![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A security methodology:
Security from a grass-roots effort - systems administrators attempt to improve the security of their system. LACKS: Participant support, organizational staying power |
Bottom Up Approach
|
|
|
A security methodology:
Initiated by upper management: policys and procedures, dictate goals and expected outcomes, and determine accountability. |
Top-down Approach
|
|
|
SecSDLC Driver:
as a result of a carefully developed implementation strategy |
Plan-driven
|
|
|
SecSDLC Driver:
started in response to some occurrence |
Event-driven
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
The objectives, constraints, and scope of the project are specified A preliminary cost/benefit analysis is developed A feasibility analysis is performed to assesses the economic, technical, and behavioral, feasibilities of the process |
Investigation
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
Consists primarily of: -Assessments of the organization -the status of current systems -capability to support the proposed systems |
Analysis
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
Based on business need, applications are selected capable of providing needed services Based on applications needed, data support and structures capable of providing the needed inputs are identified Finally, based on all of the above, select specific ways to implement the physical solution are chosen |
Logical Design
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
Specific technologies are selected to support the alternatives identified and evaluated in the logical design selected components are evaluated based on a make-or-b uy decision entire solution is presented to the end-user representatives for approval |
Physical Design
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
Components are ordered, received, assembled, and tested users are trained and documentation created users are then presented with the system for a performance review and acceptance test |
Implementation
|
|
|
SDLC Step:
Tasks necessary to support and modify the system for the remainder of its useful life The life cycle continues until the process begins again from the investigation phase When the current system can no longer support the mission of the organization, a new project is implemented |
Maintenance and Change
|
|
|
the senior technology officer
primaryily responsible for advising the senior executive(s) for strategic planning |
Chief Information Officer
|
|
|
Responsible for the assessment, management, and implementation of securing the information int he organization
May also be referred to as the manager for security, the security administrator, or a similar title |
Chief Information Security OFfficer
|
|
|
When a computer is used to conduct an attack. It is the ______ of an attack.
|
Subject
|
|
|
When a computer is the target of an attack. It is the ________ of an attack.
|
Object
|
|
|
A Normal Flow
|

What kind of information flow is this?
|
|
|
An Interruption
|
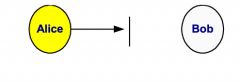
What kind of information flow is this?
|
|
|
Modification
|
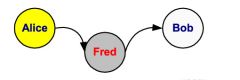
What kind of information flow is this?
|
|
|
Interception
|
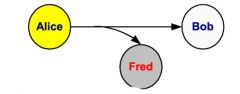
What kind of information flow is this?
|
|
|
Fabrication
|
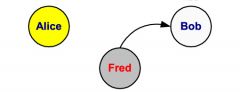
What kind of information flow is this?
|
|
|
Created to address the systematic and structural weaknesses affecting... capital markets which were revealed by repeating failures of audit effectiveness and corporate financial and broker-dealer responsibility in recent months and years.
|
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
|
|
|
What is the PCAOB
|
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board. Created by SOX.
|
|
|
-Control Environment
-Risk Assessment -Information and Communication -Control Activities -Monitoring |
Components of Internal Conrtol
|
|
|
-Recording
-Custody -Authorization |
Segregation of Duties
|
|
|
Internal Control
-Achieve performance and -profitability targets -prevent loss of resources -ensure reliable financial reporting -avoid damage to reputation and other consequences |
What internal control can do
|
|
|
The framework that provides a tool for the business process owner that facilitates the discharge of their responsibilities.
|
COBIT Framework
|
|
|
SysTrust Principal:
The system is avaliable for operation and use at times set forth in service agreements |
Availability
|
|
|
SysTrust Principal:
The system is protected against unauthorized physical and logical access |
Secuirty
|
|
|
SysTrust Principal:
System processing is complete, accurate, timely and in accordance with the entity's transaction approval and output distribution policy |
Integrity
|
|
|
SysTrust Principal:
System can be updated in a manner that provides continuous availability, security and integrity |
Maintainability
|
|
|
Risk management Community Role:
That best understands the threats and attacks that introduce risk into the organization. |
Information Security
|
|
|
Risk management Community Role:
play a part in the early detection and response process - they also insure sufficient resources are allocated |
Management and users
|
|
|
Risk management Community Role:
must assist in building secure systems and operating them safely |
Information Technology
|
|
|
the internal control weakness (Qualitative)
or A potential attack any of the assets that are protected. |
Threat
|
|
|
Specific avenues that threat agents can exploit to attack an information asset.
|
Vulnerability
|
|
|
assigning a rating or score to each specific information asset.
|
Risk Assessment
|
|
|
financial lost expected due to internal control weakness (Financial)
|
Exposure
|
|
|
probability of internal control weakness materializing (Statistical)
|
Risk
|
|
|
Percentage of time in SDLC spent on everything except maintenance
|
5-10%
|
|
|
Access Control Type:
Implemented at the discretion or option of the data user. |
Discretionarya Access Conrols
|
|
|
Access Control Type:
Structured and coordinated with a data classification scheme, and required |
Mandatory Access Controls
|
|
|
Access Control Type:
Those determined by a central authroity in the organization and can be based on that individual's role (Role-Based Controls) or a specified set of duties or tasks the individual is assigned (Task-Based Controls) or can be based on specified lists maintained on subjects or objects |
Nondiscretionary Controls
|
|
|
apply safeguards
|
avoidance
|
|
|
Transfer the risk
|
transference
|
|
|
Reduce the impact
|
mitigation
|
|
|
Inform themselves of all of the consequences and accept the risk without control or mitigation
|
acceptance
|
|
|
__________ controls stop attempts to exploit vulnerability by implementing enforcement of an organizational policy or a security principle, such as authentication or confidentiality
|
Preventive
|
|
|
___________ controls warn of violations of security principles, organizational policies, or attempts to exploit vulnerabilities
|
Detective
|
|
|
___________ controls use techniques such as audit trails, intrusion detection, or configuration monitoring
|
Detective
|
|
|
examines how well the proposed information security alternatives will contribute to the efficiency, effectiveness, and overall operation of an organization
|
Organizational Feasibility
|
|
|
Addresses user acceptance and support, management acceptance and support, and the overall requirements of the organization’s stakeholders
|
Operational Feasibility
|
|
|
Examines whether or not the organization has or can acquire the technology necessary to implement and support the control alternatives
|
Technical Feasibility
|
|
|
what can and cannot occur based on the consensus and relationships between the communities of interest
|
Political Feasibility
|
|
|
The analysis of measures against established standards
|
Baselining
|
|
|
When we have controlled any given vulnerability as much as we can, there is often risk that has not been completely removed or has not been completely shifted or planned for
|
Residual Risk
|
|
|
A plan or course of action intended to influence and determine decisions, actions and other matters.
|
Policy
|
|
|
Sets the strategic direction, scope, and tone for all security efforts within the organization
|
Security Program Policy
|
|
|
-addresses specific areas of technology
-requires frequent updates -contains an issue statement on the organization’s position on an issue |
Issue-Specific Security Policy(ISSP)
|
|
|
Formalized as written documents, distributed to users, and agreed to in writing, ______ are frequently codified as standards and procedures used when configuring or maintaining systems
|
Systems-Specific Policy(SysSP)
|
|
|
-Who can use the system
-What authorized users can access -When authorized users can access the system -Where authorized users can access the system from -How authorized users can access the system |
ACL Policies
|
|
|
Policy that stipulates at the end of the business day, all classified information must be properly stored and secured
|
clean desk policy
|
|
|
the basic skeletal structure within which additional detailed planning of the blueprint can be placed as it is developed of refined
|
framework
|
|
|
The people must become a layer of security, a ____________ that protects the information from unauthorized access and use
|
Human firewall
|
|
|
Continuity Strategies:
focuses on immediate response; if attack escalates or is disastrous, process changes to disaster recovery |
Incident response plans (IRPs)
|
|
|
Continuity Strategies:
typically focuses on restoring systems after disasters occur |
Disaster recovery plans (DRPs)
|
|
|
Continuity Strategies:
when damage is major or long term, requiring more than simple restoration of information and information resources |
Business continuity plans (BCPs)
|
|
|
high-level manager to support, promote, and endorse findings of project
|
Champion
|
|
|
leads project and makes sure sound project planning process is used, a complete and useful project plan is developed, and project resources are prudently managed
|
Project manager
|
|
|
should be managers or their representatives from various communities of interest: business, IT, and information security
|
Team Members
|
|
|
-Most common occurrence is complaint about technology support, often delivered to help desk
-Careful training needed to quickly identify and classify an incident -Once attack is properly identified, organization can respond |
Incident Detection
|
|
|
-Consists of actions that guide organization to stop incident, mitigate impact of incident, and provide information for recovery from incident
|
Incident Reaction
|
|
|
-Once incident has been contained, and control of systems regained
-First task is to identify human resources needed and launch them into action -Full extent of the damage must be assessed -Organization repairs vulnerabilities, addresses any shortcomings in safeguards, and restores data and services of the systems |
Incident Recovery
|
|
|
Several sources of information on ______, including system logs; intrusion detection logs; configuration logs and documents; documentation from incident response; and results of detailed assessment of systems and data storage
|
Damage Assessment
|
|
|
-Once extent of damage determined, _______ process can begin
-Process involves much more than simple restoration of stolen, damaged, or destroyed data files |
Recovery
|
|
|
-New systems can respond to incident threat autonomously
|
Automated Response
|
|
|
Positive identification of person/system seeking access to secured information/services (Username and Password)
|
Authentication
|
|
|
Predetermined level of access to resources (Access Level)
|
Authorization
|
|
|
Logging use of each asset (System logs)
|
Accounting
|
|
|
Unique alphanumeric identifier used to identify an individual when logging onto a computer/network
|
Username
|
|
|
Secret combination of keystrokes that, when combined with a username, authenticates a user to a computer/network
|
Password
|
|
|
Small, fixed-length numerical value
|
Checksum
|
|
|
-a (network) authentication protocol, NOT an authorization protocol.
-It is designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications by using secret-key cryptography. |
Kerberos
|
|
|
Secret key used during logon session between client and a service
|
Session key
|
|
|
Device (eg, PPP network server) that requires authentication from a peer and specifies authentication protocol used in the configure request during link establishment phase
|
Authenticator
|
|
|
Set of electronic information used to authenticate identity of a principal to a service
|
Ticket
|
|
|
Allows principal to authenticate itself to gain access to services in a distant part of a Kerberos system
|
Cross-realm authentication
|
|
|
-Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) mechanism used by an authenticator to authenticate a peer
-Uses an encrypted challenge-and-response sequence |
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
|
|
|
Piece of data that claims that a specific, named individual wrote or agreed to the contents of an electronic document to which the signature is attached
|
Digital signature
|
|
|
Converts plain text message into secret message
|
Encryption
|
|
|
Converts secret message into plain text message
|
Decryption
|
|
|
Uses only one key
|
Symmetric cipher
|
|
|
Uses a key pair (private key and public key)
|
Asymmetric cipher
|
|
|
Trusted, third-party entity that verifies the actual identity of an organization/individual before providing a digital certificate
|
Certificate authority (CA)
|
|
|
Practice of using a trusted, third-party entity to verify the authenticity of a party who sends a message
|
Nonrepudiation
|
|
|
-Authentication devices assigned to specific user
-Small, credit card-sized physical devices -Incorporate two-factor authentication methods -Utilize base keys that are much stronger than short, simple passwords a person can remember |
Security Tokens
|
|
|
Types of Security Tokens:
-Act as a storage device for the base key -Do not emit, or otherwise share, base tokens |
Passive
|
|
|
Types of Security Tokens:
-Actively create another form of a base key or encrypted form of a base key that is not subject to attack by sniffing and replay -Can provide variable outputs in various circumstances |
Active
|
|
|
-Uses measurements of physical or behavioral characteristics of an individual
-Generally considered most accurate of all authentication methods -Traditionally used in highly secure areas Expensive |
Biometric authentication
|
|
|
Error Rates:
-What percent of the time will an authorized person be rejected by the system? -Occurrence of an authorized person not being authenticated by a biometric authentication process when they are who they claim to be |
FRR (False Rejection Rate) Type 1 error rate / False Negatives
|
|
|
Error Rates:
-What percent of the time will an unauthorized person be accepted by the system? -Occurrence of an unauthorized person being authenticated by a biometric authentication process |
FAR (False Acceptance Rate) Type 2 error rate / False Positives
|
|
|
Error Rates:
Point at which FRR and FAR cross over. |
Equal Error Rate (ERR)
|
|
|
Biometric Technologies:
Looks at the details of how we sign our name, the loops in letters and angles in them. |
Dynamic Signature Verification
|
|
|
Biometric Technologies:
Checks for a unique typing pattern. |
Keystroke dynamics
|
|
|
Combination of password, tokens, bio (multiple of these)
|
Multi-factor authentication
|
|
|
This merges biometrics with the art of cryptography.
|
Biometric Encryption
|
|
|
a process effected by an entity's board of directors, management, and other personnel, designed to provide reasonable assurance.
|
Internal Control
|
|
|
True of False:
Risk "control" is the process of examining and documenting the security posture of and organization's information technology and the risks it faces. |
False
Identification |
|
|
True of False:
Each of the threats must be examined to assess its potential to endanger the organization and explore ways to reduce the risk it poses. This examination is know as a threat "profile". |
False
assessment |
|
|
True of False:
"Likelihood" risk is the risk that remains to the information asset even after the existing control has been applied. |
False
Residual |
|
|
True of False:
"Major" risk is a combined function of (1) threat less the effect of threat-reducing safeguards, (2) a vulnerability less the effect of vulnerability reducing safeguards, and (3) an asset less the effect of asset value reducing safeguards. |
False
Residual |
|
|
True of False:
The "standard" should begin with a clear statement of purpose. |
False
Policy |
|
|
True of False:
"Systems" specific security policies are formalized as written documents to be distributed to users and agreed to in writing. |
True
|
|
|
True of False:
"VISA" promotes a series of security modules with links to practices and implementation that represents a security methodology. |
False
CERT |
|
|
True of False:
One of the basic tenets of security architectures is the implementation of security in layers. This layered approach is called defense in "layers" |
False
depth |
|
|
True of False:
A(n) "IRP) ensures that critical business functions continue, if a catastrophic incident or disaster occurs by establishing operations at an alternative site. |
False
BCP |
|
|
True of False:
The false "detect" rate is the percentage or or value associated with the rate at which supplicants who are not legitimate users are allowed access to systems or areas as a result of a failure in the biometric device. |
False
Accept |
|
|
Information has ________ when it is whole, complete, and uncorrupted.
|
integrity
|
|
|
Weaknesses or faults in a system or protection mechanism that expose information to attack or damage are known as ___________.
|
Vulnerabilities
|
|
|
A(n) _________ is an object, person, or other entity that represents a constant danger to an asset.
|
Threat
|
|
|
A(n) _________ is an act or action that takes advantage of a vulnerability to compromise a controlled system.
|
Attack
|
|
|
A(n) __________ is a private word or combination of characters that only the user should know.
|
Password
|
|
|
_______ security addresses the issues necessary to protect the tangible items, objects, or areas of an organization from unauthorized access and misuse.
|
Physical
|
|
|
_______ of information is the quality or state of being genuine or orignial.
|
Authenticity
|
|
|
An Information System is the entire set of _________, people, procedures, and networks necessary to use information as a resource in the organization.
|
Software, Hardware, Data
|
|
|
The most successful kind of top-down approach involves a formal development strategy referred to as a(n)_______.
|
Systems Development Life cycle
|
|
|
In the ______ phase of the systems development life cycle, solutions are evaluated, selected and acquired through make-or-buy process.
|
Implementation.
|
|
|
-Protects the organiztion's ability to function
-Enables the safe operation of applications implemented on the organization's IT systems -Protects the data the organization collects and uses |
The functions performed by Information security
|
|
|
The formal processed used in decision making regarding the adoption of specific controls is called a(n) ______.
|
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA)
|
|
|
_________ Feasability addresses the user acceptance and support, managment acceptance and suppor and the overall requirements of the organization's stakeholders.
|
Operation
|
|
|
A buffer against the outside attacks is frequently referred to as a(n) ______.
|
Firewall
|
|
|
What is the most secure Biometric authentication system?
|
Retina Pattern Recognition
|
|
|
Steps of SecDLC
|
Investigate
Analyze Design Implement Maintinece |
|
|
Steps of SDLC.
|
Investigate
Analyze Design (logical) Design (Physical) Implement Maintinence |

