![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What imaging technique has the highest image contrast for soft tissues?
|
MRI (nonionizing radiation!)
|
|
|
Describe the precess of protons in water/fat. How does MRI take utilize this?
|
Spin (Precess) of protons in water/fat is randomly oriented and creates no net magnetic vector
Upon application of a strong magnetic field (0.2-3.0 Tesla) there is a small net magnetization in longitudinal (Z-axis) The precessing protons change the magnetic field and induce a current which is detected by the conductor |
|
|
How do protons influence signal intensity?
|
Signal intensity determined by
Number of protons Relaxation properties of protons Biochemical environment |
|
|
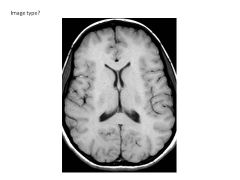
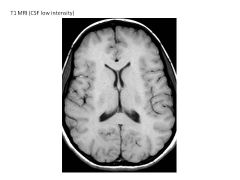
What occurs in T1 relaxation? How does it differ with tissue?
|
External B shut off; magnetic field in Z plane increases and protons relax
Fat relaxes more quickly (highest Z plane magnetization; highest intensity) WM/GM about the same CSF has SLOWEST relaxation (lowest intensity) |
|
|
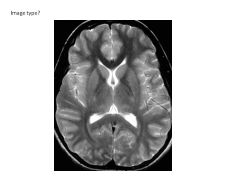
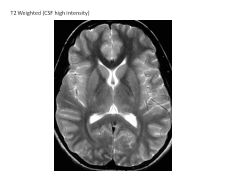
What occurs in T2 relaxation? How does it differ with tissue?
|
Magnetization in XY plane decrease over time
CSF has longest relaxation (highest intensity) WM/GM shorter (lower intensity) |
|
|
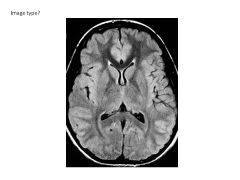
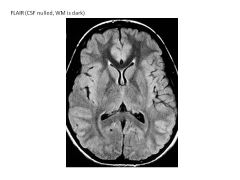
Describe FLAIR imaging.
|
T2-weighted but CSF signal nulled (CSF like T1-weighted image)
Fluid (CSF) Attenuated Inversion Recovery |
|
|
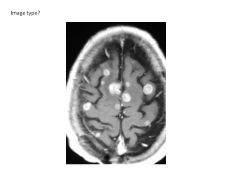
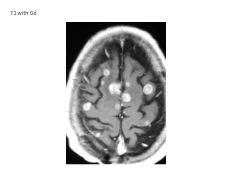
What is the effect of gadolinium on MRI?
|
Shortens T1 of tissues with deficient BBB, thus it enhances lesions (gives them greater intensity)
|
|
|
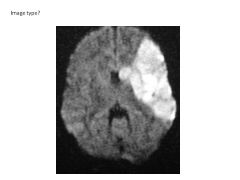
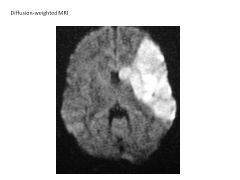
Describe Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Applications?
|
Modifited T2-weighted image that detects water movement in tissue.
Thus, areas of decreased blood flow have increased intensity. Great for detecting areas of stroke. |
|
|
Why is nephrogenic systemic fibrosis considered a contraindication for MRI?
|
Contrast agent can make Gd detach from chelate and stick around longer in pt; decreased clearange (renal dz)
|
|
|
What are the contraindications of MRI?
|
Missile Effect (magnet is always on)
Pacemaker Internal Defibrillator Cochlear Implant (Generally safe: surgical clips, vascular stents, cardiac valces, joint prostheses, implantable pumps) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Describe the differences in x-ray attenuation based on tissue.
|
Metal, Bone, Calcifications are RADIODENSE (RADIO-OPAQUE)--good attenuators of x-rays
Air, Fat, Muscle are RADIOLUCENT (poor absorbers) |
|
|
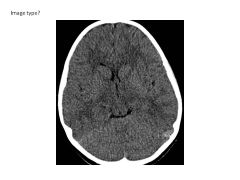
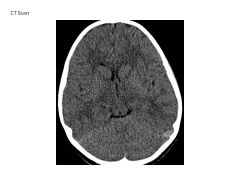
Describe the differences on CT scans based on tissue.
|
Same as x-ray:
Air is radiolucent CSF is radiolucent Bone and acute blood are radiodense (-opaque) (higher attenuation values = more radiodense) |
|
|
Pixel vs Voxel
|
Pixel: picture element
Voxel: cuboidal pixel |
|
|
When are CT scans useful?
|
Traumatic injury of head, face, spine (acute hemorrhage, fracture)
Acute stroke (exclude hemorrhage) Headache Temporal Bone and paranasal sinuses |
|
|
When is Catheter Angiography useful? Risks?
|
Diagnosis of aneurysm, arteriovenous malformations, vasculitis
Risks: Invasive procedure! Risk of neurologic complication (ischemia, stroke, death) |
|
|
When is a Single Photon Emission CT useful?
|
Diagnosis of dementia or seizure focus (ex: in AD would have decreased flow in temporal and parietal association areas)
|
|
|
When is Pittsburgh Compound-B useful?
|
Dx of AD (PCB binds amyloid proteins and emits positrons which are then detected by PET device)
|
|
|
What are the limitations of ultrasound?
|
Cannot penetrate ossified bone (can see brain if patient has carniotomy; or in neonates)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

