![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
364 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the SI system of measurement?
|
The International System
|
|
|
What are the names of the SI units for mass, length, time, and temperature?
|
kilogram, meter, second, and Kelvin
|
|
|
What is the mega- unit of measure?
|
M, million
|
|
|
What is the micro- unit of measure?
|
u, 0.000001 (10^-6)
|
|
|
What is the nano- unit of measure?
|
n, 0.000000001 (10^-9)
|
|
|
What is the volume of 1L in meters cubed?
|
1 dm^3
|
|
|
How do you determine the significant number for addition and subtraction?
|
Go by the number with the smallest number of decimal places
|
|
|
What is a conversion factor?
|
A ratio of the two parts of the ‘equivalence statement’ that relates two units ie 12/1 dozen or 1 dozen/12 (the one we want to know goes at the top)
|
|
|
What is dimensional analysis?
|
Changing from one unit to another via conversion factors (based on the equivalence statements between the units)
|
|
|
What are the boiling and freezing points of water in Fahrenheit?
|
212F and 32F
|
|
|
What is another name for the Kelvin scale?
|
the absolute scale
|
|
|
What is density?
|
The amount of matter present in a given volume of substance (mass/volume)
|
|
|
How do you convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
|
Tf = 1.80 (Tc) + 32
|
|
|
What is specific gravity?
|
the ratio of the density of a given liquid to the density of water at 4*C
|
|
|
What is a “model”?
|
A theory; a set of tested hypotheses that gives an overall explanation of some part of nature
|
|
|
What is a law?
|
a summary of observed behaviour
|
|
|
What is the difference between a law and a theory?
|
-a law is a summary of observed (measurable) behaviour, and a theory is an explanation
-a law tells what happens, a theory is our attempt to explain why it happens |
|
|
What are the non-metallic gaseous elements?
|
O, N, F, Cl, H, and the noble gases
|
|
|
Are most of the chemical elements found in nature in the elemental form or combined in compounds? Why?
|
Most elements are too reactive to be found in uncombined form in nature and are found only in compounds
|
|
|
Simple negative ions formed from single atoms are given names that end in:
|
-ide
|
|
|
How many different elements are there?
|
About 116, 88 which occur naturally
|
|
|
What are the nine elements that account for most of the compounds found in the Earth’s crust?
|
In order of their abundance: O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K, Mg, H
|
|
|
What four elements form the basis for all biologically important molecules?
|
In order of abundance: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
|
|
|
Which elements are diatomic?
|
group 7 (halogens) + H, N, O
|
|
|
What is the law of constant composition?
|
A given compound always has the same composition (water = H2O)
|
|
|
What are the 5 main ideas of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
|
1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms
2. All atoms of a given element are identical 3.The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form other compounds + law of constant composition 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes, not created or destroyed |
|
|
How/why did Dalton’s theory become widely accepted?
|
He was able to correctly predict the formation of multiple compounds between two elements
|
|
|
How do the three subatomic particles compare to each other in mass?
|
protons and neutrons are roughly same size, electrons are ~2k times smaller
|
|
|
What really determines the chemical behaviour of an atom?
|
# of electrons
|
|
|
What is an atom’s atomic number?
|
number of protons
|
|
|
What are isotopes?
|
atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
|
|
|
What is an atom’s mass number?
|
neutrons + protons
|
|
|
What do 1 4 and A mean in ₁⁴A ?
|
1=atomic number, 4=atomic mass, A=elemental symbol
|
|
|
What do the subscripts before an elemental symbol mean?
|

|
|
|
How is the periodic table organized?
|
By atomic number (number of protons)
|
|
|
What is group 1 of the periodic table?
|
Alkali metals
|
|
|
What is group 2 of the periodic table?
|
Alkaline earth metals
|
|
|
What is group 7 of the periodic table?
|
halogens
|
|
|
What are the transition metals?
|
-center of periodic table
|
|
|
What are the physical properties of metals?
|
-efficient conduction of heat and electricity
-malleability (can be hammered into thin sheets) -ductility (can be pulled into wires) -a lustrous (shiny) appearance |
|
|
Can non-metals have one or more metallic properties?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What are the elements called that are close to the “stair-step” on the periodic table?
|
metalloids or semimetals (often show a mix of metallic and nonmetallic properties
|
|
|
What are the only two elements that are liquid in their elemental forms at 25*C? Others?
|
bromine and mercury, all others are solid
|
|
|
What are allotropes?
|
different forms of a given element
|
|
|
How are cations named?
|
by taking the name of the parent atom and adding “cation” or “ion”
|
|
|
How is an anion named?
|
by adding –ide to the root of the atom name
|
|
|
What is the most common way ions are formed?
|
metallic elements combine with non-metallic elements
|
|
|
Metals always form ______ ions.
|
positive
|
|
|
Which ion charges are easy to predict using their group in the periodic table?
|
Group 1 = +, 2 = 2+, 3 = 3+, 6 = 2-, 7= -
|
|
|
A substance containing ________________ can conduct an electric current.
|
ions that can move
|
|
|
What is an ionic compound?
|
when a compound forms between a metal and a non-metal
|
|
|
What are the prefixes 1-8 for indicating numbers in chemical names?
|
mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa
|
|
|
What is NH4+ called?
|
ammonium
|
|
|
What is NO2- called?
|
nitrite
|
|
|
What is NO3- called?
|
nitrate
|
|
|
What is SO32- called?
|
sulfate
|
|
|
What is SO42+ called?
|
sulfate
|
|
|
What is PO43- called?
|
phosphate
|
|
|
What is HPO42- called?
|
hydrogen phosphate
|
|
|
What is H2PO4- called?
|
dihydrogen phosphate
|
|
|
What is CO32- called?
|
carbonate
|
|
|
What is HCO3- called?
|
bicarbonate or hydrogen carbonate
|
|
|
What is ClO¬¬3- called?
|
chlorate
|
|
|
What is ClO4- called?
|
perchlorate
|
|
|
What is Cr2O72- ¬called?
|
dichromate
|
|
|
What is CrO42- called?
|
chromate
|
|
|
How do we name binary ionic compounds?
|
cation + anion-ide
|
|
|
What is a binary ionic compound?
|
-metal cation + non-metal anion
|
|
|
What is a type I binary compound?
|
contains type I cations (atom has only one possible ion form)
|
|
|
What is a type II binary compound?
|
metal + metal (usually transition!) contains type II cations (atom has more than one possible ion form)
|
|
|
How do we name type II binary compounds?
|
using roman numerals to specify the charge of the cation
|
|
|
What is a type III binary compound?
|
non-metal + non-metal
|
|
|
How do we name type III binary compounds?
|
-first element in formula is named first; full element name is used
-second element is named as though it were an anion -prefixes denote the numbers of atoms present |
|
|
What prefix is never used for naming the first element in a type III binary compound?
|
mono (ie carbon monoxide, NOT monocarbon monoxide)
|
|
|
What is an oxyanion?
|
a series of polyatomic anions that contain an atom of a given element and a different number of oxygen atoms
|
|
|
When there are only two members in an oxyanion series, how are they named?
|
smaller number of oxygen = -ite, larger number of oxygen = -ate
|
|
|
When more than two oxyanions make up a series, how are they named?
|
fewest O = hypo-, most O = per-
ie: hypochlorite, chlorite, chlorate, perchlorate |
|
|
What is C2H3O2- called?
|
acetate
|
|
|
What is O22- called?
|
peroxide
|
|
|
What is an acid?
|
a molecule with one or more H+ ions attached to an anion
|
|
|
What are some observable “signals” that a chemical reaction has occurred?
|
colour changes, solid forms, bubbles/gas forms, production/absorption of heat
|
|
|
A chemical change always involves a __________
|
rearrangement in which the atoms are grouped
|
|
|
What are the most common “driving forces” that make reactants “want” to form products?
|
form a solid (precipitation), form water, transfer electrons, form a gas
|
|
|
What is precipitation?
|
formation of a solid
|
|
|
What is a solid that forms in a chemical reaction called?
|
precipitate
|
|
|
When each unit of a substance that dissolves in water produces separated ions, the substance is called a ____________
|
strong electrolyte
|
|
|
What is a soluble solid?
|
a solid that readily dissolves in water
|
|
|
Do insoluble and slightly soluble solid mean the same thing? What?
|
Yes: a solid where such a tiny amount dissolves in water that is undetectable with the naked eye
|
|
|
Another word for ionic compound is _____
|
salt
|
|
|
What salts are always soluble compounds?
|
anything with NO3-, Na+, K+, and NH4-
|
|
|
What salts are usually soluble compounds? Exceptions?
|
Cl-, Br-, I- (except those containing Ag+, Hg2+, or Pb2+)
SO42- (except those containing Ba2+, Pb2+, or Ca2+) |
|
|
What salts are always insoluble compounds?
|
S2-, CO32-, and PO43-
|
|
|
What salt is usually insoluble? Exceptions?
|
OH- (except for those containing Na+, K+, Ca2+, or Ba2+)
|
|
|
What is dissociation?
|
the separation of an ionic compound into individual ions when dissolved in water (to form electrolytes)
|
|
|
What is a strong base?
|
A compound that dissociates completely in aqueous solution to yield hydroxide ion OH-
|
|
|
What are the most common strong bases?
|
the soluble hydroxides of the IA and IIA elements
|
|
|
What are strong acids?
|
A compound that dissociates completely in water to yield the proton H+
|
|
|
What are the six common strong acids?
|
HCl, HNO3, HBr, HI, HClO4, and H2SO4
|
|
|
Most important chemistry, including virtually all of the reactions that make life possible occur in:
|
aqueous solutions
|
|
|
What is in a molecular equation?
|
shows the complete formulas of all reactants and products
|
|
|
What is a complete ionic equation?
|
all substances that are strong electrolytes are represented as ions, all reactants and products are included
|
|
|
What are spectator ions?
|
ions that don’t participate directly in a reaction in a solution (present before and after reaction)
|
|
|
What is a net ionic equation?
|
includes only those components that are directly involved in the reaction (no spectator ions)
|
|
|
What fundamental change always occurs when strong acids and strong bases are mixed?
|
the H+ ions react with OH- ions to form water
|
|
|
What is always the net ionic equation for the reaction of a strong acid and a strong base?
|
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) -> H2O(l)
|
|
|
When a strong acid and strong base react, what are the two products that always form?
|
water and salt (ionic compound)
|
|
|
What is another word for “dissociate”?
|
ionize
|
|
|
What is an acid-base reaction?
|
the reaction of H+ and OH-
|
|
|
What sort of reaction occurs when a metal and non-metal react?
|
an oxidation-reduction reaction
|
|
|
what is an oxidation-reduction reaction?
|
a reaction that involves a transfer of electrons
|
|
|
When two metals react, the compound formed is _______
|
not ionic
|
|
|
How can we recognize two non-metals undergoing an oxidation-reduction reaction?
|
by looking for O2 as a reactant or product
|
|
|
What is a double-exchange or double-displacement reaction?
|
AB + CD -> AD + CB
|
|
|
What are two other names for a precipitation reaction?
|
double-exchange or double-displacement reaction
|
|
|
What is an acid-base reaction?
|
when a strong base and strong acid react (forms water)
|
|
|
What is a single-replacement reaction?
|
A + BC -> B + AC
|
|
|
What is a useful clue to identify a combustion reaction?
|
look for O2(g) and a carbon-containing molecule as reactants: product of most combustion reactions are therefore CO2(g) and water
|
|
|
What is a combustion reaction?
|
a reaction that involves oxygen and produces energy so rapidly that a flame results
|
|
|
What are the three “subclasses” of oxidation-reduction reactions?
|
combustion, synthesis, and decomposition
|
|
|
What are the three main chemical reactions?
|
precipitation (solid forming), oxidation-reduction, and acid-base
|
|
|
What is a synthesis reaction?
|
when a given compound is formed from simpler materials
|
|
|
What is another name for a synthesis reaction?
|
combination reaction
|
|
|
How was the number a mole determined?
|
it is the number equal to the number of carbon atoms in 12.01 grams of carbon
|
|
|
What is a limiting reactant?
|
the reactant that that runs out first, limiting the amount of product that can be made (also limiting reagent)
|
|
|
What is percent yield?
|
The percentage of actual yield compared to the theoretical yield
|
|
|
What are units of pressure?
|
mm Hg (torr), standard atmosphere (atm), pascal (SI unit)
|
|
|
What is 1 atm in mmHg (torr), Pa, and psi?
|
760torr = 101 325 Pa = 14.69psi
|
|
|
What is Boyle’s law?
|
PV = k (constant at a specific temp)
|
|
|
What is Charles’ Law?
|
V1/T1 = V2/T2
|
|
|
What is Avogadro’s Law?
|
at constant temperature and pressure, if # of moles goes up, volume goes up proportionally
V1/n1 = V2/n2 |
|
|
What is the universal gas constant?
|
R = 0.08206 L atm/mol K
|
|
|
What is the combined gas law? When does it hold?
|
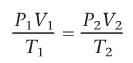
holds when the amount of gas (moles) is held constant
|
|
|
For a mixture of gases in a container, the total pressure exerted is the __________
|
sum of the partial pressures of the gases present
|
|
|
What is partial pressure?
|
the pressure that a gas would exert if it were alone in a container
|
|
|
What is Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures?
|
The total pressure exerted in a container is a sum of the partial pressures of the gases present
|
|
|
What are the postulates of the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases?
|
1. Gases consist of tiny particles (atoms or molecules)
2. These are so small, compared with the distance between them, that the size/volume of the individual particles can be assumed to be 0 3. The particles are in constant random motion, colliding with the walls of container (causing pressure) 4. The particles are assumed to neither attract or repel each other 5. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the K of the gas |
|
|
The greater the _____ or ______ of a particle, the greater its kinetic energy.
|
mass or velocity
|
|
|
What is STP?
|
0*C (273 K) and 1atm (ideal gas occupies 22.4L)
|
|
|
What is a solution?
|
a homogeneous mixture: a mixture in which the components are uniformly intermingled
|
|
|
Can a solution be a gas? Solid?
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a solvent?
|
the substance present in the largest amount in a solution
|
|
|
What is a solute?
|
the other substance(s) in a solution other than the solvent (so, everything but the largest amount)
|
|
|
What is an aqueous solution?
|
a solution with water as the solvent (largest amount in solution)
|
|
|
Describe a visual representation of an ionic (polar) substance dissolving in H¬2O
|
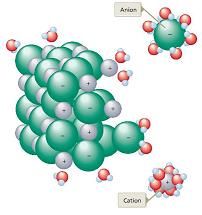
|
|
|
Why would a molecule containing OH- group(s) dissolve in water?
|
the O-H groups are polar, and just like hydrogen bonds form among water molecules in pure water, the O-H groups can bond to a water molecule
|
|
|
Why doesn’t a substance like oil dissolve in water?
|
it contains carbon, which has similar electronegativities to hydrogen, the bonding electrons are shared almost equally and the bonds are essentially nonpolar, so it can’t form attractions to the polar water molecules
|
|
|
a given solvent usually dissolves solutes that____________________.
|
have polarities similar to its own
|
|
|
Water dissolves most ______ solutes. Why?
|
polar, because the solute-solvent interactions formed in the solution are similar to the water-water interactions present in the pure solovent
|
|
|
What is a saturated solution?
|
a solution that contains as much solute as will dissolve at that temperature (ie even very soluble substances, like sugar, have a limit... sugar eventually starts collecting at the bottom as a solid)
|
|
|
If a solid solute is added to a solution already saturated with that solute, ______________.
|
The added solute doesn’t dissolve
|
|
|
A solution that has not reached the limit of solute that will dissolve in it is called ___________.
|
unsaturated
|
|
|
A relatively large amount of solute is dissolved in a __________ solution, a relatively small amount of solute is dissolved in a ________ solution.
|
concentrated, dilute (think strong/weak coffee)
|
|
|
Describing the composition of a solution means specifying ________________.
|
the amount of solute present in a given quantity of the solution
|
|
|
The two typical ways of giving the amount of solute is in terms of __________ or _______
|
mass or moles
|
|
|
What is the mass percent of a solution?
|
the mass of solute present in a given mass of solution
|
|
|
What is the “concentration” of a solution?
|
the amount of solute in a given volume of solution
|
|
|
What is the most commonly used expression of concentration?
|
Molarity (M)
|
|
|
What is molarity?
s |
the number of moles of solute per volume of a solution in liter
|
|
|
How do we calculate molarity?
|

|
|
|
What is a stock solution?
|
a solution in concentrated form, that water (or another solvent) is added to to achieve the molarity desired for a particular solution
|
|
|
What is the calculation for molarity before and after dilution?
|
M1 x V1 = moles of solute = M2 x V2 ***only works if m never changes***
|
|
|
What are the steps for solving stoichiometric problems involving solutions?
|
1. Write balanced equation, if ions = net ionic equation
2. Calculate moles of reactants 3. Determine limiting reactant 4. Calculate the moles of other required reactants or products 5. Convert to grams or other units if required |
|
|
What is a neutralization reaction?
|
an acid-base reaction
|
|
|
What is another name for a base?
|
alkali
|
|
|
How do bases taste/feel?
|
bitter, slippery
|
|
|
What is the more general definition of acids and bases?
|
The Bronsted-Lowry model: an acid is a proton (H+) doner, and a base is a proton acceptor
|
|
|
According to the Bronsted-Lowry model, how is the reaction that occurs when an acid is dissolved in water represented?
|
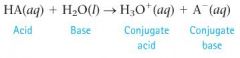
as an acid (HA) donating a proton to a water molecule to form a new acid (the conjugate acid) and a new base (the conjugate base)
|
|
|
What becomes the conjugate base?
|
acid - proton
|
|
|
What becomes the conjugate acid?
|
base + proton
|
|
|
What is a conjugate acid-base pair?
|
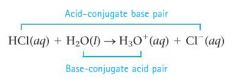
two substances related to each other by the donating and accepting of a single proton
|
|
|
How and why do strong or weak acids occur?
|
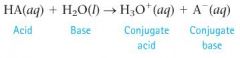
Because the reaction of acids and bases can go either way, the H¬2O (base, in the forward reaction) and the A- (conjugate base, in the reverse reaction) compete for the H+ ion. Whichever has the higher attraction for the H+ (stronger base) “wins”
forward reaction = strong acid, reverse action = weak acid |
|
|
A strong acid can be described as an acid whose conjugate base is a _______ base than water
|
much weaker
|
|
|
A strong acid is ________________ in water.
|
completely dissociated
|
|
|
Acid strength and conjugate base strength are
|
inversely proportionate
|
|
|
What are the common strong acids?
|
H¬2SO¬4(aq) sulphuric acid, HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid, HNO3(aq) nitric acid, and HClO4(aq) perchloric acid
|
|
|
What is a diprotic acid?
|
an acid that can furnish two protons (ie H¬2SO¬4(aq) sulphuric acid)
|
|
|
what is an oxyacid?
|
the acidic hydrogen is attached to an oxygen (most acids are this)
|
|
|
What is an organic acid?
|
those with a carbon-atom backbone, commonly contain the carboxyl group (COOH)
|
|
|
What is a hydrohalic acid?
|
HX, where X represents a halogen atom (ie HCl)
|
|
|
What is an amphoteric substance?
|
a substance that can behave either as an acid or as a base
|
|
|
What is the chemical equation for the ionization of water?
|
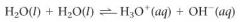
|
|
|
In pure water, the concentration of H¬3O+ and OH- are always ______.
|
equal
|
|
|
In pure water, the mathematical product of H3O+ and OH- at 25*C is always
|
1.0 x 10^-14
|
|
|
What is Kw?
|
the ion-product constant for water 1.0 x 10-14 (the the mathematical product of H3O+ and OH- in water at 25*C)
|
|
|
What is the significance of Kw?
|
it means that in ANY aqueous solution, no matter what it contains, the product of H+ and OH- is ALWAYS 1.0 x 10^-14 (Kw)
|
|
|
What is the calculation for the pH scale?
|
pH = (-1) x log[H+] = -log[H+]
|
|
|
the pH decreases as the H+ _________.
|
increases
|
|
|
The lower the pH, the more _______ the solution
|
acidic
|
|
|
What does the symbol p mean in pH and pOH?
|
-log
|
|
|
pH + pOH =
|
14.00
|
|
|
How do you calculate H+ from pH, or OH- from pOH?
|
use inverse log (or trial and error!)
|
|
|
What is a buffered solution?
|
one that resists a change in its pH even when a strong acid or base is added to it
|
|
|
A solution is buffered by the presence of ____________.
|
a weak acid and its conjugate base
|
|
|
How does a buffer resist changes in pH when an acid or base is added?
|
it reacts with any added H+ or OH- so that these ions can’t accumulate
|
|
|
What happens when H+ is added to a buffered solution?
|
it reacts with the conjugate base A- (so ions can’t accumulate)
|
|
|
What happens when OH- is added to a buffered solution?
i |
t reacts with the weak acid HA (so ions can’t accumulate)
|
|
|
What is the collision model?
|
the idea that reactions occur during molecular collisions where bonds get broken
|
|
|
What does the collision model explain?
|
why a reaction proceeds faster if the concentrations of the reacting molecules are increased (higher concentrations = more collisions = more events); also explains why reactions go faster at higher temperature
|
|
|
What is activation energy?
|
Ea = the minimum energy needed for a reaction to occur (if less, the molecules will bounce apart unchanged)
|
|
|
Why do reactions occur faster as the temperature increases?
|
higher temp -> higher speeds -> more high energy collisions -> more collisions that break bonds -> faster reaction
|
|
|
What is a catalyst?
|
a substance that speeds up a reaction WITHOUT being consumed
|
|
|
Why do catalysts work?
|
they provide a new pathway for the reaction, one that h as lower activation energy than the original pathway
|
|
|
What is the equilibrium expression?
|
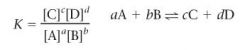
*brackets indicate concentrations of the chemical species at equilibrium in units of mol/L
-K is a constant: equilibrium constant |
|
|
What is the equilibrium constant?
|
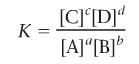
|
|
|
Equilibrium concentrations are __________ the same, but the equilibrium constant, which depends on the ratio of the concentrations, ____________.
|
not always, remains the same
|
|
|
each set of equilibrium concentrations is called an ______________.
|
equilibrium position
|
|
|
How many equilibrium positions are possible?
|
an infinite number
|
|
|
There is one equilibrium constant for each ______________.
|
particular system at a particular temperature
|
|
|
What is homogeneous equilibria?
|
when all substances of a reaction are in the same state
|
|
|
What is heterogeneous equilibria?
|
when the substances of a reaction are in more than one state
|
|
|
Why does the position of a heterogeneous equilibrium not depend on the amounts of pure solids or liquids present?
|
the concentrations of pure solids and liquids cannot change (and so, their concentrations are constants)
|
|
|
The concentrations of pure solids or pure liquids involved in a chemical reaction are __________ in the equilibrium expression for the reaction.
|
not included
|
|
|
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
|
when a change is imposed at equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium shifts in a direction that tends to reduce the effect of that change
|
|
|
What does Le Chatelier’s principle allow us to predict?
|
the effects of changes in concentration, pressure, and temperature on a system at equilibrium
|
|
|
A reaction that produces heat is _______
|
exothermic
|
|
|
A reaction that absorbs heat is _______.
|
endothermic (heat is a reactant)
|
|
|
A value of K much larger than 1 means that at equilibrium, the reaction system will consist of _______.
|
mostly products
|
|
|
What is the solubility product?
|
solubility product constant, Ksp , the constant for the solubility equilibrium of a nearly insoluable or slightly soluble ionic compound
|
|
|
Why does the amount of excess solid present not affect the position of the solubility equilibrium?
|
because both dissolving and re-forming the solid occurs at the surface of the solid, so both rates stay the same relative to each other
|
|
|
How do we calculate solubility products?
|
By inserting the compound’s measured solubility into the Ksp expression
|
|
|
What is the Ksp expression?
|
Aa + Bb would have the expression [A+]^a[B-]^b
|
|
|
How do we calculate the solubility of a solid given the Ksp value?
|
square root of the Ksp value
|
|
|
When writing an equilibrium expression for a heterogeneous equilibria containing no gases on one side, what do we do?
|
use 1
|
|
|
What is an oxidation-reduction reaction?
|
in which one or more electrons are transferred
|
|
|
What is oxidation?
|
loss of electrons
|
|
|
What is reduction?
|
gain of electrons
|
|
|
What is LEO GER?
|
in a redox reaction, it means lose electrons = oxidation, gain electrons = reduction
|
|
|
How do we decide whether a reaction between non-metals is a redox reaction?
|
using oxidation states
|
|
|
What is an oxidation state/number?
|
an imaginary charge to an element in a compound, determined by assuming that the most electronegative atom in a bond controls or possesses BOTH of the shared electrons
|
|
|
What is fluorine’s oxidation state? Why?
|
always -1, because it is very electronegative
|
|
|
What are the most electronegative elements? In general, what is their oxidation state?
|
F, O, N, and Cl (in order of electroneg) OS is generally equal to it’s charge as an anion
|
|
|
How are oxidation states assigned in binary compounds?
|
the element with the greater electronegativity is assigned a negative OS equal to its charge as an anion in ionic compounds
|
|
|
the OS of an atom in an uncombined element is:
|
0
|
|
|
what is the most important exception of oxygen’s oxidation state?
|
in peroxides (containing O2^-), each oxygen is assigned an OS of -1
|
|
|
What is an oxidizing agent?
|
accepts electrons, contains the element reduced (**whole compound)
|
|
|
What is a reducing agent?
|
donates electrons, contains the element oxidized (**whole compound)
|
|
|
How do we balance the equations for oxidation-reduction reactions?
|
we separate the reaction into two half-reactions
|
|
|
What is a half-reaction?
|
equations that have electrons as reactants or products (one half represents a reduction process, and the other half represents an oxidation process)
|
|
|
What are the steps in the half-reaction method for balancing equations for redox reactions in acidic solution?
|
1. Write half-reactions
2. For each half: balance elements except H and O, balance O using H2O, balance hydrogen using H+, balance the charge using electrons 3. Equalize number of electrons in half reactions 4. Add half-reactions and cancel identical species that are on both sides 5. Make sure everything balances |
|
|
What is electrochemistry?
|
the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy
|
|
|
What are the two types of processes involved in electrochemistry?
|
-the production of an electric current from a chemical (redux) reaction
-the use of an electric current to produce a chemical charge |
|
|
How can we harness the energy from a redux reaction?
|
separate the oxidizing agent (electron acceptor) from the reducing agent (electron donor), thus requiring the electron transfer to occur through a wire (the current produced in the wire can then be directed through a device)
|
|
|
What is an electrochemical battery? aka
|
aka galvanic cell, a device powered by a redox reaction where the oxidizing agent is separated from the reducing agent so that the electrons must travel through a wire from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent
|
|
|
What is an anode?
|
the electrode where oxidation occurs
|
|
|
What is a cathode?
|
the electrode where reduction occurs
|
|
|
What is electrolysis?
|
a process where electrical energy is used to produce a chemical change
-a process that involves forcing a current through a cell to produce a chemical change that would not otherwise occur |
|
|
What is the “potential” of a battery? How is it measured?
|
the “pressure” on electrons to flow from one electrode to the other, measured in volts
|
|
|
What is corrosion?
|
the process of returning metals to their natural state (the ores from which they were originally obtained); involves the oxidation of the metal
|
|
|
Why does corrosion not prevent the use of metals in air?
|
most metals develop a thin oxide coating, which protects their internal atoms against further oxidation, ie aluminum forms aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which inhibits further corrosion
|
|
|
What are some ways to prevent corrosion?
|
paint, metal plating, alloys, and cathodic protection
|
|
|
What is cathodic protection?
|
when a metal that furnishes electrons more easily than the one that needs protecting is connected by a wire, so electrons flow through it and get furnished
|
|
|
Why do batteries need to be recharged or replaced?
|
because the substances in it that furnish and accept electrons are consumed
|
|
|
How are batteries recharged?
|
by forcing current through the battery in the opposite direction, which reverses the ocidation-reduction reaction (so it can restart)
|
|
|
what is electromagnetic radiation?
|
energy being transmitted from one place to another by light
|
|
|
What are waves characterized by?
|
wavelength, frequency, and speed
|
|
|
What is wavelength?
|
the distance between two consecutive wave peaks
|
|
|
what is frequency of a wave?
|
how many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time period
|
|
|
what is the speed of a wave?
|
indicates how fast a given peak travels
|
|
|
What is a photon?
|
a stream of tiny packets of energy
|
|
|
in general, the longer the wavelength of light, _________________________.
|
the lower the energy of its photons
|
|
|
When atoms receive energy from a source and become excited, how is the energy carried away?
|
by a proton that corresponds exactly to the energy change experienced by the emitting atom
|
|
|
red light has a ________ wavelength than blue does, so it carries _____ energy.
|
longer, less
|
|
|
what is a ground state?
|
the lowest possible energy state of an atom
|
|
|
how can an excited atom release some (or all) of its excess energy?
|
by emitting a photon and moving to a lower energy state
|
|
|
different wavelengths of light carry different amounts of __________.
|
energy per proton
|
|
|
What is a quantized energy level?
|
only certain values are allowed (like a step) (aka discrete?)
|
|
|
What is an orbital?
|
a probability map for where an electron might be
|
|
|
How do we determine the size of an orbital?
|
the sphere that contains 90% of the total electron probability
|
|
|
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
|
an atomic orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, and those two electrons must have opposite spins
|
|
|
The shape of an orbital indicates _______________.
|
the probability distribution for an electron residing in that orbital
|
|
|
What is electron configuration?
|
Ab^c , where A=principle energy level (#), b=type of sublevel, c= # of electrons
|
|
|
How can we abbvebiate electron configurations?
|
[largest full noble element] + extra
|
|
|
What is a valance level?
|
the outermost level that contains electrons
|
|
|
What are core electrons?
|
the inner electrons, not involved in bonding atoms to each other
|
|
|
the atoms of elements in the same group have the same number __________
|
of electrons in a given type of orbital (sublevel), except that the orbitals are in different principal energy levels
|
|
|
elements with the same valence electron arrangement show_____________
|
very similar chemical behaviour
|
|
|
What are the lanthanide series of elements?
|
corresponds to the filling of the seven 4f orbitals (14 of them)
|
|
|
What are the actinide series of elements?
|
corresponds to the filling of the seven 5f orbitals
|
|
|
As a general rule, most chemically active metals appear where on the periodic table?
|
lower-left
|
|
|
Where are the most chemically active non-metals on the periodic table?
|
upper-right
|
|
|
What is ionization energy?
|
the energy required to remove an electron from an individual atom in the gas phase
|
|
|
Ionization energies tend to decrease vertically from ___________. Why?
|
top to bottom of a group (because the further away the electrons are from the nucleus, easier it is to remove them
|
|
|
ionizations energies tend to increase horizontally from _______.
|
left to right
|
|
|
atomic size decreases horizontally from _______.
|
left to right
|
|
|
Why does atomic size decrease from left to right?
|
the number of protons increases, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus
|
|
|
What is bond energy?
|
the energy required to break the bond (used to obtain info about the strength of the bond)
|
|
|
What is a covalent bond?
|
when electrons are shared by nuclei
|
|
|
what sort of bond do diatomic atoms have?
|
covalent
|
|
|
What are the extreme bond types?
|
ionic (extremely different atoms, form oppositely charged ions) and covalent (identical atoms, share electrons equally)
|
|
|
What is a polar covalent bond?
|
atoms are not different enough to cause electrons to be completely transferred (like ionic), but different enough that they share (like covalent) but UNEQUALLY
|
|
|
What are the four most electronegative elements?
|
F, O, N, Cl (fat uncle?!)
|
|
|
What is electronegativity?
|
the relative ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself
|
|
|
the higher the atom’s electronegativity value, the ________ the shared electrons tend to be to that atom when it forms a bond
|
closer
|
|
|
How is electronegativity determined?
|
by measuring the polarities of the bonds between various atoms
|
|
|
What does the polarity of a bond depend on?
|
the difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms forming the bond: zero=covalent similar= electrons shared almost equally (little polarity), different=very polar bond
|
|
|
What is a dipole moment?
|
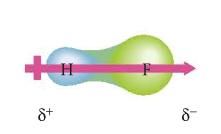
when a molecule has a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge
|
|
|
What molecules will have a dipole moment?
|
any diatomic (two atom) molecule with a polar bond, and some polyatomic
|
|
|
What would happen if water molecules were nonpolar?
|
it would be a gas
|
|
|
Why is water being polar so important?
|
they can surround and attract both positive and negative ions, which allow ionic materials to dissolve in it AND since they are polar, they attract each other strongly which allows water to be liquid, since it takes a lot of energy to separate them to form gas
|
|
|
The structures of virtually all binary ionic compounds can be explained by what model?
|
packing the ions as if they were hard spheres; the larger spheres get packed together, and the small ions occupy the spaces between them
|
|
|
how does a cation’s size compare to its parent atom?
|
smaller (loses its valance electron)
|
|
|
describe the bond between polyatomic ions in ionic bonds? Ie NH4NO3
|
the ions form ionic bonds with each other, but the individual polyatomic ions are held together by covalent bonds
|
|
|
What is resonance?
|
a molecule shows resonance when more than one Lewis structure can be drawn from the molecule
|
|
|
What are the exceptions to the Lewis diagram?
|
some molecules have atoms that are electron-deficient, like Boron, which has only 6 electron pairs (they react violently), there is no Lewis structure that explains why O2¬ ¬ is so paramagnetic (contains unpaired electrons), ALSO any molecule that contains an odd number of electrons
|
|
|
What is molecular structure? Aka
|
geometric structure; the three-dimentional arrangement of the atoms on a molecule
|
|
|
What is a trigonal planar structure?
|
flat with three 130 bond angles
|
|
|
what is a tetrahedral structure?
|
four connecting atoms are identical, each as far away from another as they can get
|
|
|
What does VSEPR stand for?
|
valence shell electron pair repulsion model
|
|
|
What is the VSEPR model used for?
|
predicting the molecular structures formed from non-metals
|
|
|
What is the main idea of the VSEPR model?
|
the structure around a given atom is determined by minimizing repulsions between electron pairs
|
|
|
What is a trigonal pyramid?
|
one side is different from the other three
|
|
|
How do we determine the molecular structure of molecules that have single bonds?
|
imagine the electron pair arrangement, then take away any lone pairs
|
|
|
What two elements form the basis of most natural substances?
|
carbon and silicon
|
|
|
what are biomolecules?
|
molecules that make possible the maintenance and reproduction of life
|
|
|
Are there any carbon compounds that are inorganic?
|
yes, some: ie oxides of carbon and carbonates
|
|
|
What is the simplest class of organic compounds?
|
hydrocarbons
|
|
|
What is methane?
|
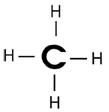
CH4
|
|
|
What is ethylene?
|
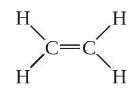
C2H4
|
|
|
What is acetylene?
|
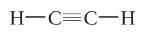
C2H2
|
|
|
What is the smallest hydrocarbon with a double bond?
|
C2H4, ethylene
|
|
|
What is the smallest hydrocarbon with a triple bond?
|
C2H2, acetylene
|
|
|
What is an alkane?
|
a saturated hydrocarbon (only single bonds)
|
|
|
What does it mean when a compound is saturated?
|
contains only single carbon-carbon bonds
|
|
|
What is ethane?
|
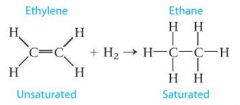
ethylene + H2
|
|
|
What is propane?
|
C3H8
|
|
|
What is butane?
|
C4H10
|
|
|
What are the alkanes with 1, 2, and 3 carbons called?
|
methane, ethane, propane
|
|
|
What is the alkane with 4 carbons called?
|
n-butane
|
|
|
What does the n- mean in terms of alkane molecules?
|
normal, exists as a straight-chain molecule
|
|
|
What structure represents most alkanes?
|
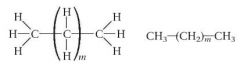
|
|
|
What is the general formula for alkanes?
|
CnH2(n+2)
|
|
|
What is structural isomerism?
|
when two molecules have the same atoms but different bonds (one or more branches)
|
|
|
What is isobutene?
|
butane (C4H10) with one branch off of it
|
|
|
What is neopentane?
|
pentane (C5H12) with a carbon in the middle with two (4 sorta) branches
|
|
|
What are the greek roots for numbers 5-10?
|
pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec
|
|
|
How do we name alkanes?
|
-base name = longest continuous chain of carbon
-then go in the direction starting with the closest branch -identify which carbon the branch is on plus the carbon number (ie 3-methyl) -if there is more than one of the same substituent, use di or tri, plus the # (ie 2,3-dimethyl) -use alphabetical order |
|
|
How do we name substituants?
|
drop the –ane, add –yl
|
|
|
What is methyl?
|
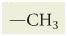
|
|
|
What is ethyl?
|
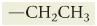
|
|
|
What is isopropyl?
|
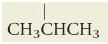
|
|
|
What is sec-butyl?
|

|
|
|
What is isobutyl?
|
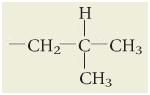
|
|
|
What is tert-butyl?
|
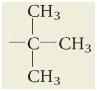
|
|
|
What is an alkyl?
|
the general name for an aklane when it functions as a substituent
|
|
|
What are alkenes?
|
hydrocarbons that contain double bonds
|
|
|
What are alkynes?
|
hydrocarbons that contain triple bonds
|
|
|
What is the general formula of an alkene?
|
CnH2n
|
|
|
What is the simplest alkene?
|
ethylene, C2H4
|
|
|
What are the extra rules for naming alkenes and alkynes?
|
-select the longest continuous chain of C that contains the double/triple bond
-end in –ene or –yne instead of ane -number the parent chain starting at the end closest to the double/triple bond, then give the location of the multiple bond by naming the lowest numbered C involved in the bond -substituents are treated the same |
|
|
What are the most important reactions of alkenes and alkynes? define
|
addition reactions - when new atoms form single bonds to the carbons formerly involved in the double or triple bonds
|
|
|
What is a hydrogenation reaction?
|
uses H2 as a reactant, and leads to the addition of a hydrogen atom to each carbon formerly involved in the double bond
|
|
|
What is halogenation?
|
adding halogen atoms to an unsaturated hydrocarbon
|
|
|
What is polymerization?
|
a process where many small molecules are joined together to form a large molecule
|
|
|
What is an aromatic hydrocarbon?
|
mixtures of hydrocarbons that, when separated, certain of the compounds that emerge have pleasant odors
|
|
|
What causes aromatic hydrocarbons?
|
a benzene ring
|
|
|
What is a benzene ring?
|
a six-membered ring of carbon atoms (C6H6), flat structure
|
|
|
What is a monosubstituted benzene?
|
a benzene ring with one substituent
|
|
|
How are monosubstituted benzenes named?
|
the substituent name as a prefix for benzene (ie chlorobenzene, ethylbenzene)
|
|
|
What is another name for methylbenzene?
|
toluene
|
|
|
What is another name for hydroxybenzene?
|
phenol
|
|
|
When a benzene ring is used as a substituent, what is it called?
|
phenyl (ie 3-phenyl-1-butene)
|
|
|
What is a disubstituted benzene?
|
when there is more than one substituent on the benzene ring (ie 1,2-dichlorobenzene)
|
|
|
What do the prefixes ortho- meta- and para- mean on benzene rings?
|
two side-by side, two with one carbon between, two across
|
|
|
what is xylene?
|
benzene with two methyl substituents
|

