![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Physical Layer |
Describes the media that interconnects networking devices |
|
|
EIA |
Electronic Industries Alliance |
|
|
TIA |
Telecommunications Industry Association |
|
|
Campus Network |
Interconnected LANs within a limited geographic area |
|
|
EIA/TIA 568-B |
The standard that defines the six subsystems of a structured cabling system |
|
|
Building Entrance |
The point where the external cabling and wireless services interconnect with the internal building cabling |
|
|
Entrance Facilities (EF) |
A room set aside for complex electronic equipment |
|
|
Equipment Room (ER)/Backbone Cabling |
Cabling that interconnects telecommunication closets in the same building and between buildings |
|
|
Telecommunications Closet |
The location of the cabling termination points that includes the mechanical terminations and the distribution frames |
|
|
Telecommunications Room (TR) |
Another name for the Telecommunications Closet |
|
|
Horizontal Cabling |
Cabling that extends out from the telecommunications closet into the LAN work area |
|
|
TCO |
Telecommunications Outlet |
|
|
Work Area |
The location of the computers and printers, patch cables, jacks, computer adapter cables, and fiber jumpers |
|
|
Main Cross-connect (MC) |
Usually connects two or more building and is typically the central telecommunications connection point for a campus or building. It is also called the main distribution frame (MDF) or main equipment room. The MC connects to Telco, an ISP, and so on. Another term for the MC is the campus distributor. (CD) |
|
|
Intermediate Cross-connect (IC) |
Also called the building distributor (BD), this is the building's connection point to the campus backbone. The IC links the MC to the horizontal cross-connect (HC).
|
|
|
Cross-connect |
A space where you are going to take one or multiple cables and connect them to one or more cables or equipment |
|
|
Horizontal Cross-connect (HC) |
The connection between the building distributors and the horizontal cabling to the work area or workstation outlet - another term used for the HC is the floor distributors (FD).
|
|
|
Workstation or Work Area Outlet (WO) |
Also called the TO (telecommunications outlet), it's used to connect devices to the cable plant. The cable type typically used is CAT3, CAT5, CAT5e, CAT6, CAT6A, and various coaxial cables. Devices typically connected to these outlets are PCs, printers, servers, phones, televisions, and wireless access points. |
|
|
Terminated |
Define later |
|
|
Patch Cable |
a cable used to make the physical connection from the computer to the wall plate. |
|
|
UTP - Unshielded Twisted-pair |
a cable that plays an important role in computer networking |
|
|
Balanced Mode |
Neither wire in the wire pairs connects to ground and the balance of the two wire pairs helps maintain the required level of performance in terms of crosstalk and noise rejection |
|
|
FastEthernet |
An Ethernet system operating at 100Mbps |
|
|
Network Congestion |
A slowdown on network data traffic movement |
|
|
Full Duplex |
Computer system that can transmit and receive at the same time |
|
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
An Ethernet system operating at 1000Mbps |
|
|
CAT7/7a and CAT6a |
UPT cable standards that support 10GB date rates for a length of 100 meters |
|
|
10GBASE-T |
10GBDB over twisted-pair copper |
|
|
STP |
Shielded twisted-pair |
|
|
EMI |
Electromagnetic Interference |
|
|
T568A |
Wire color guidelines specified under the EIA/TIA568A standard |
|
|
T568 |
Wire color guidelines specified under the EIA/TIA568B standard |
|
|
Color Map |
The specification of which wire color connect to which pin on the connector |
|
|
TX |
Abbreviation for transmit |
|
|
RX |
Abbreviation for receive |
|
|
Straight-through Cable |
The wire pairs in the cable connect to the same pin numbers on each end
A B 1 -------------- 1 2 -------------- 2 3 -------------- 3 4 -------------- 4 5 -------------- 5 6 -------------- 6 7 -------------- 7 8 -------------- 8 |
|
|
Crossover Cable |
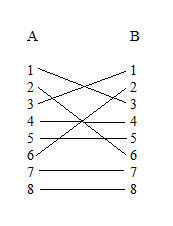
Transmit and receiver wire pairs are crossed
|
|
|
Link |
Point from one cable termination to another |
|
|
Full Channel |
Consists of all the link elements from the wall plate to the hub or switch |
|
|
Attenuation (Insertion Loss) |
The amount of loss in the signal strength as it propagates down a wire or fiber strand |
|
|
Near-end Crosstalk (NEXT) |
A measure of the level of crosstalk or signal coupling within the cable, with a high NEXT (dB) value being desirable |
|
|
Crosstalk |
Signal coupling in a cable or in other words it is what you occasionally hear on the telephone when you can faintly hear another conversation |
|
|
Power Sum NEXT (PSNEXT) |
Power Sum Testing measures the total crosstalk of all cable pairs. This test ensures that the cable can carry data traffic on all four pairs at the same time with minimal interference. A HIGHER PSNEXT value is the best. |
|
|
Equal Level FEXT (ELFEXT) |
This measurement is for the far end of the cable and it does not depend on the length of the cable. This measurement is obtained by subtracting the attenuation value from the far-end crosstoalk (FEXT) loss. A larger ELFEXT value is the best. |

