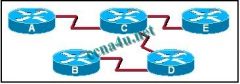
Refer to the exhibit. When Router D is configured to use a link-state routing protocol and is added to the network, what is the first thing that it does to begin learning the network topology?
a. It sends LSP packets to Routers B and C. b. It sends LSP packets to all routers in the network. c. It sends Hello packets to all routers in the network. d. It sends information about its directly connected neighbors to Routers A and E. e. It sends information about its directly connected neighbors to all routers in the network. f. It learns about its directly connected networks when its interfaces reach the up state. |
f. It learns about its directly connected networks when its interfaces reach the up state.
|
|
|
A new network administrator is given the task of selecting an appropriate dynamic routing protocol for a software development company. The company has over 100 routers, uses CIDR and VLSM, requires fast convergence, and uses both Cisco and non-Cisco equipment. Which routing protocol is appropriate for this company?
a. RIP version 2 b. IGRP c. EIGRP d. OSPF e. BGP |
d. OSPF
|
|
|
What two events will cause a link state router to send LSPs to all neighbors? (Choose two.)
a. 30 second timer expires b. whenever the network topology changes c. immediately after the Bellman-Ford algorithm has run d. immediately after the DUAL FSM has built the topology database e. upon initial startup of router or routing protocol |
b. whenever the network topology changes
e. upon initial startup of router or routing protocol |
|
|
What is the final step in the link state routing process?
a. successors are placed into the routing table b. SPF computes best path to each destination network c. LSPs are flooded to all neighbors to converge the network d. DUAL algorithm is run to find best path to destination networks |
b. SPF computes best path to each destination network
|
|
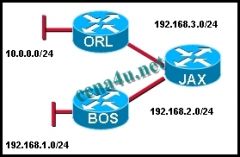
Refer to the exhibit. What does JAX do with link-state packets from ORL?
a. sends out its updated routing table to both ORL and BOS routers b. sends out the individual link-state packets out the interface connected to BOS c. queries BOS to see if it has a better route d. only adds it to the local routing table and performs no other actions |
b. sends out the individual link-state packets out the interface connected to BOS
|
|
|
What two statements correctly describe the link state routing process? (Choose two.)
a. each router in the area floods LSPs to all neighbors b. all routers in the area have identical link state databases b. LSPs use the reserved multicast address of 224.0.0.10 to reach neighbors c. routing loops are prevented by running the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) d. Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) is the protocol used by for the delivery and reception of LSPs |
a. each router in the area floods LSPs to all neighbors.
b. all routers in the area have identical link state databases. |
|
|
Which database or table must be identical on all link-state routers within an area in order to construct an accurate SPF tree?
a. routing table b. adjacency table c. link-state database d. neighbor table e. topology database |
c. link-state database
|
|
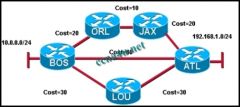
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement correctly describes the path traffic would take from the 10.0.0.0/24 network to the 192.168.1.0/24 network if a link-state routing protocol was in use?
a. BOS -> ATL because this path is the least hops b. BOS -> ATL because this path is highest cost c. BOS -> ORL -> JAX -> ATL because this path is the lowest cost d. traffic would load balance across all links |
c. BOS -> ORL -> JAX -> ATL because this path is the lowest cost
|
|
|
What feature do modern link-state protocols provide to minimize processing and memory requirements?
a. splitting routing topologies into smaller areas b. assigning lower process priorities to route calculations c. using update timers to restrict routing updates d. strict split horizon rules to reduce routing table entries |
a. splitting routing topologies into smaller areas
|
|
|
What speeds up convergence in a network using link-state routing?
a. updates triggered by network changes b. updates sent at regular intervals c. updates sent only to directly connected neighbors d. updates that include complete routing tables |
a. updates triggered by network changes
|
|
|
Which algorithm is run by link-state routing protocols to calculate the shortest path to destination networks?
a. DUAL b. Dijkstra c. Bellman-Ford d. Diffie-Hellman |
b. Dijkstra
|
|
|
What are some of the advantages of using a link-state routing protocol instead of a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two.)
a. The topology database eliminates the need for a routing table. b. Frequent periodic updates are sent to minimize the number of incorrect routes in the topological database. c. Routers have direct knowledge of all links in the network and how they are connected. d. After the inital LSA flooding, they generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology. e. Link-state protocols require less router processor power than distance vector protocols. |
c. Routers have direct knowledge of all links in the network and how they are connected.
d. After the inital LSA flooding, they generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology. |
|
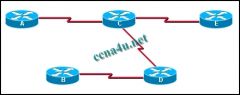
Refer to the exhibit. If all routers and interfaces are configured to use a link-state routing protocol, from which routers will router D receive hello packets?
a. A and E b. B and C c. A, B, C, and E d. C only |
b. B and C
|
|
|
Which two routing protocols use Dijkstra’s shortest path first algorithm? (Choose two.)
a. RIPv1 b. RIPv2 c. IS-IS d. BGP e. EIGRP f. OSPF |
c. IS-IS.
f. OSPF |
|
|
When are link-state packets sent to neighbors?
a. every 30 seconds b. every 180 seconds c. after the holddown time expires d. when a link goes up or down e. when a routing loop occurs |
d. when a link goes up or down
|
|
|
What are two advantages of using a link-state routing protocol instead of a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two.)
a. The topology database eliminates the need for a routing table. b. Each router independently determines the route to each network. c. Link-state protocols require less router processor power than distance vector protocols. d. After the inital LSP flooding, they generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology. e. Frequent periodic updates are sent to minimize the number of incorrect routes in the topological database. |
b. Each router independently determines the route to each network.
d. After the inital LSP flooding, they generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology. |
|
|
To achieve network convergence, what three steps does each link state router take? (Choose three.)
a. use automatic summarization to reduce the size of routing tables b. build a Link State Packet (LSP) containing the state of each directly connected link c. flood the LSP to all neighbors, who then store all LSPs received in a database d. send hello packages at regular intervals to discover neighbors and establish adjacencies e. construct a complete map of the topology and compute the best path to each destination network f. use the DUAL FSM to select efficient, loop-free paths, and insert routes into the routing table |
b. build a Link State Packet (LSP) containing the state of each directly connected link.
c. flood the LSP to all neighbors, who then store all LSPs received in a database. e. construct a complete map of the topology and compute the best path to each destination network. |
|
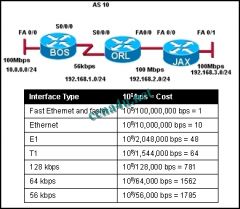
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are running OSPF. What cost would JAX put in its routing table for the 10.0.0.0/24 network?
a. 2 b. 156 c. 1564 d. 1785 e. 1787 |
e. 1787
|
|
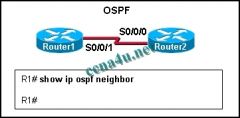
Refer to the exhibit. Router1 and Router2 are running OSPF. The show ip ospf neighbor command reveals no neighbors. What is a possible cause?
a. OSPF autonomous system IDs do not match. b. OSPF process IDs do not match. c. OSPF network types are identical. d. OSPF hello or dead timers do not match. |
d. OSPF hello or dead timers do not match.
|
|
|
A fully converged five router OSPF network has been running successfully for several weeks. All configurations have been saved and no static routes are used. If one router looses power and reboots, what information will be in its routing table after the configuration file is loaded but before OSPF has converged?
a. All routes for the entire network will be present. b. Directly connected networks that are operational will be in the routing table. c. Because the SPF algorithm has not completed all calculations, no routes will be in the table. d. A summary route for all previously learned routes will automatically appear in the routing table until all LSPs have been received by the router. |
b. Directly connected networks that are operational will be in the routing table.
|
|
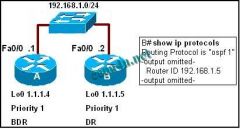
Refer to the exhibit. What configuration statements would give the results that are shown in the output of the show ip protocols command?
a. B(config)# int fa0/0 B(config-if)# router-id 192.168.1.5 b. B(config)# int lo0 B(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.5 c. B(config)# router ospf 1 B(config-router)# router-id 192.168.1.5 d. B (config)# router ospf 1 B(config-router)# ip address 192.168.1.5 |
c. B(config)# router ospf 1
B(config-router)# router-id 192.168.1.5 |
|
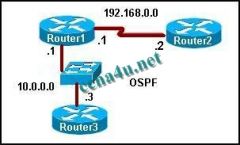
Refer to the exhibit. When OSPF is operational in the exhibited network, what neighbor relationship is developed between Router1 and Router2?
a. A FULL adjacency is formed. b. A 2WAY adjacency is formed. c. Router2 will become the DR and Router1 will become the BDR. d. Both routers will become DROTHERS. |
a. A FULL adjacency is formed.
|
|
|
What does OSPF use to calculate the cost to a destination network?
a. bandwidth b. bandwidth and hop count c. bandwidth and reliability d. bandwidth, load, and reliablity |
a. bandwidth
|
|
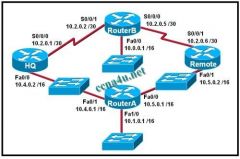
Refer to the exhibit. The routers in the exhibit are using default OSPF configuration settings to advertise all attached networks. If all of the routers start at the same time, what will be the result of the DR and BDR elections for this single area OSPF network? (Choose three.)
a. HQ will be DR for 10.4.0.0/16. b. Router A will be DR for 10.4.0.0/16. c. HQ will be BDR for 10.4.0.0/16. d. Router A will be DR for 10.5.0.0/16. e. Remote will be DR for 10.5.0.0/16. f. Remote will be BDR for 10.5.0.0/16. |
b. Router A will be DR for 10.4.0.0/16.
c. HQ will be BDR for 10.4.0.0/16. e. Remote will be DR for 10.5.0.0/16. |
|
|
What does OSPF use to reduce the number of exchanges of routing information in networks where large numbers of neighbors are present? (Choose two.)
a. root router b. backup root router c. domain router d. backup domain router e. designated router f. backup designated router |
e. designated router
f. backup designated router |
|
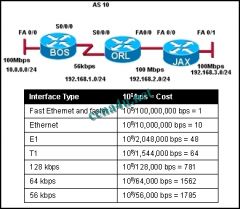
Refer to the exhibit. All routers have been configured with the interface priorities that are shown. All routers were restarted simultaneously. The results of the DR/BDR election are shown. What can be concluded about this network?
a. Router C cannot win a DR election under any circumstances. b. If the link for interface 192.168.1.4 goes down, router B will become the new DR. c. The highest router ID was most likely determined via an OSPF router-id statement or statements. d. If a new router is added with a higher router ID than router D, it will become the DR. |
c. The highest router ID was most likely determined via an OSPF router-id statement or statements.
|
|

Refer to the exhibit. Router A is correctly configured for OSPF. Which OSPF configuration statement or set of statements was entered for router B to generate the exhibited routing table?
a. B(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 b. B(config-router)# network 10.16.1.0 0.0.0.224 area 0 c. B(config-router)# network 10.16.1.0 255.255.255.224 area 0 d. B(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.255 area 0 e. B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0 |
a. B(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
|
|
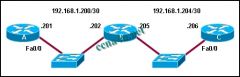
Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that the routers have default interface OSPF priorities and no configured loopback interfaces, what two roles will router B play on each network segment? (Choose two.)
a. DR for network 192.168.1.200 b. BDR for network 192.168.1.200 c. DROTHER on 192.168.1.200 d. DR for network 192.168.1.204 e. BDR for network 192.168.1.204 f. DROTHER on network 192.168.1.204 |
a. DR for network 192.168.1.200.
e. BDR for network 192.168.1.204. |
|
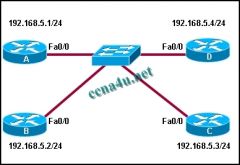
Refer to the exhibit. Routers A, B, C, and D are all running OSPF with default router IDs and OSPF interface priorities. Loopback interfaces are not configured and all interfaces are operational. Router D is the DR and router C is the BDR. What happens immediately after the following commands are entered on router A?
a. A(config)# interface fa0/0 b. A(config-if)# ip ospf priority 255 c. A will become the DR. D will become the BDR. d. A will become the DR. C will remain the BDR. e. D will remain the DR. A will become the BDR. f. D will remain the DR. C will remain the BDR. |
f. D will remain the DR. C will remain the BDR.
|
|
|
What range of networks will be advertised in the OSPF updates by the command Router1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 100?
a. 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.0.15/24 b. 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.15.0/24 c. 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.31.0/24 d. 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24 e. 192.168.16.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24 |
b. 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.15.0/24
|
|
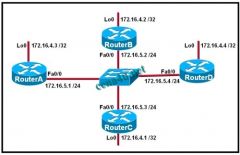
Refer to the exhibit. RouterA, RouterB, and RouterC in the diagram are running OSPF on their Ethernet interfaces. Router D was just added to the network. Routers are configured with the loopback interfaces (Lo 0) that are shown in the exhibit. What happens to the OSPF DR/BDR after RouterD is added to the network?
a. RouterB takes over as DR and RouterD becomes the BDR. b. RouterD becomes the BDR and RouterA remains the DR. c. RouterD becomes the DR and RouterA becomes the BDR. d. RouterC acts as the DR until the election process is complete. e. RouterD becomes the DR and RouterB remains the BDR. f. There is no change in the DR or BDR until either current DR or BDR goes down. |
f. There is no change in the DR or BDR until either current DR or BDR goes down.
|
|
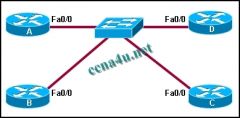
Refer to the exhibit. How many OSPF adjacencies must be formed to build the complete topology if a DR or BDR were not elected in this OSPF network?
a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7 e. 10 |
c. 6
|
|
|
What is the default administrative distance for OSPF?
a. 90 b. 100 c. 110 d. 115 e. 120 |
c. 110
|
|
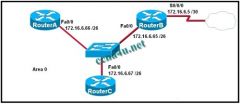
Refer to the exhibit. Which command sequence on RouterB will redistribute a gateway of last resort to the other routers in OSPF area 0?
a. RouterB(config)# router ospf 10 RouterB(config-router)# gateway-of-last-resort 172.16.6.6 RouterB(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0/0 b. RouterB(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.6.6 RouterB(config)# router ospf 10 RouterB(config-router)# default-information originate c. RouterB(config)# router ospf 10 RouterB(config-router)# default-network 172.16.6.6 0.0.0.3 area 0 RouterB(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.6.6 d. RouterB(config)# ip default-route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.6.6 RouterB(config)# router ospf 10 RouterB(config-router)# redistribute ip default-route |
b. RouterB(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.6.6
RouterB(config)# router ospf 10 RouterB(config-router)# default-information originate |
|
|
Which two statements describe the use of OSPF DR/BDR elections? (Choose two.)
a. Elections are always optional. b. Elections are required in all WAN networks. c. Elections are required in point-to-point networks. d. Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks. e. Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks. |
d. Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks.
e. Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks. |
|
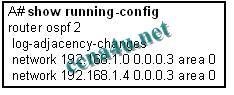
Refer to the exhibit. What does the “2″ stand for in the router ospf 2 statement?
a. The number 2 is the autonomous system number. b. The number 2 indicates the number of networks advertised by OSPF. c. The number 2 identifies this particular instance of OSPF on this router. d. The number 2 indicates the priority of the OSPF process on this router. |
c. The number 2 identifies this particular instance of OSPF on this router.
|
|
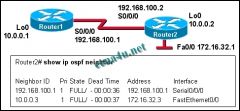
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator wants to set the router ID of Router1 to 192.168.100.1. What steps can the administrator take to accomplish this?
a. shut down the loop back interface b. use the OSPF router-id 192.168.100.1 command c. use the clear ip ospf process command d. nothing, the router-id of Router1 is already 192.168.100.1 |
d. nothing, the router-id of Router1 is already 192.168.100.1
|
|
|
Refer to the exhibit. What must be received between neighbors to prevent the dead time that is shown in the exhibit from reaching zero?
a. any traffic through the router interfaces b. routing database updates c. hello packets d. BPDU packets |
c. hello packets
|
|
![Refer to the exhibit. What does the “O*E2″ from the “O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:34, Serial0/0″ line represent?
an internal type 2 OSPF route.
an external OSPF route at least two hops away.
an external OSPF route from two different](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/607738/530317_m.jpg)
Refer to the exhibit. What does the “O*E2″ from the “O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:34, Serial0/0″ line represent?
a. an internal type 2 OSPF route. b. an external OSPF route at least two hops away. c. an external OSPF route from two different sources. d. an external OSPF route that will not increment in cost. e. a default route. f. The route was distributed into OSPF from a type 2 router. |
d. an external OSPF route that will not increment in cost.
|
|

Refer to the exhibit. Which network command or set of commands will cause OSPF to be enabled for any R1 interface connected to the exhibited subnets?
a. R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0 b. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 c. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 d. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.2.4 0.0.0.3 area 0 e. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 f. R1(config-router)# network 10.2.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 g. R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 |
b. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0.
c. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0. d. R1(config-router)# network 10.1.2.4 0.0.0.3 area 0. |
|

Refer to the exhibit. What is the cost of the route to the 10.0.0.0 network?
a. 2 b. 110 c. 1786 d. 1.544 |
c. 1786
|
|
|
What three parameters must be indentical between OSPF routers in order to form an adjacency? (Choose three.)
a. area id b. K-values c. metric value d. hello interval e. network type f. interface type |
a. area id.
d. hello interval. e. network type |
|
|
Which protocol is used by EIGRP to deliver and receive update packets?
a. FTP b. RTP c. TCP d. TFTP e. UDP |
b. RTP
|
|
|
Of the steps given, what is the final step in the link state routing process?
a. successors are placed into the routing table b. SPF computes best path to each destination network c. LSPs are flooded to all neighbors to converge the network d. DUAL algorithm is run to find best path to destination networks |
b. SPF computes best path to each destination network
|
|
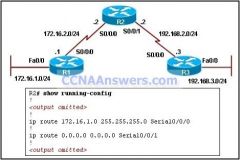
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the show running-config output, which option correctly reflects the routes that will be listed in the R2 routing table?
A. C 172.16.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S* 0.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 B. S 172.16.1.0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.1 C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 C. S 172.16.1.0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.1 C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S* 0.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 D. S 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S* 0.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 |
D. S 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 192.168.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 S* 0.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 |
|

Refer to the exhibit. A ping from R1 to 10.1.1.2 is successful, but a ping from R1 to 192.168.2.0 fails. What is the cause of this problem?
a. There is no gateway of last resort at R1. b. The serial interface between the two routers is down. c. A default route is not configured on R1. d. The static route for 192.168.2.0 is incorrectly configured. |
d. The static route for 192.168.2.0 is incorrectly configured.
|
|
|
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1, R2, and R3 have four local LANs attached. What is a correct set of network commands that will cause OSPF to be enabled for any R1 interface that is connected to its subnets?
A. R1(config-router)# network 10.10.1.0 0.0.3.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.7 area 0 B. R1(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.7 area 0 C. R1(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.8 0.0.0.3 area 0 D. R1(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.7 area 0 |
R1(config-router)# network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.7 area 0
|
|

What OSPF packets will trigger the reset of the Dead Time counter?
a. hello packets b. link-state update packets c. link-state advertisement packets d. OSPF routing database update packets |
a. hello packets
|
|
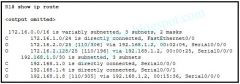
What is the cost of the route to the 172.16.2.128 network with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.128?
a. 25 b. 110 c. 196 d. 306 |
c. 196
|
|
|
Router R1 is participating in the OSPF routing protocol as well as the EIGRP routing protocol. If R1 learns of network 192.168.10.0/24 from both the OSPF and internal EIGRP routing protocols, how will the route appear in the routing table of R1?
a. Only the route learned from OSPF will appear in the routing table. b. Only the route learned from EIGRP will appear in the routing table. c. Both routes will appear in the routing table and they will be used for load balancing. d. Neither route will appear in the routing table until the network administrator selects which one to use. |
b. Only the route learned from EIGRP will appear in the routing table.
|
|
|
A technician needs to determine the value of the router ID for a branch router. What three commands can be used from the branch router to determine the router ID for a particular router that is participating in OSPF routing? (Choose three.)
a. show ip ospf b. show ip route c. show ip protocols d. show ip ospf interface e. show ip ospf neighbor f. show ip interface brief |
a. show ip ospf.
c. show ip protocols. d. show ip ospf interface. |
|

Refer to the exhibit. What does the state “FULL/ -” indicate?
a. The DR/BDR election is currently taking place. b. The router with router ID 10.112.0.34 and RouterA are on a point-to-point network. c. RouterA could not form a neighbor relationship with the router with router ID 10.112.0.34. d. OSPF hello and dead timers between RouterA and the router with router ID 10.112.0.34 do not match. |
b. The router with router ID 10.112.0.34 and RouterA are on a point-to-point network.
|

