![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
not arranged in any particular order
|
assymetry
|
|
|
|
body parts are arranged around a central axis. like spokes on a bicycle wheel
|
radial symmetry
|
|
|
|
body is divided into left and right halves that are mirror images of each other.
|
bilateral symmetry
|
|
|
|
tissue organization for ana organsim that has an ectoderm and endoderm
|
diploblastic
|
|
|
|
tissue organization of an organism that contans ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
|
triploblastic
|
|
|
|
three body cavity possibilities for triploblastic organisms
|
acoelomate,pseudocoelomate, coelomate
|
|
|

animals such as flatworms which lack a body cavity
|
acoelomate
|
|
|

animals such as round worms have fluid filled body cavity, separating the gut from the body wall and only the body wall is lined with mesoderm.
|
psuedocoelomate
|
|
|
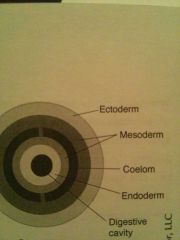
animals have body cavity where organs are suspended by mesentery membranes, and both of the organs are completely lined with mesoderm
|
coelomate
|
|
|
|
undergo spinal cleavage and develop so that the first opening in the embryo is the mouth
|
protosomes
|
|
|
|
undergo radial cleavage and develop the anus first, then the mouth at the other end of the embryo
|
deuterostomes
|
|
|
|
the phylum for sponge?
|
porifera
|
|
|
|
tissue organization for sponge?
|
no tissue system
|
|
|
|
mobility for sponge?
|
sessile
|
|
|

rod like structures that support the body of a sponge.
|
spicules
|
|
|
|
phylum for hydra
|
cnidaria
|
|
|
|
phylum for jellyfish
|
cnidaria
|
|
|
|
phylum for metridium
|
cnidaria
|
|
|
|
phylum for coral
|
cnidaria
|
|
|
|
cnidaria- tissue type; two different body forms; cavity type; symmetry;
|
diploblastic; polyps(sessile) and medusa(mobile); acoelomate; radial symmetry
|
|
|
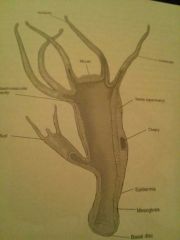
polyp life form, locate mouth and tentacles
|
hydra(underline)
|
|
|
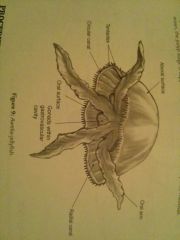
medusa life form
|
jellyfish
|
|
|
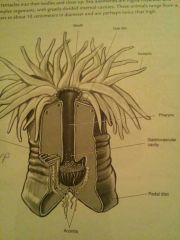
locate: oral disc, mouth, pharynx, gastrovascular cavity, pedal disc, temtacles
|
metridium
|
|
|
|
coral consits of what? what are radial ridges?
|
calcium carbonate
|
|
|
|
platyhelminths have what of the following?
symmetry, tissue type, body cavity, head development known as... |
bilateral, triploblastic, acoelomate, cephalization
|
|
|
|
pluripotent stem cells; the only mitotically active cells in dugesia
|
neoblasts
|
|
|
|
what protects tapeworms from digestion?
|
cuticle
|
|
|
|
what phylum are dugesia"planria" and "flat worm."
|
platyhelminths
|
|
|
|
phylum nematoda have what of the following:symmetry, tissue type, cavity, and what genus are studied?
|
bilateral, triploblastic, psuedocoelomate, round Trichinalla, ascaris and "vinegar eel"
|
|
|
|
what is the sex morphology of trichinella?
|
sexually dimorphic
|
|
|
|
give the following for the phylum mollusca: symmetry, tissue type, body cavity and what froups where studied?
|
bilateral, triploblastic, coelomate, gastropa, bivalvia and cephalapoda
|
|
|
|
"squids, octopus cuttlefish," and nautilus all belong to what phylum and class?
|
mollusca and cephalopoda
|
|
|
|
identify the following for animals in phylum annelida: symmetry, tissue type, body cavity, and studied genus
|
bilateral, triploblastic, coelomate, limbricus and leeches.
|
|
|
|
genus: lumbricus and "leeches" are part of which phylum?
|
annelida
|
|
|

name the organism
|
ascaris
|
nematoda
|

