![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
148 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Information age
|
-a time when knowledge is power
-businesses are using information and information technology to gain and sustain a competitive advantage |
|
|
What is MIS?
|
-planning for, developing, managing, and using IT tools to help people perform their work effectively and efficiently
|
|
|
What is Information technology(IT)?
|
*any computer-based tool that people use to work more efficiently and effectively with information
Examples: -Traditional computer (notebook, PC, etc) -Internet -Database |
|
|
Three key organizational resources in MIS
|
-Information
-People -Technology |
|
|
What is the difference between Data and Information?
|
*Data – raw facts that describe a particular phenomenon
-numbers, letters, etc. *Information – data that has meaning & that affects decision-making -Weather – when deciding what to wear |
|
|
What is Business intelligence?
|
Business intelligence – knowledge about competitors, suppliers, your own internal operations, etc
Combined forms of information to create real knowledge Encompasses everything that affects your business Helps you make strategic business decisions |
|
|
What are the 2 forms of information perspectives?
|
-Personal dimensions of information
-Organizational dimensions of information |
|
|
Personal Dimensions of Information
|
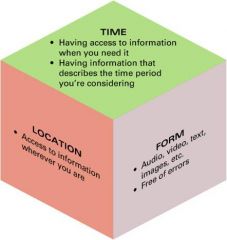
*Time
-When you need information -Describing the right time period *Location – no matter where you are -Intranet – internal organizational intranet *Form -Usable, understandable, accurate |
|
|
Organizational Dimensions of Information
|
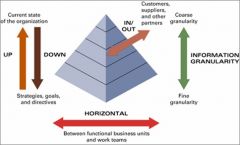
-Information flows
-Information granularity -What information describes |
|
|
Information Flows within an Organization
|
Upward – current state of organization based on transactions
Downward – Strategies, goals, directives Horizontal – between functional units, work teams Outward/inward – to/from suppliers, customers, distributors, etc |
|
|
Information Granularity
|
Information granularity – extent of detail within information
Lower org levels – information that contains a great amount of detail (fine) Upper org levels – highly summarized information (coarse) |
|
|
What Information Describes
|
Internal – operational aspects of organization
External – environment surrounding organization Objective – something that is known Subjective – something that is unknown |
|
|
Technology-literate knowledge worker
|
knows how and when to apply technology
|
|
|
Information-literate knowledge worker
|
-Defines what information is needed
-Knows how and where to obtain information -Understands information -Acts appropriately based on information |
|
|
Information technology (IT)
|
computer-based tools that people use to work with information
|
|
|
Two basic categories of technology
|
-Hardware
-Software |
|
|
Key Technology Categories
|
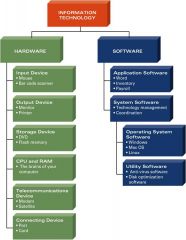
|
|
|
Hardware
|
*Hardware – physical devices of a computer
Examples: -Input devices -Output devices -Storage devices -CPU & RAM -Telecommunications devices -Connecting devices |
|
|
Input device
|
*enter information and commands
Examples: -Mouse -Bar Code Scanner |
|
|
Output device
|
*hear, see, or otherwise recognize the results of information-processing requests
Examples: -Monitor -Printer |
|
|
Storage device
|
*store information for use at a later time
Examples: -DVD -Flash Memory |
|
|
CPU
|
*interprets and executes software instructions
|
|
|
RAM
|
*temporarily holds information and software
|
|
|
Telecommunications device
|
*sends and receives information in a network
Examples: -Modem -Satellite |
|
|
Connecting device
|
*connects pieces of hardware
Examples: -Cable -Port |
|
|
Application software
|
*solves specific problems, performs specific tasks
Examples: -Word -Inventory -Payroll |
|
|
System software
|
*handles technology management tasks and coordinates all hardware
|
|
|
Two types of system software
|
-Operating system software
-Utility software |
|
|
Operating system software
|
*controls application software, manages hardware devices
Examples: -Windows -Mac -Linux |
|
|
Utility software
|
*additional functionality to your operating system
Examples: -Anti-Virus -Disk Optimization Software |
|
|
Ubiquitous computing
|
(ANYWHERE, ANYTIME)
*concept; technology support anytime, anywhere, with access to any needed information Examples: -Decentralized computing -Shared information -Mobile computing |
|
|
Decentralized computing
|
Type of Ubiquitous computing
*Distributes computing power within the organization to knowledge workers |
|
|
Shared information
|
Type of Ubiquitous computing
*Stores information in one or more central locations; allows anyone access to needed information |
|
|
Mobile computing
|
Type of Ubiquitous computing
*wireless technology to connect to needed resources and information Example: M-commerce - electronic commerce conducted wirelessly |
|
|
Competitive advantage
|
*providing a product/service in a way that customers value more than what the competition is able to do
|
|
|
Top line
|
*business activities that increase revenue
-IT can support |
|
|
Bottom line
|
*business activities that decrease costs
-IT can support |
|
|
Database
|
*stores tremendous detail on every transaction/event
|
|
|
DBMS
|
*software bridge between information/software system and information/you
|
|
|
Online transaction processing (OLTP)
|
*gathering, processing, and updating information for a transaction
|
|
|
Online analytical processing (OLAP)
|
*manipulating information to support decision making
Examples: -Executive information system -Collaboration system -Artificial intelligence |
|
|
Executive information system (EIS)
|
*supports “drilling down” in information to find problems/opportunities
-Online analytical processing (OLAP) |
|
|
Collaboration system
|
*improves team performance by supporting sharing and flow of information
-Online analytical processing (OLAP) |
|
|
Artificial intelligence (AI)
|
*science of imitating human thinking and behavior
-Online analytical processing (OLAP) |
|
|
Business Initiative Support
|
*IT use in business is all about enabling initiatives
Examples: -Supply chain management system -Customer relationship management system |
|
|
Run, Grow, Transform
|
*Framework for percentage allocation of IT dollars toward…
Run – optimizing activity execution (bottom line) Grow – increasing market reach, product offerings, etc (top line) Transform – innovating business processes |
|
|
Software
|
*set of instructions that hardware executes to carry out a specific task for you
|
|
|
Minicomputer (mid-range computer)
|
*meets needs of several people simultaneously in a small or medium-sized business
|
|
|
Mainframe computer
|
*meets needs of hundreds of people in a large business
|
|
|
Supercomputer
|
*fastest, most powerful, and most expensive type of computer
|
|
|
Binary digit (bit)
|
*smallest unit of information your computer can process (1 or 0)
|
|
|
Byte
|
*A group of eight bits that represents one natural character
|
|
|
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
|
*coding system that personal computers use to represent one natural character
|
|
|
Five Forces Model
|
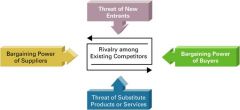
*helps determine the relative attractiveness of an industry and includes
-Buyer power -Supplier power -Threat of substitute products and services -Threat of new entrants -Rivalry among existing competitors |
|
|
Buyer power
|
*high when buyers have many choices; low when there are very few choices
-As a provider of products and services you want low buyer power -IT can help you (as a provider) reduce buyer power Examples (all enabled by IT): -Loyalty program – rewards customers for repeated business Airline industry Hotels Grocery stores |
|
|
Supplier power
|
*high when buyers have few choices; low when buyers have many choices
-As a business, you want High buyer power when making purchases. High supplier power when selling products and services |
|
|
Threat of substitute products or services
|
*high when there are many alternatives; low when there are few
|
|
|
Switching cost
|
*costs that make customers reluctant to switch
|
|
|
Threat of new entrants
|
*high when it is easy for new competitors to start; low when it is not
|
|
|
Entry barrier
|
*feature that customers want and new competition must provide to enter market
-ATMs, online banking, etc |
|
|
Rivalry among existing competitors
|
*high in a fiercely competitive market; low in a more complacent market
-Example: retail grocery Industry --Highly competitive --Use IT to compete on price |
|
|
What does the Five Forces Model do?
|
-Helps determine the attractiveness of an industry
-Should enter or expand operations in an industry? -How can IT help? --Increase/reduce buyer/supplier power? --Create/eliminate an entry barrier? |
|
|
Value chain
|
*organization as a chain – or series – of processes, each of which either add to or reduce value to products or services
|
|
|
Business process
|
*set of activities that accomplishes a specific task
-For example, “Open New Account” Business Process Credit Check -> Open Account -> Deposit Funds |
|
|
Value Chain Processes (Support and Primary)
|
Primary value processes (along bottom) – creates, delivers, markets, and sells products and services
Support value processes (along top) – support primary value processes |
|
|
Value Chain Image
|
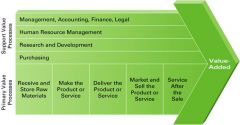
|
|
|
Major business initiatives that need IT
|
-Customer relationship management (CRM)
-Supply chain management (SCM) -Business intelligence (BI) -Integrated Collaboration Environments |
|
|
Supply Chain
|
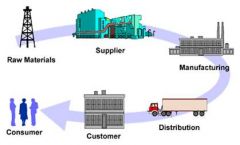
*a process from supplier to manufacture to wholesaler to retailer to consumer.
-Information and materials flow from supplier of raw materials to consumer |
|
|
Supply chain management (SCM)
|
*tracks inventory and information among processes and across companies
|
|
|
SCM system
|
*IT system that support supply chain management activities
-by automating the tracking of inventory and information |
|
|
JIT
|
*provides product/service just when needed
|
|
|
Inter-modal transportation
|
*uses multiple channels (trucks, boats, etc) of transportation
|
|
|
Strategic & Competitive Opportunities with SCM
|
Fulfillment – right quantity of parts at right time
Logistics – transportation costs low Production – production lines run smoothly Revenue and profit – no sales are lost because of stock-outs Spend – minimizing costs of purchases of material |
|
|
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
|
*Manages interaction with current and prospective customers
|
|
|
CRM system
|
*use information about customers to gain insight in order to serve them better
Includes following functions -Sales force automation -Customer service and support -Marketing campaign management and analysis |
|
|
Front office systems
|
*primary interface to customers and sales channels
|
|
|
Back office systems
|
*fulfill and support customer orders
|
|
|
Business intelligence
|
*knowledge about competitors, suppliers, your own internal operations, etc
-Combined forms of information to create real knowledge -Encompasses everything that affects your business -Helps you make strategic business decisions |
|
|
BI system
|
*support business intelligence function
-Capabilities in the firm -State of the art, trends, and future directions -External environment affecting competition -Actions of competitors |
|
|
Data warehouses
|
*collections of information (BI) from multiple operational databases
|
|
|
Data marts
|
*focused portion of a data warehouse
|
|
|
Strategic and Competitive Opportunities with BI
|
-Corporate performance management
-Optimizing customer relations -Management reporting of BI -Knowledge right time, location, and form |
|
|
Digital dashboard
|
*displays key information tailored to an individual
|
|
|
E-collaboration
|
*the use of technology tools to support:
-Work activities -Knowledge management -Social networking -Learning |
|
|
Integrated collaboration environment (ICE)
|
*environment in which virtual teams do their work
|
|
|
Virtual team
|
*a team whose members are located in varied geographical locations
|
|
|
Collaboration systems
|
*systems that are designed to improve team collaboration
-by supporting sharing and flow of information |
|
|
Workflow system
|
facilitates automation of business processes (value chain implementation)
|
|
|
Workflow
|
*steps, from beginning to end, required for a business process
|
|
|
Knowledge management (KM) system
|
*supports capturing, organization, and dissemination of knowledge (know-how)
|
|
|
Social network system
|
*links you to people you know, and from there, people they know
|
|
|
E-learning tools
|
IT systems that facilitate learning (e.g., Blackboard)
|
|
|
Strategic & Competitive Opportunities with E-Collaboration
|
-Joint ventures on large projects within an industry
-Sharing knowledge -Making the most of contacts |
|
|
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) system
|
*software for business management, supporting
-Planning and manufacturing -Sales and marketing -Distribution and accounting -Finance, HR, and project management |
|
|
Enterprise Software Image
|
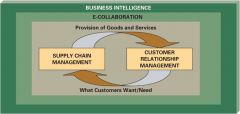
|
|
|
Operational database
|
*database that supports OLTP ( T )
|
|
|
Database
|
*logical collection of information you organize and access according to the logical structure of the information
|
|
|
Relational database
|
*uses a series of two-dimensional tables or files to store information in the form of a database
|
|
|
Data dictionary
|
*contains the logical structure of the information in a database
|
|
|
Primary key
|
*field (or group of fields in some cases) that uniquely describe each record
|
|
|
Foreign key
|
*primary key of one file that appears in another file
-Foreign keys help create relationships among tables |
|
|
Integrity constraint
|
*rule that helps ensure the quality of information
Examples: -Primary keys must be unique -Foreign keys cannot be blank -Sales price cannot be negative -Phone numbers must have an area code |
|
|
Database management system (DBMS)
|
*helps you specify the logical organization for a database and access and use the information within a database
-Word processing software = document -Spreadsheet software = workbook -DBMS software = database |
|
|
DBMS Tools
Database Image |
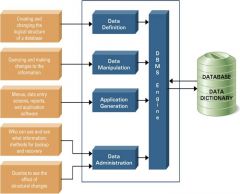
*5 software components
-DBMS engine -Data definition subsystem -Data manipulation subsystem -Application generation subsystem -Data administration subsystem |
|
|
DBMS engine
|
*accepts logical requests, converts them into their physical equivalent, and accesses the database and data dictionary
-DBMS engine separates the logical from the physical view of information |
|
|
Physical view
|
*how information is arranged, stored, and accessed on a storage device (e.g., hard disk)
|
|
|
Logical view
|
*how you (knowledge worker) need to arrange and access information
Databases – you work only with logical views |
|
|
Data definition subsystem
|
*helps you create and maintain the data dictionary and define the structure of the tables in a database
-When creating a database, you must first use the data definition subsystem to create data dictionary for a database before entering any information -Logical structure of information includes: column name, data type, data entry requirement, etc. |
|
|
Data manipulation subsystem
|
*helps you add, change, and delete information
Primary interface between you and a database -Views -Report generators -QBE tools -SQL |
|
|
Query-by-example (QBE) tool
|
*helps you graphically design the answer to a question
“What driver most often delivers concrete to Triple A Homes?” |
|
|
Structured query language (SQL)
|
*standardized fourth-generation language found in most DBMSs
-Performs same task as QBE -Uses sentence structure instead -Mostly used by IT people |
|
|
Application generation subsystem
|
*contains facilities to help you develop transaction-intensive applications
--Data entry screens (called forms in Access) --Programming languages -Mostly used by IT people |
|
|
Data administration subsystem
|
*helps you manage the overall database environment
-Backup and recovery -Security management -Query optimization -Concurrency control -Change management |
|
|
Data Warehouses & Data Mining Differences
|
-Data warehouses support OLAP and decision making
-Data warehouses do not support OLTP -Data-mining tools are tools for working with data warehouse information --DBMS software = database --Data-mining tools = data warehouse |
|
|
Data warehouse
|
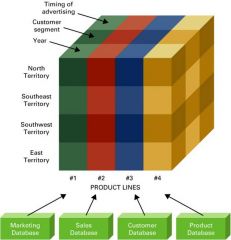
logical collection of information – gathered from operational databases – used to create business intelligence that supports business analysis activities and decision-making tasks
|
|
|
Describe a Data Warehouse
|
-Multidimensional
-Rows and columns -Also layers -Many times called hypercubes |
|
|
Data-mining tools
|
*software tools that you use to query information in a data warehouse; support the concept of OLAP
-Query-and-reporting tools -Intelligent agents -Multidimensional analysis tools -Statistical tools |
|
|
Query-and-reporting tools
|
*similar to QBE tools, SQL, and report generators in the typical database environment
-Generate simple queries and reports |
|
|
Multidimensional analysis (MDA) tools
|
*slice-and-dice techniques that allow you to view multidimensional information from different perspectives
-Bring new layers to the front -Reorganize rows and columns |
|
|
Data mart
|
*subset of a data warehouse in which only a focused portion of the data warehouse information is kept
|
|
|
Extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL)
|
*a process in which you specify
-what information you want from each database -how the information is to be associated -what rules to follow in consolidating the information *ETL ensures information cleanliness in a data warehouse |
|
|
Computer-aided decision support system
|
*a system that help you to analyze information to find out business intelligence and make good decisions
|
|
|
The Two Categories of Computer-Aided Decision Support System
|

|
|
|
Phases of decision making
|
1. Intelligence – find or recognize a problem, need, or opportunity (e.g., a threat of new competition, declining sales)
2. Design – Develop possible ways of solving the problem 3. Choice – weigh the merits of each solution 4. Implementation – carry out the solution |
|
|
Satisficing
|
*the process of making a choice that meet your needs and is satisfactory, without necessarily being the possible choice available
|
|
|
Structured decision
|
*processing a certain information in a specified way so that you will always get the right answer
Important: -Rules or criteria -No feeling or intuition |
|
|
Nonstructured decision
|
*one for which there may be several “right” answers, without a sure way to get the right answer
Important: -No rules or criteria -Feeling or intuition |
|
|
What Job Do I Take?
|
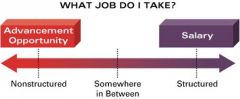
*Most decisions fall between structured and nonstructured
*Example: Choosing the Right Job -Structured: salary -Nonstructured: perception of best advancement opportunity |
|
|
Recurring decision
|
*one that happens repeatedly
Example: Calculating pay for hourly employees |
|
|
Nonrecurring (ad hoc) decision
|
*one you make infrequently
Example: A company merger |
|
|
Decision support system (DSS)
|
*a highly flexible and interactive system that is designed to support decision making when the problem is not structured
-Decision support systems help you analyze, but you must know how to solve the problem, and how to use the results of the analysis |
|
|
Model management component
|
*consists of both the DSS models and the model management system
|
|
|
Data management component
|
*stores and maintains the information that you want your DSS to use
|
|
|
User interface management component
|
*allows you to communicate with the DSS
|
|
|
Geographic information system (GIS)
|
*DSS designed specifically to analyze spatial information
-Spatial information is any information in map form -Businesses use GIS software to analyze information, generate business intelligence, and make decisions |
|
|
Artificial intelligence (AI)
|
*the science of making machines imitate human thinking and behavior
Example: Robot – a mechanical device equipped with simulated human senses and the ability to take action on its own |
|
|
Expert (knowledge-based) system
|
*an artificial intelligence system that applies reasoning capabilities to reach a conclusion
-Used for --Diagnostic problems (what’s wrong?) --Prescriptive problems (what to do?) -Built for a specific application area or domain --Accounting, medicine, process control, human resource management, financial management, production, etc. |
|
|
What Expert Systems Can and Can’t Do
|
*An expert system can
-Reduce errors -Improve customer service -Reduce cost *An expert system can’t -Use common sense -Automate the whole reasoning processes |
|
|
Neural network (artificial neural network or ANN)
|
-an artificial intelligence system that is capable of finding and differentiating patterns
-Learn and adjust to new circumstances on their own -Take part in massive parallel processing -Function without complete information -Cope with huge volumes of information -Analyze nonlinear relationships |
|
|
Fuzzy logic
|
*a mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information
-Used to make ambiguous information such as “short” usable in computer systems -Applications --Google’s search engine --Washing machines --Antilock breaks |
|
|
Genetic algorithm
|
*an artificial intelligence system that mimics the evolutionary, survival-of-the-fittest process to generate increasingly better solutions to a problem
-Take thousands or even millions of possible solutions and combine and recombine them until it finds the optimal solution -Work in environments where no model of how to find the right solution exists |
|
|
Evolutionary Principles of Genetic Algorithms
|
Selection – or survival of the fittest or giving preference to better outcomes
Crossover – combining portions of good outcomes to create even better outcomes Mutation – randomly trying combinations and evaluating the success of each |
|
|
Intelligent agent
|
*software that assists you, or acts on your behalf, in performing repetitive computer-related tasks
Types -Information agents -Monitoring-and-surveillance or predictive agents -Data-mining agents -User or personal agents |
|
|
Information Agents
|
*intelligent agents that search for information of some kind and bring it back
|
|
|
Buyer agent or shopping bot
|
an intelligent agent on a Web site that helps you, the customer, find products and services you want
|
|
|
Monitoring-and-surveillance (predictive) agents
|
*intelligent agents that constantly observe and report on some entity of interest, a network, or manufacturing equipment, for example
|
|
|
Data-mining agent
|
*operates in a data warehouse discovering information
-Most common type: Classification --Finds patterns in information and categorizes items into those classes --Neural networks do this best, so neural networks are part of many data mining tools -Detects… --A major shift in a trend or a key indicator --The presence of new information and alert you ---Example: Volkswagen |
|
|
User or personal agent
|
*intelligent agent that takes action on your behalf
Examples: -Prioritize e-mail -Act as gaming partner -Assemble customized news reports -Fill out forms for you -“Discuss” topics with you |

