![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
White Matter
|
Collections of myelinated axons.
‐ tract ‐ fasciculus ‐ lemniscus ‐ peduncle |
|
|
Gray Matter
|
Areas where cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses are concentrated.
‐ nucleus ‐ cortex ‐ ganglion |
|
|
Nucleus
|
A more or less discrete collection of cell bodies.
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
Usually a collection of neuronal cell bodies outside the CNS.
Exceptions exist (e.g. Basal Ganglia) |
|
|
Cortex
|
An extensive, layered region of gray matter covering part of the CNS surface.
|
|
|
Tract (meaning of 1st and 2nd part of name)
|
A more or less discrete collection of fibers
(which may or may not be anatomically discrete). The first part of the name indicates where the cell bodies of the tract’s axons are, while the second part indicates where the axons terminate (e.g., a corticospinal tract carries information from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord; a spinocerebellar tract carries information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum). |
|
|
Fasciculus
|
Latin for little bundle
|
|
|
Lemniscus
|
Greek for ribbon, indicating a flattened-out bundle
|
|
|
Peduncle
|
Latin for little foot, describing fibers collecting together on their way into or out of someplace
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous system Regeneration vs.
Central Nervous system Regeneration |
-No new neurons
-Peripheral Neurons can regenerate to some extent -CNS cannot regenerate, but hope exists with stem cells, etc. |
|
|
Skeletal muscle Motor Neuron Features vs.
Smooth Muscle, Cardiac Muscle and Gland Motor Neuron features |
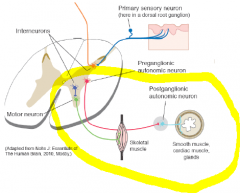
Efferent fibers (cell bodies in CNS) for go straight to destination.
For the others, Efferent fibers stop in an autonomic ganglion along the way to their destination. |
|
|
Frontal Lobe
|
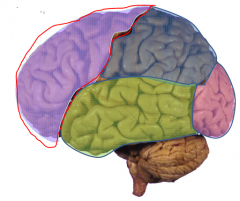
- Motor Cortex
- Personality (Phineas Cage) |
|
|
Parietal Lobe
|
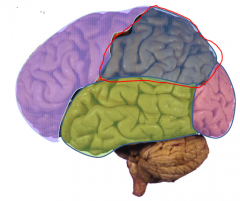
- Somatosensory cortex
- Spatial Awareness |
|
|
Occipital Lobe
|
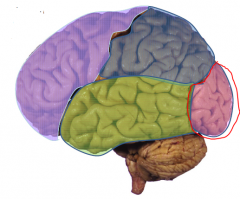
- Visual Cortex
|
|
|
Temporal Lobe
|
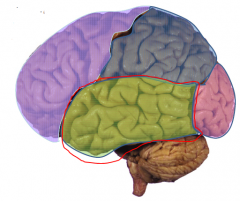
- Auditory Cortex
- Learning & Memory (Events and facts) |
|
|
Limbic System
|
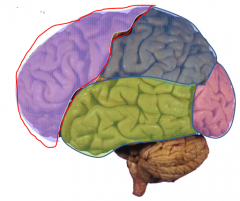
Emotion and behavior
Motivation Learning and memory Olofaction - Hippocampus - Amygdala - Cingulate gyrus |
|
|
Basal Ganglia
|
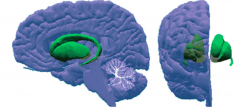
Initiation of movement
Thoughts Reward & more - Caudate Nucleus - Putamen - Globus Pallidus - Nucleus Accumbens |
|
|
Language areas of the brain
|
Bordering the lateral sulcus, usually more on R than L side
|
|
|
Brainstem
|
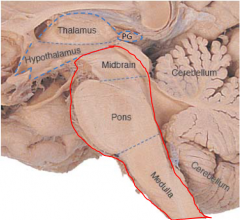
Autonomic control
(Breathing, cardiovascular function, etc) - Midbrain - Pons - Medulla |
|
|
Medulla
|
‐ Autonomic control
‐ Cranial nerves (sensory and motor) ‐ Long Tracts ‐ Levels of consciousness ‐ Many more |
|
|
Cerebellum
|
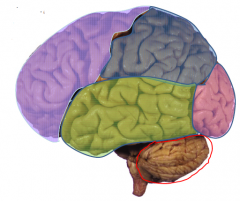
- Coordination
- Limited sensory function |
|
|
Spinal cord/Spinal Nerves
|
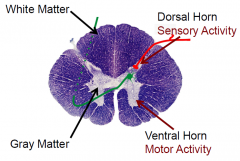
- Reflexes
- Long Tracts - Relay station for the autonomic NS (also found in brainstem) |
|
|
Brain and function summary
|
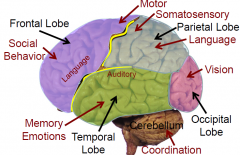
|
|
|
Diencephelon
|
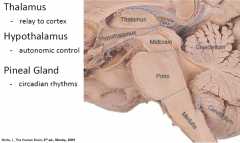
|

