![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Communication |
includes all means by which information is transmitted between a sender and a receiver |
|
|
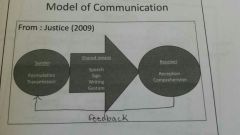
Model of communication |
|
|
|
Speech |
The oral production of the sounds, sound patterns, and intonations of a language |
|
|
Speech subsystems |

|
|
|
Language |
A code that consists of a set of symbols and the knowledge about how to combine those symbols into words, sentences, and texts in order to convey ideas |
|
|
Hearing |
The process and function of perceiving sound |
|
|
Ear anatomy |
Outer, middle, inner |
|
|
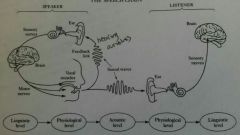
Speech chain |
|
|
|
Speech disorders |
Stuttering (fluency), articulation, voice, swallowing |
|
|
Causes of speech disorders |
Structural abnormalities, phonological disorders, accident or disease |
|
|
Hearing disorders |
Conductive Sensorineural Mixed Auditory processing disorder |
|
|
Stuttering |
an interruption in the rhythm of speech characterized by hesitations, repetitions, or prolongations of sounds, syllables, words, or phrases |
|
|
Articulation disorder |
Difficulties with the way sounds are formed and strung together usually characterized by substituting, omitting, or distorting a sound |
|
|
Voice disorders |
Inappropriate pitch, loudness, or quality (harsh, hoarse, breathy, nasal) |
|
|
Conductive hearing loss |
Sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer/middle ear, causing speech and other sounds to be heard less clearly or to sound muffled. Can be medically or surgically corrected |
|
|
Sensorineural hearing loss |
Damage to inner ear or never pathways to brain. Certain sound heard less than others causing reduced understanding of speech, usually not correctable (hearing aid, other amp device) |
|
|
Mixed hearing loss |
Combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
Causes of hearing disorders |

|
|
|
Language disorders |
Developmental Reading Acquired |
|
|
Developmental disorder |
A noticeable slowness in the development of the vocabulary and grammar necessary for expressing and understand thoughts and ideas |
|
|
Reading disorder |
Impaired language comprehension and/or production that significantly interferes with socialization and educational success |
|
|
Acquired disorder |
Language impairments caused by brain legions, often resulting from stroke or head injury |
|
|
Larynx functions |
Produce voice (phonation) Guarding airway |
|
|
Female vocal folds |
Freq 200-250 Shorter, lighter Fast vibrations |
|
|
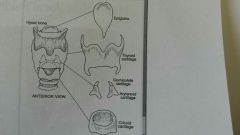
Laryngeal cartilages |
|
|
|
Vocal tract anatomy |
Nasal cavity Nasopharynx Maxilla Hard palate Velum Tongue Oral cavity Mandible Epiglottis Oropharynx Vocal folds Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Trachea Laryngopharynx |
|
|
Male vocal folds |
Freq 100-150 Longer, heavier Slower vibrations |
|
|
Abduction |
Open airways (apart) |
|
|
Adduction |
Close airways (together) |
|
|
Responsible for abduction and adduction |
Arytenoid, Cricoid cartilages and their attached muscles |
|
|
Vocal folds |
False folds: lie above true folds and only come together with considerable exertion True folds: vibrate fit phonation |
|
|
Glottis |
Space between vocal folds |
|
|
Process of phonation |
Abduct vocal folds Deep inhalation Adduct vocal folds Sibglottal air pressure build up Vocal folds blown apart Puff of air released Elasticity and air pressure being vf together One cycle complete |
|
|
Resonatory system |
Oral cavity Nasal cavity Pharyngeal cavity |
|
|
Oral cavity |
Palatine tonsils Posterior faucial pillar Anterior faucial pillar Uvula Velum Hard palate Teeth Tongue Soft palate |
|
|
Nasal cavity |
Superior nasal conchs Middle nasal Inferior nasal |
|
|
Mobile articulators |
Tongue Lower jaw Hard and soft palate Velum Lips Cheeks Oral pharynx Hyoid bone |
|
|
Pharyngeal cavity |
Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx |
|
|
Fixed articulators |
Jaw Alveolar ridge Teeth Hard palate |
|
|
Velum |
Oral sounds: Raised, nasal cavity closed Nasal sounds: lowered, nasal cavity open |
|
|
Sound waves |
Sine Complex Random |
|
|
Phone |
Speech sound |
|
|
Phoneme |
The smallest sound unit of speech represented by a ipa symbol |
|
|
Prosody |
Tempo Rhythm Intonation |
|
|
Articulation disorders |
Substitutions Omissions Distortions Additions |
|
|
Phonetic disorder |
A disorder characterized by problems learning the phonetic knowledge of language Learning correct motor movements Speech/functional disorder |
|
|
Learning based disorder |
Errors are similar to developmental errors of younger children |
|
|
Phonetic disorders |
Learning how to make sounds |
|
|
Phonological |
Learning how to use the sounds in language |
|
|
Phonological processes |

|
|
|
Ollers stages of early speech development |
0 weeks- produces reflexive, vegetative sounds 4 months-vowel like sounds 7 months- canonical babbling 10 months- protowords, jargon 12 months- first words |
|
|
Dysarthria |
A group of motor speech disorders caused by weakness paralysis, slowness, incoordination,or sensory loss in a muscle group responsible for speech Due to neurological damage to CNS/PNS Causes: Parkinson's, Huntington's, ALS, myasthenia gravis |
|
|
Dysarthria common characteristics |
Imprecise articulation Changes in prosody Poor oral motor coordination Changes in resonance Poor control over pitch, stress, rhythm |
|
|
Verbal apraxia |
A motor speech disorder characterized by poor motor planning of the movements needed for speech Inconsistent errors |
|
|
Developmental dysarthria |
Speech disorder caused by neuromuscular impairment Lesion in CNS Paralysis, paresis Not specific to speech Most common cause cerebral palsy |
|
|
Developmental dysarthria common characteristics |
Inability to produce subglottal pressure Voice often harsh and breathy Poor velar movement, leads to hypernasality |
|
|
Childhood apraxia of speech |
Due to unidentified neurological differences with possible genetic bases Severe speech sound system disorder |
|
|
CAS characteristics |
High incidence of vowel errors Frequent omissions Inconsistent articulation errors Abnormal prosidic patterns Difficulty in imitation |
|
|
Structurally based speech disorders |
Congenital craniofacial anomalies Micro/macroglossia Cleft lip/palate Dental abnormalities Tongue tie Tongue thrust Velopharyngeal insufficiency Malocclusion |
|
|
Disfluencies |

|
|
|
Diagnosogenic theory |
Normal disfluency parents react negatively Children become self conscious of speech Stuttering becomes a learned behavior |
|
|
Language basis theory |
Linguistic aspects of direct l speech affect occurrence of stuttering Begins when children are in stage of learning complete sentences |
|
|
Capacity and demand theories |
Initial faster rate of articulation is taxing to the speech production mechanism |
|
|
Developmental stuttering |
-Gradual onset -Secondary characteristics -Limited eye contact -Disfluencies initial position words and utterances -avoidance, anxiousness -situation dependent |
|
|
Acquired stuttering |
Sudden Uncommon Normal eye contact Disfluencies throughout Absent Constant across situations |
|
|
Voice dimensions |

|
|
|
Etiologies of voice disorders |

|
|
|
4 stages of swallowing |
Oral preparatory phase Oral transport phase Pharyngeal phase Esophageal phase |
|
|
Dysphagia |
Swallowing disorder Aspiration Drooling Slow eating Weight loss |

