![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
117 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Scientific Method Steps 1-4 |
1. Observation of phenomenon 2. Hypothesis 3. Test 4. Conclusion |
Moths' Wings Example |
|
|
4 Aspects of Science |
1. Repeatable (recorded in detail) 2. Verifiable (by peers) 3. Dynamic (open to change) 4. Objective (facts, not opinions) |
R V D O |
|
|
Limitations of Science |
1. Sometimes can't be tested 2. Equipment is not good enough 3. People aren't ready to accept hypothesis |
3 limitations |
|
|
Define: Theory |
Explains a broad range of phenomena - How? |
Not a "hunch" |
|
|
Define: Law |
Statement based on repeated experimental observations that describe some aspects of the universe |
Law of gravity |
|
|
Define: Chemistry |
Deals with composition and property of matter |
You should know this. |
|
|
Define: Matter |
Occupies space and has mass |
You get no hint. |
|
|
4 States of Matter |
1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas 4. Plasma |
S L G P |
|
|
Elements: Oxygen |
Number one body by mass |
Number one _____ by _____ |
|
|
Elements: Carbon |
Number one atom in organisms |
Number one _____ in _________ |
|
|
Elements: Hydrogen |
Number one in universe |
Number one in _________ |
|
|
Define: Atom |
Smallest unit of matter that maintains the properties of that element (uncuttable) |
|
|
|
3 Components of a Proton |
Charge: +1 Mass: 1 Where: nucleus |
|
|
|
3 Components of a Neutron |
Charge: 0 Mass: 1 Where: nucleus |
|
|
|
3 Components of an Electron |
Charge: -1 Mass: 0 Where: energy level |
|
|
|
Rutherford |
Gold foil experiment |
Bounced back in experiment |
|
|
Bohr |
Specific energy level |
Model of atom |
|
|
Define: Isotope |
Element that has same number of protons and different number of nutrons |
Defines the element |
|
|
Radio Isotopes |
Radioactive |
|
|
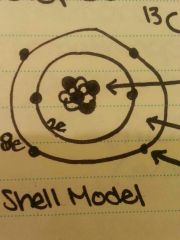
Arrow 1,2,3 |
1. Protons and Nutrons 2. Electrons 3. Can have up to 8 |
|
|
|
Purpose of bonds? |
Become more stable |
8e in outer shell |
|
|
Periodic Table: Mendeleev |
Arranged by Atomic Mass |
|
|
|
Periodic Table: Mosely |
Arranged by Atomic Number |
|
|
|
How do you figure out the atomic mass of an elememt? |
Am=p+n |
Equation |
|
|
Ionic bonds |
Share, gain or give up electrons |
|
|
|
Define: ions |
Charged particles/atoms -different number of electrons and protons |
|
|
|
Positive |
Cation |
|
|
|
Negative |
Anion |
|
|
|
Octet Rule |
8 valence e in outer shell |
|
|
|
Covalent Bond |
Sharing of electrons |
|
|
|
Nonpolar |
Share equally |
Covalent bond |
|
|
Polar |
Share unequally |
Covalent bond |
|
|
Solid line - |
Covalent bond |
2,4,6,8 hydrogen is feeling great! |
|
|
Dotted line : |
H-bond |
|
|
|
Ph |
Power of Hydrogen |
|
|
|
Acid Number |
0 |
Scale |
|
|
Acid Number |
0 |
Scale |
|
|
Neutral Number |
7 |
Scale |
|
|
Base Number |
14 |
Scale |
|
|
Acid is a H+ ________ |
Donor |
HCl - H+ Cl- |
|
|
Base is an H+ __________ |
Acceptor |
OH- + H+ -- H2O |
|
|
Define: Buffer |
Resists a change in ph |
Homeostasis |
|

Bond? |
Single bond |
|
|

Bond? |
Double bond |
|
|
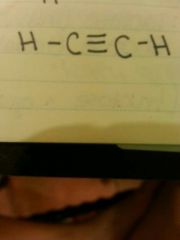
Bond? |
Triple bond |
|
|
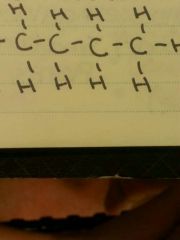
Bond? |
Hydrocarbon backbond |
6 C |
|
|
Functional Groups |
1. Hydroxyl 2. Amine 3. Carboxylic 4. Ketone/Aldehyde 5. Phosphate |
H (alcohol) A (Amino acid, need both) C K/A (sugar) P (DNA) |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Sugars |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Fats, oils |
|
|
|
Proteins (what they are made of) |
Enzyme, antibodies |
|
|
|
Nucleic acid |
DNA |
|
|
|
Monosacchoride |
Simple sugars |
5/6 carbon sugars Ex: glucose, fructose |
|
|
Disaccharide |
2 sugar units |
Lactose and sucrose ex |
|
|
Maltose |
2 glucose molecules |
Germinating seeds |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Complex carbohydrates |
Many |
|

|
1. Energy storage 2. Cell walls/structure 3. Energy storage 4. Cell walls/structure/exoskeleton |
|
|
|
Lipids function |
1. Energy storage (fat) 2. Membrane structure of cells 3. Coatings (wax of plant leaves) 4. Hormones |
4 functions |
|
|
Saturated fatty acid |
Single bonds Saturated w/ H Solid at room temp |
|
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acid |
Double bond Liquid at room temp |
|
|
|
Transfat |
Higher melting point Tightly packed |
Long chelf life |
|
|
Structure of lipids |
1.Tryglycericle 2.phospholipids 3.sterals 4.waxes |
T P S W |
|
|
Tryglycericle? |
1 glycerol & 3 fatty acids |
Glycerol & fatty acids? |
|
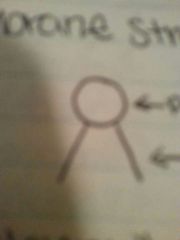
|
Polar head Nonpolar tails |
|
|
|
Sterals |
Ring structure Ex. Cholesterol |
|
|
|
Waxes |
Long chain of fatty acids and alcohols |
Coating on plants |
|
|
Proteins |
Enzymes, hormones & bodies, structure, transport |
Shape determines function |
|
|
Destroy proteins by.. |
Heat Acid |
|
|
|
1° structure |
Straight shape (primary) Peptide band |
|
|
|
2° structure |
Coil shape (helix) B sheet (silk) |
|
|
|
3° structure |
Folding on itself (Tertiary) disulfide bonds |
|
|
|
4° structure |
2 or more polypeptides together Quaternary Hemoglobin (4 total) |
|
|
|
Janssens 1590 |
2 lenses together |
|
|
|
Galileo 1600 |
Improvements in microscope and telescope |
|
|
|
Robert Hooke |
Cork, cellulae |
|
|
|
Antony van leewenhoek |
Made fine lenses Father of microscope |
|
|
|
Robert brown |
Viewed spot in cell - nucleus |
|
|
|
Schleiden |
All plants have cells |
|
|
|
Schwann |
All animals have cells |
|
|
|
Rudlof vir chow |
All cells come from previously existing cells |
|
|
|
Cell theory |
The cell is the smallest unit of life and they come from pre existing cells |
|
|
|
1930 |
Electron microscope |
|
|

|
Animal |
|
|
|
Ribosomesb |
Make proteins |
|
|
|
Animal cells have ______ and plants don't |
Centrioles Different cell wall |
|
|
|
Plant cells have _____ and animals don't |
Large central vacuole Different cell wall |
|
|
|
Tonicity |
General hypo or hyper |
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
Understanding relationships 3 domains - eubacteria, archaebacteria, own kingdom |
|
|
|
Order of classification |
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species, variety, cultivar |
|
|
|
Same species variation |
Variety: nature Cultivar: man made |
|
|
|
1st part of scientific names |
Genus Noun Capitalized |
|
|
|
2nd part of scientific name |
Specific epithet Adjective Lower case |
|
|
|
Kingdom eubacteria |
Divide rapidly |
20 min |
|
|
Archaebacteria |
Old Lack of oxygen |
|
|
|
Protista |
Eukaryotic (nucleus) Unicellular or multicellular Heterotrophic or auttrotrophic Animal like: locomotion |
|
|
|
Fungi |
Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic (saprophytic-decomposer) (parasitic - disease) |
|
|
|
Plante |
Eukaryotic Multicellular Autotrophic |
|
|
|
Animalia |
Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotrophic |
Ex herbivore, omnivore, carnivore, sponge |
|
|
Net |
Majority of particles |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Net movement of particles from area of high to low concentration No energy required |
|
|
|
Dynamic equilibrium |
Moving equally No gradient No net movement |
|
|
|
Rate if diffusion |
Steepness of concentration gradient Temp Electric gradient (ion charges) Pressure gradient (increase) Size of molecules (smaller=faster) |
|
|
|
Dialysis |
Movement of solutes across a membrane |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Movement of water across a membrane |
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
Low number of solutes cell explodes Net into cell |
|
|
|
Hypertonic |
High number if solutes Cell wall shrink Net into solution |
|
|
|
Isotonic |
Same number if solutes Natural state Net into both |
|
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Fluid mosaic model |
|
|
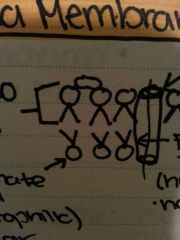
|
Phospho lipids Protein channel |
|
|
|
Bilayer |
2 layers |
|
|
|
Phosphate head |
Hydrophilic Polar |
|
|
|
Fatty acid tail |
Hydrophotic Non polar |
|
|
|
Membrane proteins |
1. Transport (channel protein) 2. Receptor (trigger activity) 3. Recognition (identify cell type) 4. Adhesion (connect cell to cell) |
4 parts |
|
|
Simple diffusion |
High to low No energy Lipid soluble |
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
High to low Channel proteion, gradient Sugars ameno acids ions |
|
|
|
Active transport |
Low to high Against gradient Energy, ATP, protein Sugars ameno acids, ions |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
Toward inside of cell Vesicle formation Macromolecules cellular material |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Toward outside of cell Vesicle fuses with membrane Macromolecules |
|

